Abstract
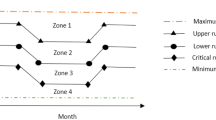
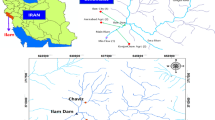
This article presents a methodology for planning a modelfor the operation of a drinking water reservoir. The hedging ruledistributes deficits over a longer period of time by rationingthe supply of water and it makes the system sustainablewith a marginal reduction in supply. A methodology isdeveloped and demonstrated through a case study withthe Chennai city (India) water supply system which isa water shortage system requiring an efficient use ofwater. It is aimed at improving the reservoiroperation performance through the simulation–optimisationprocedure with the application of the hedging rule, whichis a more appropriate rule for reservoir operationunder deficit conditions. To speed up the optimisationprocess, a neural network model is developed for thesimulation of the reservoir system operation and is usedinstead of a conventional simulation model. Thecombined neural network simulation–optimisation modelis used for screening the operation policies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alshaikh, A. A. and Taher, S.: 1995, Optimal design of irrigation canal network under uncertainty using response surface method, Water International 20, pp. 155–162.
Bayazit, M. and Unal, E.: 1990, Effects of hedging on reservoir performance, Water Resour. Res. 26(4), 713–719.
Cancelliere, A., Ancarani, A. and Rossi, G.: 1998, Susceptibility of water supply reservoirs to drought conditions, J. Hydrologic Engng 3(2), 140–148.
Freeman, J. A. and Skapura, D. M.: 1991, Neural Networks: Algorithms, Applications and Programming Techniques, Addison Wesley, New York, U.S.A.
Gate, T. K., Alshaikh, A. A., Ahmed, S. I. and Molden, D. J.: 1992, Optimal irrigation delivery system design under uncertainty, J. Irr. Drain. Engng 118(3), 433–449.
Gate, T. K. and Alshaikh, A. A.: 1993, Stochastic design of hydraulic structures in irrigation canal networks, J. Irr. Drain. Engng 119(2), 346–363.
Hashimoto, T., Stedinger, J. R. and Loucks, D. P.: 1982, Reliability, resiliency and vulnerability criteria for water resources system performance evaluation, Water Resour. Res. 18(1), 14–20.
Hrezo, M. S., Bridgeman, P. G. and Walker, W. R.: 1986, Managing drought through triggering mechanisms, J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 78(6), 46–51.
Hsu, K. L., Gupta, H. V. and Sorooshian, S.: 1995, Artificial neural network modeling of the rainfallrunoff process, Water Resour. Res. 31(10), 2517–2530.
Jain, S. K., Das, A. and Srivastava, D. K.: 1999, Application of ANN for reservoir inflow prediction and operation, Jl, Water Resour. Plann. Managt. 125(5), 263–271.
Karunanithi, N., Grenney, W. J., Whitley, D. and Bovee, K.: 1994, Neural networks for river flow prediction, J. Comp. Civil Engng 8(2), 201–220.
Klemes, V.: 1977, Value of information in reservoir optimization, Water Resour. Res. 13(5), 837–850.
Lippmann, R. P.: 1987, An introduction to computing with neural nets, IEEE, ASSP Magazine, pp. 4–22.
Loucks, D. P., Stedinger, J. R. and Haith, D. A.: 1981, Water Resources System Planning and Analysis, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., U.S.A.
Lund, J. R. and Reed, R.: 1995, Drought water rationing and transferable rations, J. Water Resour. Plann. Managt. 121(6), 429–437.
Maass, A., Hufschmidt, M. M., Dorfman, R., Thomas Jr., H. A., Marglin, S. A. and Fair, G. M.: 1962, Design of Water Resources Systems, Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass., U.S.A.
Masters, T.: 1993, Practical Neural Network Recipes in C++, Academic Press, U.S.A.
Ranjithan, S., Eheart, J. W. and Garrett, J. H.: 1993, Neural network based screening for groundwater reclamation uncertainty, Water Resour. Res. 29(3), 563–574.
Ranjithan, S., Eheart, J. W. and Garrett, J. H.: 1995, Application of neural network in groundwater remediation under conditions of uncertainty, In Z. W. Kundzewicz <nt>(ed.)</nt>, New Uncertainty Concepts in Hydrology and Water Resources, Cambridge University Press, pp. 133–140.
Rao, S. S.: 1991, Optimization Theory and Applications, Wiley Eastern Limited, New Delhi, India.
ReVelle, C., Joeres, E. and Kirby, W.: 1969, Linear decision rule in reservoir management and design, 1. Development of the stochastic model, Water Resour. Res. 5(4), 767–777.
Rogers, L. L. and Dowla, F. U.: 1994, Optimization of groundwater remediation using artificial neural networks with parallel solute transport modelling, Water Resour. Res. 30(2), 457–481.
Rosenbrock, H. H.: 1960, An automatic method for finding the greatest or least value of a function, Comp. J. 3(3), 175–84.
Shih, J. S. and ReVelle, C.: 1994, Water supply operations during drought: Continuous hedging rule, J. Water Resour. Plann. Managt. 120(5), 613–629.
Shih, J. S. and ReVelle, C.: 1995, Water supply operations during drought: A discrete hedging rule, European J. Operat. Res. 82, 163–175.
Simonovic, S. P.: 1992, Reservoir system analysis: Closing gap between theory and practice, J. Water Resour. Plant. Managt. 118(3), 262–280.
Srinivasan, K. and Philipose, M. C.: 1996, Evaluation and selection of hedging policies using stochastic reservoir simulation, Water Resour. Managt. 10(3), 163–188.
Srinivasan, K. and Philipose, M. C.: 1998, Effect of hedging on over-year reservoir performance, Water Resour. Manag. 12(2), 95–120.
Stedinger, J. R.: 1978, Comment on value of information in reservoir optimization, Water Resour. Res. 14(5), 984–986.
Stedinger, J. R.: 1984, The performance of LDR models for preliminary design and reservoir operation, Water Resour. Res. 20(2), 215–224.
Tagliarini, G. A., Christ, J. F. and Page, E. W.: 1991, Optimization using neural networks, IEEE Transactions on Computers 40(12), 1347–1358.
Zhang, Q. and Stanley, S. J.: 1999, Real-time water treatment process control with artificial neural networks, J. Environ. Engng 125(2), 153–160.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neelakantan, T.R., Pundarikanthan, N.V. Hedging Rule Optimisation for Water Supply Reservoirs System. Water Resources Management 13, 409–426 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008157316584
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008157316584