Abstract
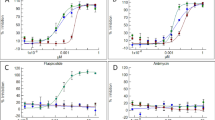
Feeding by the aphid Sipha flava produces a reddish spot on mature leaves of Sorghum halepense. The present work is aimed at determining whether this plant response entails induced resistance against the aphid. Old and young leaves showed the same response to aphid feeding (reddish coloration). Water-stressed plants displayed a similar reddish coloration to aphid-infested plants. This was verified by evaluation of absorbance peaks of the respective leaf extracts. Aphid fecundity was reduced on previously infested (and hence reddish colored) leaves. However, aphid fecundity was not affected on water stressed plants. Furthermore, aphid survival was not different on artificial diets containing increasing concentrations of the reddish pigment. It is concluded that the reddish spot is correlated with, but is not itself responsible for, the observed induced resistance of S. halepense against S. flava.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
BLACKMAN, R. L., and EASTOP, V. P. 1984. Aphids on the World's Crops. An Identification Guide. John Wiley & Sons, New York.
BREEN, J. P., and TEETES, G. L. 1986a. Relationships of yellow sugarcane aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) density to sorghum damage. J. Econ. Entomol.79:1106-1110.
BREEN, J. P., and TEETES, G. L. 1986b. Yellow sugarcane aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) infestation duration effect on sorghum. J. Econ. Entomol.79:1603-1605.
BREEN, J. P., and TEETES, G. L. 1990. Economic injury levels for yellow sugarcane aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) on seedling sorghum. J. Econ. Entomol.83:1008-1014.
CABRERA, H. M., ARGANDOÑ A, V. H., ZÚ Ñ IGA, G. E., and CORCUERA, L. J. 1995. Effect of infestation by aphids on the water status of barley and insect development. Phytochemistry40:1083-1088.
CAMPBELL, B. C., and DREYER, D. L. 1990. The role of plant matrix polysaccharides in aphid-plant interactions, pp. 149-170 in. R. K. Campbell and R. D. Eikenbary (eds.). Aphid-Plant Genotype Interactions. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
CHALKER-SCOTT, L. 1999. Environmental significance of anthocyanins in plant stress response. Photochem. Photobiol.70:1-9.
COLEMAN, J. S., and JONES, C. G. 1991. A phytocentric perspective of phytochemical induction by herbivores, pp. 3-46. inD. W. Tallamy and M. J. Raupp (eds.). Phytochemical Induction by Herbivores. Wiley, New York.
DIXON, A. F. G. 1998. Aphid Ecology. Chapman & Hall, London, p. 38.
DORSCHNER, K. W., RYAN, J. D., JOHNSON, R. C., and EIKENBARY, R. D. 1987. Modification of host nitrogen levels by the greenbug (Homoptera: Aphididae): Its role in resistance of winter wheat to aphids. Environ. Entomol.16:1007-1011.
FERN ÁNDES, G. W. 1990. Hypersensitivity: A neglected plant resistance mechanism against insect herbivores. Environ. Entomol.19:1173-1182.
FORMUSOH, E. S., WILDE, G. E., and REESE, J. C. 1992. Reproduction and feeding behavior of greenbug biotype E (Homoptera, Aphididae) on wheat previously fed upon by aphids. J. Econ. Entomol.85:789-793.
GABRYS, B., TJALLINGII, W. F., and VAN BEEK, T. A. 1997. Analysis of EPG recorded probing by cabbage aphid on host plant parts with different glucosinolate contents. J. Chem. Ecol.23:1661-1674.
GIANOLI, E. 1999. Within-plant distribution of Rhopalosiphum padion wheat seedlings is affected by induced responses. Entomol. Exp. Appl.93:227-230.
GIANOLI, E. 2000. Competition in cereal aphids on wheat plants. Environ. Entomol.29:213-219.
GIANOLI, E., and NIEMEYER, H. M. 1996. Environmental effects on the induction of wheat chemical defences by aphid infestation. Oecologia107:549-552.
GIANOLI, E., and NIEMEYER, H. M. 1997. Characteristics of hydroxamic acid induction in wheat triggered by aphid infestation. J. Chem. Ecol.23:2695-2705.
GIANOLI, E., and NIEMEYER, H. M. 1998. Allocation of herbivory-induced hydroxamic acids in the wild wheat Triticum uniaristatum. Chemoecology8:19-23.
GONZáLES, W. L., FUENTES-CONTRERAS, E., and NIEMEYER, H. M. 1998. Una nueva especie de áfido (Hemiptera: Aphididae) detectada en Chile: Sipha flava(Forbes). Rev. Chil. Entomol.25:87-90.
GONZáLES, W. L., GIANOLI, E., and NIEMEYER, H. M. 2001. Plant quality versus risk of parasitism: Within-plant distribution and performance of the corn leaf aphid, Rhopalosiphum maidis(Fitch) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Agric. For. Entomol.In press.
HEDIN, P. A., JENKINS, J. N., COLLUM, D. H., WHITE, W. H., and PARROTT, W. L. 1983. Multiple factors in cotton contributing to resistance to the tobacco budworm, Heliothis virescensF., pp. 347-365. inP. A. Hedin (ed.). Plant Resistance to Insects. American Chemical Society, Washington, D.C.
HOLMAN, J. 1974. Los áfidos de Cuba. Instituto Cubano del Libro, La Habana.
KARBAN, R. 1987. Environmental conditions affecting the strength of induced resistance against mites in cotton. Oecologia73:414-419.
KARBAN, R., and BALDWIN, I. T. 1997. Induced Responses to Herbivory. University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
LARSSON, S., WIRéN, A., LUNDGREN, L., and ERICSSON, T. 1986. Effects of light and nutrient stress on leaf phenolic chemistry in Salix dasycladosand susceptibility to Galerucella lineola(Coleoptera). Oikos47:205-210.
LESZCZYNSKI, B. 1985. Changes in phenols content and metabolism in leaves of susceptible and resistant winter wheat cultivars infested by Rhopalosiphum padi(L.) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Z. Angew. Entomol.100:343-348.
LO, S. C. C., and NICHOLSON, R. L. 1998. Reduction of light-induced anthocyanin accumulation in inoculated sorghum mesocotyls. Plant Physiol.116:979-989.
LONG, W. H., and HENSLEY, S. D. 1972. Insect pest of sugar cane. Annu. Rev. Entomol.17:149-176.
MATTHEI, O. J. 1995. Manual de las malezas que crecen en Chile. Alfabeta Impresores, Santiago.
MCWHORTHER, C. G. 1989. History, biology, and control of Johnsongrass. Rev. Weed Sci.4:85-121.
MEDINA-GAUD, S., MARTORELL, L. F., and BONILLA, R. R. 1965. Notes on the biology and control of the yellow sugarcane aphid of sugarcane, Sipha flava(Forbes) in Puerto Rico, pp. 1307-1320. inJ. Bague (ed.). Proceedings, 12th Congress of the International Society Sugar-Cane Technologists. San Juan, Puerto Rico.
MERRITT, S. Z. 1996. Within-plant variation in concentration of amino acids, sugar, and sinigrin in phloem sap of black mustard, Brasicca nigra(L.) Korch (Cruciferae). J. Chem. Ecol.22:1133-1145.
MONAGHAN, N. 1979. The biology of Johnson grass (Sorghum halepense). Weed Res.19:261-267.
NICHOLSON, R. L., KOLLIPARA, S. S., VINCENT, J. R., LYONS, P. C., and CADENA-GÓ MEZ, G. 1987. Phytoalexin synthesis by the sorghum mesocotyl in response to infection by pathogenic and nonpathogenic fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.84:5520-5524.
RYAN, J. D., MORGHAM, A. T., RICHARDSON, P. E., JOHNSON, R. C., MORT, A. J., and EIKENBARY, R. D. 1990. Greenbugs and wheat: A model system for the study of phytotoxic Homoptera, pp. 171-186. inR. K. Campbell and R. D. Eikenbary (eds.). Aphid-Plant Genotype Interactions, Elsevier, Amsterdam.
SCHUTT, C., and NETZLY, D. 1991. Effect of apiforol and apigeninidin on the growth of selected fungi. J. Chem. Ecol.17:1123-1125.
SHICHIJO, C., HAMADA, T., HIRAOKA, M., JOHNSON, C. B., and HASHIMOTO, T. 1993. Enhancement of red light-induced anthocyanin synthesis in sorghum first internodes by moderate low temperature given in the pre-irradiation culture period. Planta191:238-245.
SHICHIJO, C., HAMADA, T., JOHNSON, C. B., and HASHIMOTO, T. 1996. Effects of moderately low temperature (20 C) on phytochrome response during preirradiation: Anthocyanin synthesis in Sorghum bicolorat high-and low-Pfr Ptotratios. Photochem. Photobiol.63:328-335.
SMITH, C. F., and CERMELI, M. M. 1979. An annotated list of Aphididae (Homoptera) of the Caribbean islands and South and Central America. N.C. Agric. Res. Serv. Tech. Bull.259:1-131.
SNYDER, B. A., and NICHOLSON, R. L. 1990. Synthesis of phytoalexins in sorghum as a site-specific response to fungal ingress. Science248:1637-1639.
STARKS, K. J., and MIRKES, K. A. 1979. Yellow sugarcane aphid: Plant resistance in cereal crops. J. Econ. Entomol.72:486-488.
STONECIPHER, L. L., HURLEY, P. S., and NETZLY, D. H. 1993. Effect of apigeninidin on the growth of selected bacteria. J. Chem. Ecol.19:1021-1027.
WEBSTER, J. A. 1990. Yellow sugarcane aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae): Detection and mechanisms of resistance among Ethiopian sorghum lines. J. Econ. Entomol.83:1053-1057.
YOUNG, W. R., and TEETES, G. L. 1977. Sorghum entomology. Annu. Rev. Entomol.22:193-218.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Costa-Arbulú, C., Gianoli, E., Gonzáles, W.L. et al. Feeding by the Aphid Sipha flava Produces a Reddish Spot on Leaves of Sorghum halepense: an Induced Defense. J Chem Ecol 27, 273–283 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005676321251
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005676321251