Abstract
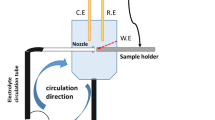
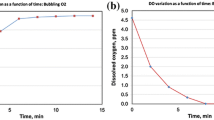
The erosive wear in an alkaline slurry containing alumina particles of three typical engineering materials, the mild steel BS 6323 (Fe-C), the AISI 410 stainless steel (Fe-Cr-C), and the AISI 304 stainless steel (Fe-Cr-Ni), was carried out, by means of rotating cylinder, three-electrode erosion-corrosion test, with a view to investigation into the roles of the typical elements and the mechanical and chemical properties in the erosive wear under simultaneous controlled corrosion. The total weight loss of erosion-corrosion was obtained by precision weighing and the result was compared and interpreted, for each material, by a full microscopical examination of the erosion-corrosion scars using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). It was found that the overall performance under erosion-corrosion in an descending order was the stainless steels AISI 304, AISI 410, and the mild steel, although the precise difference in performance was dependent upon the process conditions. Such a ranking of performance was not in total consistence with that expected only from the mechanical or the chemical property differences of the materials concerned. The individual contribution of each erosion and corrosion process was thus further separated through corrosion charge conversion using the Faraday's second law and the results were interpreted by discussion, on basis of the experimental and microscopical evidences, of the main factors that influenced the mechanical and wear behaviour, in conjunction with those influencing corrosion and passivity. Finally, schematic diagrams were proposed to outline the typical erosion and corrosion features thus obtained for all the three materials during erosion-corrosion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. ZHENG, Z. YAO, X. WEI and W. KE,Wear 186/187 (1995) 555.
R. J. K. WOOD and S. P. HUTTON, ibid. 140 (1990) 387.
I. M. HUTCHINGS, "Tribology: Friction andWear of Engineering Materials" (Edward Arnold, London, 1992).
I. FINNIE, Wear 186/187 (1995) 1.
A. W. RUFF and S. M. WIEDERHORN, in "Treatise on Materials Science and Technology," Vol. 16, edited by C. M. Preece (Academic Press, New York, 1979) p. 69.
R. BROWN, S. KOSCO and E. J. JUN, Wear 88 (1983) 181.
I. G. WRIGHT, V. NAGARAJAN and R. B. HERCHENROEDER, in "Corrosion-Erosion Behaviour of Materials," edited by K. Natesan (The Metallurgical Society of AIME., Philadelphia, 1980) p. 268.
J. C. SCULLY, "The Fundamentals of Corrosion" 3rd ed. (Pergamon Press, Oxford, 1990).
L. P. MYERS, in "Handbook of Stainless Steels," edited by D. Peckner and I. M. Bernstein (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1977) p. 11-1.
E. SNAPE, in "Handbook of Stainless Steels," edited by D. Peckner and I. M. Bernstein (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1977) p. 12-1.
L. R. SCHARFSTEIN, in "Handbook of Stainless Steels," edited by D. Peckner and I. M. Bernstein (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1977) p. 15-1.
H. W. WANG and M. M. STACK, Surf. Coat. Technol. 105 (1998) 141.
M. M. STACK, H. W. WANG and W. D. MUNZ, ibid. 113 (1999) 52.
B. WALLEN and J. OLSSON, in "Handbook of Stainless Steels," edited by D. Peckner and I. M. Bernstein (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1977) p. 16-1.
M. DROGOWSKA, H. MENARD and L. BROSSARD, J. Appl. Electrochem. 26 (1996) 217.
Idem., ibid. 27 (1997) 169.
M. DROGOWSKA, H. MENARD, A. LASIA and L. BROSSARD, ibid. 26 (1996) 1169.
B. VYAS, in "Treatise on Materials Science and Technology," Vol. 16, edited by C. M. Preece (Academic Press, New York, 1979) p. 357.
B. J. LANCE and F. SADEGHI, J. Tribo-Trans. ASME. 115 (1993) 445.
H. YOSHIZAWA, P. M C GUIGGAN and J. ISRAELACHVILI, Science 259 (1993) 1305.
S. V. PRASAD and K. R. MECKLENBURG,Wear 162 (1993) 47.
S. C. TUNG and S. S. WANG, Tribo. Trans. 35 (1992) 298.
J. POSTOLETHWAITE, E. D. B. TINKER and M. W. HAWRYLAK, Corro. 30 (1974) 285.
J. POSTOLETHWAITE and D. N. HOLDER, Can. J. Chem. Eng. 54 (1976) 255.
Y. OKA, H. KOUZAI and M. MATSUMURA, Corro. Eng. 35 (1986) 320.
Y. OKA and M. UHKUBO, Corro. 46 (1990) 687.
A. A. ONO, N. ALONSON and A. P. TSCHIPTSCHIN, ISIJ International 36 (1996) 813.
D. A. MORENO, M. F. L. D EMELE, J. R. IBARS and H. A. VIDELA, Corro. 47 (1991) 2.
A. JOSHI and D. F. STEIN, ibid. 28 (1972) 321.
G. SUNDARARAJAN and R. MANISH, Tribo. International 30 (1997) 339.
G. SUNDARARAJAN, in Proceedings of Corrosion-Erosion-Wear of Materials at Elevated Temperatures, edited by A. V. Levy (National Association of Corrosion Engineers, Texas, 1991) p. 11.
A. V. LEVY, E. SLAMOVCH and N. JEE, Wear 110 (1986) 117.
I. G. WRIGHT, V. NAGARAJAN and J. STRINGER, Oxid.Met. 25 (1986) 175.
A. V. LEVY and B. WANG, Surf. Coat. Technol. 11 (1955) 22.
J. J. HEGER and J. L. HAMILTON, Corro. 11 (1955) 22.
A. J. SEDRIKS, "Corroison of Stainless Steels" (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H.W., Stack, M.M. The erosive wear of mild and stainless steels under controlled corrosion in alkaline slurries containing alumina particles. Journal of Materials Science 35, 5263–5273 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004865107688
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004865107688