Abstract
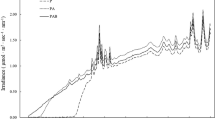
Photoinhibition in outdoor cultures of Spirulina platensis was studied by measuring the polyphasic rise of chlorophyll fluorescence transients, which provide information on the primary photochemistry of PSII. The maximum efficiency of PSII photochemustry (Fv/Fm) declined in response to daily increasing irradiance and recovered as daily irradiance decreased. The greatest inhibition (15%) in Fv/Fm was observed at 12:00 hr which responded to the highest irradiance. The absorption flux, the trapping flux, and the electron transport flux per PSII reaction center increased in response to daily increasing irradiance and decreased as irradiance decreased. The daily change in the concentration of PSII reaction centers followed the same pattern as Fv/Fm. However, no significant changes in the probability of electron transport beyond QA (Ψo) were observed during the day. The results suggest that the decrease in Fv/Fm induced by photoinhibition in outdoor Spirulina cultures was a result of the inactivation of PSII reaction centers. The results also suggest that the measurement of polyphasic fluorescence transients is a powerful tool to study the mechanism of photoinhibition in outdoor Spirulina cultures and to screen strains for photoinhibition tolerance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker NR, Bowyer JR (eds) (1994) Photoinhibition of Photosynthesis from Molecular Mechanisms to the Field. Bios Scientific Publishers, Oxford.
Krüger GHJ, Tsimilli-Michae M, Strasser RJ (1997) Light stress provokes plastic and elastic modifications in structure and function of photosystem II in camellia leaves. Physiol. Plant. 101: 265–277.
Lu C-M, Vonshak A (1999) Characterization of PSII photochemistry in salt-adapted cells of cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. New Phytol. 141: 231–239.
Lu C-M, Torzillo G, Vonshak A (1999) Kinetic response of photosystem II photochemistry in cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis to high salinity is characterized by two distinct phases. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 26: 283–292.
Meinander O, Somersalo S, Holopainen T, Strasser RJ (1996) Scots pines after exposure to elevated ozone and carbon dioxide probed by reflectance spectra and chlorophyll a fluorescence transients. J. Plant Physiol. 148: 229–236.
Srivastava A, Guissé B, Greppin H, Strasser RJ (1997) Regulation of antenna structure and electron transport in photosystem II of Pisum sativum under elevated temperature probed by the fast polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence transient: OKJIP. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1320: 95–106.
Strasser BJ (1997) Donor side capacity of photosystem II probed by chlorophyll a fluorescence transients. Photosynth. Res. 52: 147–155.
Strasser RJ (1978) The grouping model of plant photosynthesis. In Akoyunoglou G, Argyroudi-Akoyunoglou J (eds), Chloroplast Development. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam: 513–524.
Strasser RJ (1981) The grouping model of plant photosynthesis: heterogeneity of photosynthetic units in thylakoids. In Akoyunoglou G ed.), Photosynthesis III. Structure and Molecular Organization of the Photosynthetic Apparatus. Balaban International Science Services, Philadelphia: 727–737.
Strasser RJ, Srivastava A, Govindjee (1995) Polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence transients in plants and cyanobacteria. Photochem. Photobiol. 61: 32–42.
Strasser BJ, Strasser RJ (1995) Measuring fast fluorescence transients to address environmental questions: the JIP test. In Mathis P (ed.), Photosynthesis from Light to Biosphere, Vol. 5. Kluwer, Dordrecht: 977–980.
Torzillo G, Accolla P, Pinzani E, Masojidek J (1996) In situ monitoring of chlorophyll fluorescence to assess the synergistic effect of low temperature and high irradiance stresses in Spirulina cultures grown outdoors in photobioreactors. J. appl. Phycol. 8: 282–291.
Torzillo G, Bernardini P, Masojidek J (1998) On-line monitoring of chlorophyll fluorescence to assess the extent of photoinhibition of photosynthesis induced by high oxygen concentration and low temperature and its effect on the productivity of outdoor cultures of Spirulina platensis (cyanobacteria). J. Phycol. 34: 504–510.
Vonshak A (1990) Recent advances in microalgal biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 8: 709–727.
Vonshak A, Guy R (1992) Photodadaptation, photoinhibition and productivity in the blue-green alga Spirulina platensis grown outdoors. Plant Cell Environ. 15: 613–616.
Vonshak A, Torzillo G, Accolla P, Tomaselli L (1996) Light and oxygen stress in Spirulina platensis (cyanobacteria) grown outdoors in tubular reactors. Physiol. Plant. 97: 175–179.
Vonshak A, Torzillo G, Tomaselli L (1994) Use of chlorophyll fluorescence to estimate the effect of photoinhibition in outdoor cultures of Spirulina platensis. J. appl. Phycol. 6: 31–34.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, C., Vonshak, A. Photoinhibition in outdoor Spirulina platensis cultures assessed by polyphasic chlorophyll fluorescence transients. Journal of Applied Phycology 11, 355–359 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008195927725
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008195927725