Abstract
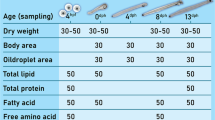
Repeated injections of salmon pituitary extract (20 mg per fish per week) induced vitellogenesis in feminized, cultivated Japanese eels (Anguilla japonica). Oocytes were attained at the migratory nucleus stage after 11 or 12 injections. Addition of 17,20β-dihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one (DHP) into the incubation medium induced germinal vesicle breakdown (GVBD) in the oocytes at the migratory nucleus stage. An injection of DHP (2 µg g-1 BW), given 24h after an injection of salmon pituitary extract (20 mg fish-1), succeeded in inducing maturation and ovulation in females which contained occytes at the migratory nucleus stage. Most fish ovulated 15–18h following the DHP injection. Eggs that were ovulated within 15h after the DHP injection showed high fertility and hatchability, but eggs ovulated 18 or 21h after the DHP injection, showed considerably lower fertility and hatchability. A delay between ovulation and stripping of the eggs rapidly decreased both the fertility and hatchability within 6–9h after ovulation, indicating that artificial fertilization must be carried out immediately after ovulation. Repeated injections of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) at a concentration of 1 IU g-1 BW week-1 induced spermatogenesis, spermiation, and the acquisition of potential for sperm motility in cultivated males. Most males spermiated after the fifth or sixth injection of hCG, and the milt weight gradually increased and remained constant (1–2 g) from the 11th to 31th injection. Sperm motility peaked 24h after each weekly injection, and decreased from the 3rd day after the injection. Potassium ions are an essential constituent for the maintenance of motility in the eel spermatozoa. Artificial seminal plasma containing 15.2 mM KCl is applicable as a milt diluent. Using these techniques developed for female and male eels, we have succeeded in obtaining many fertilized eggs from cultivated eels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Chiba, H., Miura, T., Nakamura, M. and Yamauchi, K. 1996. Differentiation of steroid-producing cells and induction of spermatogenesis during testicular differentiation in the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. In Proc. 3rd Congr. Asia and Oceania Soc. Comp. Endocrinol. pp. 232–233. Edited by J. Joss. Macquarie University, Sydney.
Ishida, O. and Ishii, T. 1970. Induction of testicular maturation in the Japanese eel. Suisanzoshoku 17: 263–271.
Kagawa, H., Tanaka, H., Ohta, H., Okuzawa, K. and Hirose, K. 1995. In vitro effects of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 17α,20ß-dihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one on final maturation of oocytes at various developmental stages in artificially matured Japanese eel Anguilla japonica. Fish. Sci. 61: 1012–1015.
Kurokawa, T., Kagawa, H., Ohta, H., Tanaka, H., Okuzawa, K. and Hirose, K. 1995. Development of digestive organs and feeding ability in larvae of Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 52: 1030–1036.
Kurokawa, T., Tanaka, H., Kagawa, H. and Ohta, H. 1996. Absorption of protein molecules by the rectal cells in eel larvae Anguilla japonica. Fish. Sci. 62: 832–833.
Matsumaru, Y. and Ishii, T. 1979. Studies on the seed production of eels – VIII. Exp. Rep. Inland Branch, Chiba Pref. Fish. Exp. Stn. 3: 21–31.
Miura, T., Yamauchi, K., Nagahama, Y. and Takahashi, H. 1991a. Induction of spermatogenesis in male Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica, by a single injection of human chorionic gonadotropin. Zool. Sci. 8: 63–73.
Miura, T., Yamauchi, K., Takahashi, H. and Nagahama, Y. 1991b. Involvement of steroid hormones in gonadotropin-induced testicular maturation in male Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). Biomed. Res. 12: 241–248.
Motonobu, T., Yamashita, K. and Oka, H.P. 1976. A memoir on the hatched larva of the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica, from the adults matured artificially. Bull. Shizuoka Pref. Fish. Exp. Stn. 10: 87–90.
Nagahama, Y. 1987. 17α,20ß-dihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one: a teleost maturation-inducing hormone. Dev. Growth Differ. 29: 1–12.
Oka, H.P. 1979. Studies on the artificial maturation in the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica-III. On the relation between the changes in body weight and the oogenesis during the course of maturation. Bull. Shizuoka Pref. Fish. Exp. Stn. 13: 101–111.
Ohta, H. and Izawa, T. 1996. Diluent for cool storage of the Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica) spermatozoa. Aquaculture 142: 107–118.
Ohta, H., Kagawa, H., Tanaka, H., Okuzawa, K. and Hirose, K. 1996a. Changes in fertilization and hatching rates with time after ovulation induced by 17,20ß-dihydroxy-4-pregnen-3-one in the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Aquaculture 139: 291–301.
Ohta, H., Kagawa, H., Tanaka, H., Okuzawa, K. and Hirose, K. 1996b. Milt production in the Japanese eel Anguilla japonica induced by repeated injections of human chorionic gonadotropin. Fish. Sic. 62: 44–49.
Ohta, H. and Takano, K. 1996. Testicular maturation induced by methyltestosterone in elvers of the Japanese eel. Fish. Sci. 62: (in press).
Ohta, H. and Tanaka, H. 1997. Relationship between serum levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and 11-ketotestosterone after a single injection of hCG and induced maturity in the male Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Aquaculture (In press).
Sakai, K., Nomura, M., Ishida, O. and Ishii, T. 1972. Studies on the seed production of the Japanese eel – III. Structure of the ovarian oocytes and ovulated eggs. Suisanzoshoku 19: 201–209.
Satoh, H., Nakamura, N. and Hibiya, T. 1962. Studies on the sexual maturation of the eel-I. On the sex differentiation and the maturing process of the gonads. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 28: 579–584.
Satoh, H., Yamamori, K. and Hibiya, T. 1992. Induced spawning of the Japanese eel. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 58: 825–832.
Stoss, J. 1983. Fish gamete preservation and spermatozoan physiology. In Fish Physiology. Vol. 9, Part B. pp. 305–350. Edited by W.S. Hoar, D.J. Randall and E.M. Donaldson. Academic Press, New York.
Sugimoto, Y., Takeuchi, Y., Yamauchi, K. and Takahashi, H. 1976. Induced maturation of female Japanese eels (Anguilla japonica) by administration of salmon pituitaries, with notes on changes of oil droplets in eggs of matured eels. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 27: 107–120.
Tachiki, H. and Nakagawa, T. 1993. Induction of spawning in female cultured eel Anguilla japonica. Bull. Aichi Fish. Res. Inst. 1: 79–83.
Takai, H. and Morisawa, M. 1995. Change in intracellular K+ concentration caused by external osmolality change regulates sperm motility of marine and freshwater teleosts. J. Cell Sci. 108: 1175–1181.
Tanaka, H., Kagawa, H., Ohta, H., Okuzawa, K. and Hirose, K. 1995. The first report of eel larvae ingesting rotifers. Fish. Sci. 61: 171–172.
Wang, Y., Zhao, C., Shi, Z., Tan, Y., Zhang, K. and Li, T. 1980. Studies on the artificial inducement of reproduction in common eel. J. Fish. China 4: 147–156.
Yamamoto, K., Hiroi, O., Hirano, T. and Morioka, T. 1972. Artificial maturation of cultivated male Japanese eels by synahorin injection. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 38: 1083–1090.
Yamamoto, K. and Yamauchi, K. 1974. Sexual maturation of Japanese eel and production of eel larvae in the aquarium. Nature, Lond. 251: 220–222.
Yamamoto, K., Morioka, T., Hiroi, O. and Oomori, M. 1974a. Artificial maturation of female Japanese eels by the injection of salmonid pituitary. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 40: 1–7.
Yamamoto, K., Oomori, M. and Yamauchi, K. 1974b. Oogenesis of the Japanese eel. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 40: 9–15.
Yamauchi, K., Nakamura, M., Takahashi, H. and Takano, K. 1976. Cultivation of larvae of Japanese eel. Nature, Lond. 263: 412.
Yamauchi, K. and Yamamoto, K. 1982. Experiments on artificial maturation and fertilization of the Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). In Proc. Sec. Int. Symp. Reproductive Physiology of Fishes. pp. 185–189. Edited by C.J.J. Richter and H.J.Th. Goos. Pudoc Press, Wageningen.
Yamauchi, K. 1990. Studies of gonadal steroids involved in final gonadal maturation in the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica, a review. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 75: 859–860.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohta, H., Kagawa, H., Tanaka, H. et al. Artificial induction of maturation and fertilization in the Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 17, 163–169 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007720600588
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007720600588