Crossref Citations
This article has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by
Crossref.
Karpitschka, S.
2018.
The value of a fading tracer.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 856,
Issue. ,
p.
1.
Li, Yaxing
Diddens, Christian
Lv, Pengyu
Wijshoff, Herman
Versluis, Michel
and
Lohse, Detlef
2019.
Gravitational Effect in Evaporating Binary Microdroplets.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 122,
Issue. 11,
Hegde, Omkar
Kabi, Prasenjit
Agarwal, Shashwat
and
Basu, Saptarshi
2019.
Controlling self-assembly and buckling in nano fluid droplets through vapour mediated interaction of adjacent droplets.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,
Vol. 541,
Issue. ,
p.
348.
Gim, Yeonghyeon
Jang, Dong Kyu
Sohn, Dong Kee
Kim, Hyoungsoo
and
Ko, Han Seo
2020.
Three-dimensional particle tracking velocimetry using shallow neural network for real-time analysis.
Experiments in Fluids,
Vol. 61,
Issue. 2,
Li, Yaxing
Salvator, Valentin
Wijshoff, Herman
Versluis, Michel
and
Lohse, Detlef
2020.
Evaporation-Induced Crystallization of Surfactants in Sessile Multicomponent Droplets.
Langmuir,
Vol. 36,
Issue. 26,
p.
7545.
Malinowski, Robert
Parkin, Ivan P.
and
Volpe, Giorgio
2020.
Nonmonotonic contactless manipulation of binary droplets via sensing of localized vapor sources on pristine substrates.
Science Advances,
Vol. 6,
Issue. 40,
Li, Yaxing
Diddens, Christian
Segers, Tim
Wijshoff, Herman
Versluis, Michel
and
Lohse, Detlef
2020.
Rayleigh–Taylor instability by segregation in an evaporating multicomponent microdroplet.
Journal of Fluid Mechanics,
Vol. 899,
Issue. ,
Lee, Yeawan
Shin, Seungwon
Choi, Geunhyeok
Jeon, Hyejun
Kim, Youngdo
and
Kim, Hyoungsoo
2020.
Symmetry breaking of Worthington jets by gradients in liquid pool depth.
Physics of Fluids,
Vol. 32,
Issue. 11,
Jaime, María del Sol
Maisonet, Shayra G.
and
Ramírez, Carlos A.
2020.
Effect of liquid phase composition on the experimental determination of binary gas diffusivities in an isothermal Stefan diffusion column.
Chemical Engineering Communications,
Vol. 207,
Issue. 12,
p.
1658.
Lohse, Detlef
and
Zhang, Xuehua
2020.
Physicochemical hydrodynamics of droplets out of equilibrium.
Nature Reviews Physics,
Vol. 2,
Issue. 8,
p.
426.
Park, Jonghyeok
Ryu, Junil
Sung, Hyung Jin
and
Kim, Hyoungsoo
2020.
Control of solutal Marangoni-driven vortical flows and enhancement of mixing efficiency.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,
Vol. 561,
Issue. ,
p.
408.
Pahlavan, Amir A.
Yang, Lisong
Bain, Colin D.
and
Stone, Howard A.
2021.
Evaporation of Binary-Mixture Liquid Droplets: The Formation of Picoliter Pancakelike Shapes.
Physical Review Letters,
Vol. 127,
Issue. 2,
Abo Jabal, Mohammad
Homede, Ekhlas
Zigelman, Anna
and
Manor, Ofer
2021.
Coupling between wetting dynamics, Marangoni vortices, and localized hot cells in drops of volatile binary solutions.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,
Vol. 588,
Issue. ,
p.
571.
Jeong, Chan Ho
Lee, Hyung Ju
Choi, Chang Kyoung
and
Lee, Seong Hyuk
2021.
Review of the binary mixture droplet evaporation studies.
Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology,
Vol. 35,
Issue. 12,
p.
5259.
Jeong, Chan Ho
Lee, Hyung Ju
Kim, Dae Yun
Ahangar, Shahab Bayani
Choi, Chang Kyoung
and
Lee, Seong Hyuk
2021.
Quantitative analysis of contact line behaviors of evaporating binary mixture droplets using surface plasmon resonance imaging.
International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,
Vol. 165,
Issue. ,
p.
120690.
Shardt, Nadia
Wang, Yingnan
Jin, Zhehui
and
Elliott, Janet A.W.
2021.
Surface tension as a function of temperature and composition for a broad range of mixtures.
Chemical Engineering Science,
Vol. 230,
Issue. ,
p.
116095.
Zeng, Binglin
Chong, Kai Leong
Wang, Yuliang
Diddens, Christian
Li, Xiaolai
Detert, Marvin
Zandvliet, Harold J. W.
and
Lohse, Detlef
2021.
Periodic bouncing of a plasmonic bubble in a binary liquid by competing solutal and thermal Marangoni forces.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,
Vol. 118,
Issue. 23,
Wu, Mengmeng
Doi, Masao
and
Man, Xingkun
2021.
The contact angle of an evaporating droplet of a binary solution on a super wetting surface.
Soft Matter,
Vol. 17,
Issue. 34,
p.
7932.
Guo, Wei
Kinghorn, Andrew B.
Zhang, Yage
Li, Qingchuan
Poonam, Aditi Dey
Tanner, Julian A.
and
Shum, Ho Cheung
2021.
Non-associative phase separation in an evaporating droplet as a model for prebiotic compartmentalization.
Nature Communications,
Vol. 12,
Issue. 1,
Seyfert, Carola
and
Marin, Alvaro
2022.
Yarning droplets: Marangoni bursting with a partially soluble component.
Physical Review Fluids,
Vol. 7,
Issue. 11,
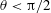 $\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}<\unicode[STIX]{x03C0}/2$) the suspended polystyrene particles begin to disappear from near the contact line, which indicates that the volatile component, here water, evaporates rapidly compared to the other component(s). Finally, we show that a diffusion-dominated model for evaporation of a binary mixture can predict well the experimental results where convective and diffusive mixing effects are negligible, in which case there is significant chemical segregation in the drop.
$\unicode[STIX]{x1D703}<\unicode[STIX]{x03C0}/2$) the suspended polystyrene particles begin to disappear from near the contact line, which indicates that the volatile component, here water, evaporates rapidly compared to the other component(s). Finally, we show that a diffusion-dominated model for evaporation of a binary mixture can predict well the experimental results where convective and diffusive mixing effects are negligible, in which case there is significant chemical segregation in the drop.




