Abstract
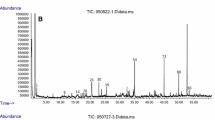
Many investigators have attempted to identify the allelochemicals in alfalfa (Medicago sativa), that cause autotoxicity. The autotoxic compounds from fresh alfalfa leaves were separated and quantified, and their biological activity was determined. Chemical separation procedures involved an 80% methanol extract of fresh alfalfa leaves, treatment with activated charcoal, microcrystalline cellulose thin-layer chromatography (MCTLC), and finally separation by Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography. The various fractions were examined further by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Preliminary identification by HPLC analysis resulted in peaks with retention times close to those of chlorogenic (m/z = 354) and salicylic acid (m/z = 138) standards, and these compounds were confirmed with GC-MS. Several other peaks remain unidentified. Chlorogenic acid occurs in relatively large amounts (0.39 mg/g) in alfalfa aqueous extracts as compared to salicylic acid (0.03 mg/g), and bioassays suggest that chlorogenic acid is involved in alfalfa autotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abdul-Rahman,Ñ A.ÑA.,ÑandÑ Habib,Ñ S.ÑA.Ñ1989.ÑAllelopathicÑeffectÑofÑalfalfaÑ(MedicagoÑsativaÑL.)ÑonÑbladygrassÑ(ImperataÑcylindrica).ÑJ.ÑChem.ÑEcol.Ñ15:2289–2300.
Banwart,Ñ W.ÑL.,Ñ Porter,Ñ P.ÑM.,Ñ Granato,Ñ T.ÑC.,ÑandÑ Hassett,Ñ J.ÑJ.Ñ1985.ÑHPLCÑseparationÑandÑwavelengthÑareaÑratiosÑofÑmoreÑthanÑ50ÑphenolicÑacidsÑandÑflavonoids.ÑJ.ÑChem.ÑEcol.Ñ11:383–395.
Bohnenblust,Ñ K.ÑE.Ñ1983.ÑEffectÑofÑallelopathyÑorÑautotoxicityÑonÑalfalfaÑseedlingÑestablishment,Ñp.Ñ25,ÑinÑReportÑ28thÑAlfalfaÑImprovementÑConference,ÑDavis,ÑCalifornia.
Chung,Ñ Ill-Min,ÑandÑ Miller,Ñ D.ÑA.Ñ1995a.ÑEffectÑofÑalfalfaÑplantÑandÑsoilÑextractsÑonÑgerminationÑandÑgrowthÑofÑalfalfa.ÑAgron.ÑJ.Ñ87:762–767.
Chung,Ñ Ill-Min,ÑandÑ Miller,Ñ D.ÑA.Ñ1995b.ÑNaturalÑherbicideÑpotentialÑofÑalfalfaÑresidueÑonÑselectedÑweekÑspecies.ÑAgron.ÑJ.Ñ87:920–925.
Dornbos,Ñ D.ÑL.,ÑJr.,Ñ Spencer,Ñ G.ÑF.,ÑandÑ Miller,Ñ R.ÑW.Ñ1990.ÑMedicarpinÑdelaysÑalfalfaÑseedÑgerminationÑandÑseedlingÑgrowth.ÑCropÑSci.Ñ30:162–166.
Goplen,Ñ B.ÑP.,ÑandÑ Webster,Ñ G.ÑR.Ñ1969.ÑSelectionÑinÑMedicagoÑsativaÑL.ÑforÑtoleranceÑtoÑalfalfaÑsickÑsoilsÑinÑcentralÑAlberta.ÑAgron.ÑJ.Ñ61:589–590.
Guenzi,Ñ W.ÑD.,Ñ Kehr,Ñ W.ÑR.,ÑandÑ MCCALLA,Ñ T.ÑM.Ñ1964.ÑWaterÑsolubleÑphytotoxicÑsubstancesÑinÑalfalfaÑforage:ÑVariationÑwithÑvariety,Ñcutting,Ñyear,ÑandÑstageÑofÑgrowth.ÑAgron.ÑJ.Ñ56:499–500.
Hall,Ñ M.ÑH.,ÑandÑ Henderlong,Ñ P.ÑR.Ñ1989.ÑAlfalfaÑautotoxicÑfractionÑcharacterizationÑandÑinitialÑseparation.ÑCropÑSci.Ñ29:425–428.
Hedge,Ñ R.ÑS.,ÑandÑ Miller,Ñ D.ÑA.Ñ1992.ÑConcentrationÑdependencyÑandÑstageÑofÑcropÑgrowthÑinÑalfalfaÑautotoxicity.ÑAgron.ÑJ.Ñ84:940–946.
Kehr,Ñ W.ÑR.,Ñ Watkins,Ñ J.ÑE.,ÑandÑ Ogden,Ñ R.ÑL.Ñ1983.ÑAlfalfaÑestablishmentÑandÑproductionÑwithÑcontinuousÑalfalfaÑandÑfollowingÑsoybeans.ÑAgron.ÑJ.Ñ75:435–438.
Klein,Ñ R.ÑR.,ÑandÑ Miller,Ñ D.ÑA.Ñ1980.ÑAllelopathyÑandÑitsÑroleÑinÑagriculture.ÑCommun.ÑSoilÑPlantÑAnal.Ñ11:435–6.
Mabry,Ñ T.ÑJ.,Ñ Markham,Ñ K.ÑR.,ÑandÑ Thomas,Ñ M.ÑB.Ñ1970.ÑTheÑSystematicÑIdentificationÑofÑFlavonoids.ÑSpringer-Verlag,Ñ NewÑYork,Ñ354Ñpp.
McElgunn,Ñ J.ÑD.ÑandÑ Heinrichs,Ñ D.ÑH.Ñ1970.ÑEffectsÑofÑrootÑtemperatureÑandÑaÑsuspectedÑphytotoxicÑsubstanceÑonÑtheÑgrowthÑofÑalfalfa.ÑCan.ÑJ.ÑPlantÑSci.Ñ50:307–311.
Miller,Ñ D.ÑA.Ñ1983.ÑAllelopathicÑeffectsÑofÑalfalfa.ÑJ.ÑChem.ÑEcol.Ñ9:1059–1071.
Miller,Ñ R.ÑW.,Ñ Kleiman,Ñ R.,Ñ Powell,Ñ R.ÑW.,ÑandÑ Putnam,Ñ A.ÑR.Ñ1988.ÑGerminationÑandÑgrowthÑinhibitorsÑofÑalfalfa.ÑJ.ÑNat.ÑProd.Ñ51:328–330.
Nielsen,Ñ K.ÑF.,Ñ Cuddy,Ñ T.,ÑandÑ Woods,Ñ W.Ñ1960.ÑTheÑinfluenceÑofÑtheÑextractÑofÑsomeÑcropsÑandÑsoilÑresiduesÑonÑgerminationÑandÑgrowth.ÑCan.ÑJ.ÑPlantÑSci.Ñ40:188–197.
Porter,Ñ P.ÑM.,Ñ Banwart,Ñ W.ÑL.,ÑandÑ Hassett,Ñ J.ÑJ.Ñ1985.ÑHPLCÑisolationÑandÑGC-MSÑidentificationÑofÑgenistein,Ñdaidzein,ÑandÑcoumestrolÑfromÑunhydrolyzedÑsoybeanÑrootÑextracts.ÑEnviron.ÑExp.ÑBot.Ñ25:229–232.
Putnam,Ñ A.ÑR.Ñ1985.ÑAllelopathicÑresearchÑinÑagriculture:ÑPastÑhighlightsÑandÑpotential,Ñpp.Ñ1–8,ÑinÑA.ÑC.Ñ ThompsonÑ(ed.).ÑTheÑChemistryÑofÑAllelopathy.ÑACSÑSymposiumÑSeries.ÑAmericanÑChemicalÑSociety,Ñ Washington,ÑD.C.
Rice,Ñ E.ÑL.Ñ1984.ÑAllelopathy.ÑAcademicÑPress,Ñ Orlando,ÑFlorida.Ñ422Ñpp.
SASÑInstitute.Ñ1988.ÑSASÑ?STATÑUser'sÑGuide,Ñ6.03Ñed.ÑSASÑInstitute,Ñ Cary,ÑNorthÑCarolina.Ñ108Ñpp.
Waller,Ñ G.ÑR.,Ñ Jurysta,Ñ M.,ÑandÑ Thorne,Ñ R.ÑL.ÑZ.Ñ1993.ÑAllelopathicÑactivityÑofÑrootÑsaponinsÑfromÑalfalfaÑ(MedicagoÑsativaÑL.)ÑonÑweedsÑandÑwheat.ÑBot.ÑBull.ÑAcad.ÑSin.Ñ34:1–10.
Williams,Ñ R.ÑD.,ÑandÑ Hoagland,Ñ R.ÑE.Ñ1982.ÑTheÑeffectsÑofÑnaturallyÑoccurringÑphenolicÑcompoundsÑonÑseedÑgermination.ÑWeedÑSci.Ñ30:206–212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, IM., Seigler, D., Miller, D.A. et al. Autotoxic Compounds from Fresh Alfalfa Leaf Extracts: Identification and Biological Activity. J Chem Ecol 26, 315–327 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005466200919
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005466200919