Abstract
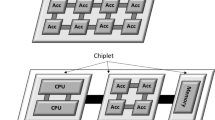
In this paper, we describe the implementation of MorphoSys, a reconfigurable processing system targeted at data-parallel and computation-intensive applications. The MorphoSys architecture consists of a reconfigurable component (an array of reconfigurable cells) combined with a RISC control processor and a high bandwidth memory interface. We briefly discuss the system-level model, array architecture, and control processor. Next, we present the detailed design implementation and the various aspects of physical layout of different sub-blocks of MorphoSys. The physical layout was constrained for 100 MHz operation, with low power consumption, and was implemented using 0.35 μm, four metal layer CMOS (3.3 Volts) technology. We provide simulation results for the MorphoSys architecture (based on VHDL model) for some typical data-parallel applications (video compression and automatic target recognition). The results indicate that the MorphoSys system can achieve significantly better performance for most of these applications in comparison with other systems and processors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.H. Mangione-Smith, B. Hutchings, D. Andrews, A. DeHon, C. Ebeling, R. Hartenstein, O. Mencer, J. Morris, K. Palem, V.K. Prasanna, and H.A.E. Spaaneburg, “Seeking Solutions in Configurable Computing,” IEEE Computer, 1997, pp. 38–43.
S. Brown and J. Rose, “Architecture of FPGAs and CPLDs: A Tutorial,” IEEE Design and Test of Computers, vol. 13, no.2, 1996, pp. 42–57.
E. Tau, D. Chen, I. Eslick, J. Brown, and A. DeHon, “A First Generation DPGA Implementation,” FPD'95, Canadian Workshop of Field-Programmable Devices, May 1995.
J.R. Hauser and J. Wawrzynek, “Grap: A MIPS Processor with a Reconfigurable Co-processor,” Proc. of the IEEE Symposium on FPGAs for Custom Computing Machines, 1997.
D.C. Chen and J.M. Rabaey, “A Reconfigurable Multi-processor IC for Rapid Prototyping of Algorithmic-Specific HighSpeed Datapaths,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 27, no.12, 1992.
E. Mirsky and A. DeHon, “MATRIX: A Reconfigurable Computing Architecture with Configurable Instruction Distribution and Deployable Resources,” IEEE Symposium on FCCM, pp. 157–166, 1996.
C. Ebeling, D. Cronquist, and P. Franklin, “Configure Computing: The Catalyst for High-performance Architectures,” Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Applicationspecific Systems, Architectures and Processors, July 1997, pp. 364–372.
T. Miyamori and K. Olukotun, “A Quantitative Analysis of Reconfigurable Coprocessors for Multimedia Applications,” Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines, April 1998.
J. Babb, M. Frank, V. Lee, E. Waingold, R. Barua, M. Taylor, J. Kim, S. Devabhaktuni, and A. Agrawal, “The RAW Benchmark Suite: Computation Structures for General-Purpose Computing,” Proc. IEEE Symposium on Field-Programmable Custom Computing Machines, FCCM 97, 1997, pp. 134–143.
A. Abnous, C. Christensen, J. Gray, J. Lenell, A. Naylor, and N. Bagherzaheh, “Design and Implementation of TinyRISC Microprocessor,” Microprocessors and Microsystems, vol. 16, no.4, 1992, pp. 187–194.
H. Singh, M. Lee, G. Lu, F. Kurdahi, N. Bagherzadeh, T. Lang, R. Heaton, and Filho, “Morphosys: An Integrated Re-configurable Architecture,” NATO Symposium on Concepts and Integration, April 1998.
M. Gokhale, W. Holmes, A. Kopser, S. Lucas, R. Minnich, D. Sweely, and D. Lopresti, “Building and Using a Highly Parallel Programmable Logic Array,” IEEE Computer, 1991, pp. 81–89.
K. Yano, T. Yamanaka, T. Nishida, M. Saito, K. Shimohigashi, and A. Shimizu, “A 3.8-ns CMOS 16 £ 16-b Multiplier Using Complementary Pass-Transistor Logic,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 25, no.2, 1990, pp. 388–395.
T.K. Callaway and E.E. Swartzlander, Jr., “The Power Consumption of CMOS Adders and Multipliers,” Low Power CMOS Design, A. Chandrakasan and R. Brodersen (Eds.), IEEE Press, 1998.
C.S. Wallace, “A Suggestion for a Fast Multiplier,” IEEE Transactions on Electronic Computer, vol. EC-13, 1964, pp. 14–17.
L. Dadda, “Some Schemes for Parallel Multipliers,” Alta Freq., vol. 34, 1965, pp. 349–356.
C.R. Baugh and B.A. Wooly, “A Two's Complement Parallel Array Multiplication Algorithm,” IEEE Transactions on Computer, vol. C-22, no.12, 1973, pp. 1045–1047.
I. Koren, Computer Arithmetic Algorithms, Prentice Hall Inc., 1993.
J.M. Rabaey, Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective, Prentice Hall Inc., 1996.
SUIF Compiler system, The Stanford SUIF Compiler Group, http://suif.stanford.edu.
C. Hsieh and T. Lin, “VLSI Architecture For Block-Matching Motion Estimation Algorithm,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, vol. 2, 1992, pp. 169–175.
K.-M. Yang, M.-T. Sun, and L. Wu, “A Family of VLSI Designs for Motion Compensation Block Matching Algorithm,” IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, vol. 36, no.10, 1989, pp. 1317–1325.
Intel Application Notes for Pentium MMX, http://developer.intel.com/drg/mmx/appnotes/
W.-H. Chen, C.H. Smith, and S.C. Fralick, “A Fast Computational Algorithm for the Discrete Cosine Transform,” IEEE Transactions on Communication, vol. COM-25, no.9, 1997.
T. Arai, I. Kuroda, K. Nadehara, and K. Suzuki, “V830R/AV: Embedded Multimedia Superscalar RISC Processor,” IEEE MICRO, 1998, pp. 36–47.
J. Villasenor, B. Schoner, K. Chia, C. Zapata, H.J. Kim, C. Jones, S. Lansing, and B. Mangione-Smith,“Configurable Computing Solutions for Automatic Target Recognition,” Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on FPGAs for Custom Computing Machine, April 1996.
M. Rencher and B.L. Hutchings, “Automated Target Recognition on SPLASH 2,” Proceedings of IEEE Symposium on FPGAs for Custom Computing Machine, April 1997.
XC 4000 Series High-Density Strategy, http://www.xilinx.xom.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, MH., Singh, H., Lu, G. et al. Design and Implementation of the MorphoSys Reconfigurable Computing Processor. The Journal of VLSI Signal Processing-Systems for Signal, Image, and Video Technology 24, 147–164 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008189221436
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008189221436