Abstract
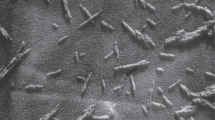
Stable colloidal suspensions of cellulose microcrystallites may be prepared from filter paper by sulfuric acid hydrolysis. Above a critical concentration, the suspensions form a chiral nematic ordered phase, or ‘colloid crystal’. The preparation conditions govern the properties of the individual cellulose microcrystallites, and hence the liquid crystalline phase separation of the cellulose suspensions. The particle properties and the phase separation of the suspensions were strongly dependent on the hydrolysis temperature and time, and on the intensity of the ultrasonic irradiation used to disperse the particles. The particle size of the microcrystallites was characterized with transmission electron microscopy and photon correlation spectroscopy. The surface charge was determined by conductometric titration. It was possible to fractionate the microcrystallites by size using the partitioning between isotropic and liquid crystalline phases; the longer microcrystallites migrate to the liquid crystalline phase
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abe, A. and Flory, P. J. (1978) Statistical thermodynamics of mixtures of rod-like particles. 2. Ternary systems. Macromolecules 11, 1122–1126.
Battista, O. A. (1956) Level-off degree of polymerization. Relation to polyphase structure of cellulose fibers. Ind. Eng. Chem. 48, 333–335.
Battista, O. A. (1975) Microcrystalline Polymer Science. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Dong, X. M. and Gray, D. G. (1997) Effect of counterions on ordered phase formation in suspensions of charged rodlike cellulose crystallites. Langmuir 13, 2404–2409.
Dong, X. M., Kimura, T., Revol, J. F. and Gray, D. G. (1996) Effects of ionic strength on the phase separation of suspensions of cellulose crystallites. Langmuir 12, 2076–2082.
Manning, G. and Zimm, B. H. (1965) Cluster theory of polyelectrolyte solutions I Activity coefficients of the mobile ions. J. Chem. Phys. 43, 4250–4259.
Marchessault, R. H., Morehead, F. F. and Koch, M. J. (1961) Some hydrodynamic properties of neutral suspensions of cellulose crystallites as related to size and shape. J. Colloid Sci. 16, 327–344.
Millet, M. A., Moore, W. E. and Saeman, J. F. (1954) Preparation and properties of hydrocelluloses. Ind. Eng. Chem. 46, 1493–1497.
Odijk, T. (1986) Theory of lyotropic liquid crystals. Macromolecules 19, 2313–2329.
Odijk, T. and Lekkerkerker, H. N. W. (1985) Theory of the isotropic-liquid crystalline phase separation for a solution of bidisperse rodlike macromolecules. J. Phys. Chem. 89, 2090–2096.
Onsager, L. (1949) The effect of shape on the interactions of colloid particles. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 51, 627–659.
Ranby, B. G. (1951) The colloidal properties of cellulose micelles. Discussions Faraday Soc. 11, 158–164.
Revol, J.-F., Bradford, H., Giasson, J., Marchessault, R. H. and Gray, D. G. (1992) Helicoidal self-ordering of cellulose microfibrils in aqueous suspension. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 14, 170–172.
Revol, J.-F., Godbout, L., Dong, X. M., Gray, D. G., Chanzy, H. and Maret, G. (1994) Chiral nematic suspensions of cellulose crystallites; phase separation and magnetic field orientation. Liq. Cryst. 16, 127–134.
Semenov, A. N. and Khokhlov, A. R. (1988) Statistical physics of liquid-crystalline polymers. Sov. Phys. Usp. 31, 988–1014.
Zero, K. M. and Pecora, R. (1982) Rotational and translational diffusion in semidilute solutions of rigid-rod macromolecules. Macromolecules 15, 87–93.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DONG, X.M., REVOL, JF. & GRAY, D.G. Effect of microcrystallite preparation conditions on the formation of colloid crystals of cellulose. Cellulose 5, 19–32 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009260511939
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009260511939