Abstract
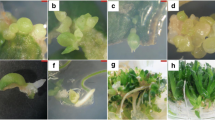
NAA and 2,4-D were compared for their ability to induce somatic embryogenesis in cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). In all seven cultivars tested, only 2,4-D had the capacity to induce primary somatic embryos from leaf explants, however, both NAA and 2,4-D were capable of inducing secondary somatic embryos. More secondary somatic embryos were formed in NAA than in 2,4-D medium. Furthermore, the maturation period for secondary somatic embryos was shorter in NAA medium than in 2,4-D medium. In some cultivars, repeated subculture of secondary somatic embryos in NAA medium resulted in a gradual shift from somatic embryogenesis to adventitious root formation. This shift could be stopped and reversed by subculture of the material in 2,4-D medium. In NAA medium the most secondary somatic embryos were formed when they were subcultured every 15 days whereas in 2,4-D a 20 day subculture interval was optimal. Subculture of secondary somatic embryos at a high inoculum density (>1.5 g jar−1) in NAA medium did not result in the formation of secondary somatic embryos, whereas in 2,4-D it lead to the formation of globular secondary somatic embryos. With 2,4-D the newly induced secondary somatic embryos were connected vertically to the explant and with NAA medium horizontally. For all cultivars tested, desiccation stimulated normal germination of NAA-induced somatic embryos. However, the desiccated, secondary somatic embryos required a medium supplemented with BA for high frequency germination. The concentration of BA needed for high frequency germination was higher when the desiccated secondary somatic embryos were cultured in light instead of dark. In only one cultivar desiccation enhanced germination of 2,4-D induced secondary somatic embryos and in three other cultivars it stimulated only root formation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammirato PV (1983) Embryogenesis. In: Evans DA, Sharp WR, Ammirato PV & Yamada Y (eds) Handbook of Plant Cell Culture Vol. 1 (pp 82–123). Macmillan, New York
Anonymous (1993) FAO Yearbook 1992 (pp 101–102). Rome
Bocks KK & Woods RD (1983) The etiology of African Cassava Mosaic Virus disease. Plant Disease 67: 994–995
Byrne D (1984) Breeding Cassava. In: Janick J (eds) Plant Breeding Reviews, Vol 2 (pp 73–113). AVI, Westport CT
Chang WC (1991) Bamboos. In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol 16 (pp 211–237). Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Cock JH (1985) Cassava: new potential for a neglected crop. Wetview Press, Boulder and London.
Lazzeri PA, Hildebrandt DF & Collins GB (1987) Soybean somatic embryogenesis: effect of hormones and culture manipulations. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 10: 197–208
Kartha KK & Gamborg OL (1975) Elimination of cassava mosaic disease by meristem culture. Phytopathology 65: 862–868
Kermode AR (1990) Regulatory mechanisms involved in the transition from seed development to germination. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 9: 155–195
Konan NK, Sangwan RS & Sangwan BS (1994) Somatic embryogenesis from cultured mature cotyledons of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 37: 91–102
Mante S, Scorza R & Cordts J (1989) A simple, rapid protocol for adventitious shoot development from mature cotyledons of Glycine max cv Bragg. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 25: 385–388
Mathews H, Schöpke C, Carcamo R, Chavarriaga P, Fauquet C & Beachy RN (1993) Improvement of somatic embryogenesis and plant recovery in cassava. Plant Cell. Rep. 12: 328–333
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Ozias-Akins P (1989) Plant regeneration from immature somatic embryos of peanut. Plant Cell Rep. 8: 217–218
Özcan S, Barghchi M, Firek S & Draper J (1993) Efficient adventitious shoot regeneration and somatic embryogenesis in pea. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 34: 271–277
Parrot WA, Merkle SA & Wiliams EG (1991) Somatic Embryogenesis: potential for use in propagation and gene transfer systems. In: Murray DR (ed) Advanced Methods in Plant Breeding and Biotechnology (pp 158–200). CAB International Wallingford, Oxon
Raemakers CJJM (1993) Primary and cyclic somatic embryogenesis in cassava Manihot esculenta Crantz. PhD thesis Agricultural University Wageningen, The Netherlands
Raemakers CJJM, Bessembinder J, Staritsky G, Jacobsen E & Visser RGF (1993a) Induction, germination and shoot development of somatic embryos in cassava. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 33: 151–156
Raemakers CJJM, Amati M, Staritsky G, Jacobsen E & Visser RGF (1993b) Cyclic somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in cassava. Ann. Bot. 71: 289–294
Raemakers CJJM, Schavemaker cm, Jacobsen E & Visser RGF (1993c) Improvements of cyclic somatic embryogenesis of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Plant Cell Rep. 12: 226–229
Smith MK, Biggs BJ & Scott KJ (1986) In vitro propagation of cassava ( Manihot esculenta Crantz). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 6: 221–229
Soenarjo R, Poespodarsono S & Nugroho JH (1987) Cassava Breeding and Agronomy Research in Asia. Proceeding of Regional Workshop held in Ryong, Thailand (pp 27–33)
Stamp JA & Henshaw GG (1982) Somaticembryogenesis in cassava. Zeits. Pflanzenphysiol. 105: 183–187.
Stamp JA & Henshaw GG (1987a) Somatic embryogenesis from clonal leaf tissue of cassava. Ann. Bot. 59: 445–450
Stamp JA & Henshaw GG (1987b) Secondary somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in cassava. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 10: 227–233
Szabados L, Hoyos R & Roca W (1987) In vitro somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration of cassava. Plant Cell Rep. 6: 248–25
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sofiari, E., Raemakers, C., Kanju, E. et al. Comparison of NAA and 2,4-D induced somatic embryogenesis in Cassava. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 50, 45–56 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005844414258
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005844414258