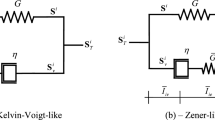
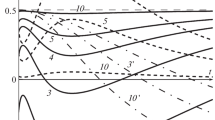
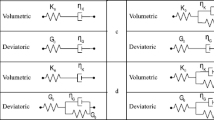Abstract
It is proven that time-independent viscoelastic Poisson ratios (PR) can only exist under separation of variable solutions which severely limits the class of applicable problems to quasi-static ones with incompressible homogeneous materials and non-moving boundaries under separable stress or displacement boundary conditions without any thermal expansions. Therefore, composites which are inherently anisotropic and sandwich structures which are nonhomogeneous and anisotropic are generally precluded from having time-independent PRs. Equal time variations for material properties in all directions are shown to be another simultaneous requirement instead of the incompressibility condition for achieving time-independent PRs. However, such restricted models lead to physically unrealistic bulk moduli responses when compared to experimentally determined relaxation moduli and are not generally achievable in current real materials. Consequently, viscoelastic materials are best characterized in terms of relaxation or creep functions, moduli or compliances rather than combinations of the latter with Poisson's ratios. Additionally, the assumption of constant PRs in problems involving thermal and chemical expansions, such as curing and manufacture of viscoelastic composites, is shown to be unjustified and insupportable. The distinct viscoelastic PR definitions, as found in the literature, are examined and classified into five categories. It is further shown that each is inherently unrelated to the others and all are always time-dependent, unless the above extremely limiting conditions are imposed. An extensive literature review indicates that experimental results overwhelmingly confirm the time dependent nature of viscoelastic PRs as no constant experimentally observed PRs were reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
W.T. Kelvin, On the elasticity and viscosity of metals. Proc. Royal Soc. 14(1865) 289–297.
J.C. Maxwell, On the dynamical theory of gases. Phil. Trans. Royal Soc. London A 157(1867) 49–88.
W. Voigt, Theoretischen Studien über das Elasticitatsverhaltnisse der Kristalle. Abhandlung Geselschaft der Wissenschaft zu Göttingen 34(1887) 52–79.
V. Volterra, Sulle equazioni integrodifferenzialli dela teoria dell'elastica. Atti Reale Accademia Nazionale dei Lincei 18(1909) 295–301.
T. Alfrey, Jr., Non-homogeneous stress in viscoelastic media. Quart. Appl. Math. 2(1944) 113–119.
T. Alfrey, Jr., Mechanical Behavior of High Polymers. Interscience Publishers, New York (1948).
D.R. Bland, The Theory of Linear Viscoelasticity. Pergamon Press, New York (1960).
R.M. Christensen, Theory of Viscoelasticity – An Introduction, 2nd edn. Academic Press, New York (1981).
B.D. Coleman and W. Noll, The foundations of linear viscoelasticity. Rev. Modern Phys. 33(1961) 239–249.
B.D. Coleman, Thermodynamics of materials with memory. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 17(1964) 1–46.
A. Drozdov, Viscoelastic Structures – Mechanics of Growth and Aging. Academic Press, New York (1998).
J.D. Ferry, Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers.Wiley, New York (1961).
B. Gross, Mathematical Structure of the Theories of Viscoelasticity. Hermann, Paris (1953).
M.E. Gurtin, Variational principles in the linear theory of viscoelasticity. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 13(1963) 179–185.
M.E. Gurtin and E. Sternberg, On the linear theory of viscoelasticity. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 11(1962) 291–356.
M.E. Gurtin and E. Sternberg, A reciprocal theory of anisotropic viscoelastic solids. SIAM J. 11(1963) 607–613.
A.C. Pipkin, Lectures on Viscoelasticity Theory. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1972).
M. Renardy, W.J. Hrusa and J.A. Nohel, Mathematical Problems in Viscoelasticity. Longman, New York (1987).
N.W. Tschoegl, The Phenomenological Theory of Linear Viscoelasticity. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1989).
H.H. Hilton and S. Yi, The significance of (an)isotropic viscoelastic Poisson ratio stress and time dependencies. Inter. J. Sol. Struct. 35(1998) 3081–3095.
S.D. Poisson, Mémoire sur l'équilibre et le mouvement des corps élastiques. Mémoires de l'Académie Royal des Sciences de l'Institut de France 8(1829) 357–570.
S.D. Poisson, Addition au mémoire sur l'équilibre et le mouvement des corps élastiques. Mémoires de l'Académie Royal des Sciences de l'Institut de France 8(1829) 623–627.
K. Ravi-Chandar, Simultaneous measurement of nonlinear bulk and shear relaxation behavior. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Mechanics of Time-Dependent Materials, SEM, Ljubljana, Slovenia (1998), pp. 30–31.
K. Ravi-Chandar, Inelastic deformation in polymers under multiaxial compression. Mechanics of Time-Dependent Materials 4(2000) 333–357.
H.H. Hilton, On the inadmissibility of separation of variable solutions in linear anisotropic viscoelasticity. Internat. J. Mech. Comp. Mat. Struct. 3(1996) 97–100.
H. Bertilsson, M. Delin, J. Kubát, W.R. Rychwalski and M.J. Kubát, Strain rates and volume changes during short-term creep of PC and PMMA. Rheologica Acta 32(1993) 361–369.
A.D. Drozdov, Mechanics of Viscoelastic Solids. Wiley, New York (1998).
W.N. Findley, J.S. Lai and K. Onaran, Creep and Relaxation of Nonlinear Viscoelastic Materials with an Introduction to Linear Viscoelasticity. North-Holland, New York (1976).
W. Flügge, Viscoelasticity. Springer-Verlag, New York (1975).
H.H. Hilton, An introduction to viscoelastic analysis. In: E. Baer (ed.), Engineering Design for Plastics, Reinhold Publishing Corp., New York (1964), pp. 199–276.
Yu.N. Rabotnov, Elements of Hereditary Solid Mechanics. Mir, Moscow (1980).
N. Kh. Arutyunyan, Some Problems in the Theory of Creep.Gostekizdat, Moscow (1952) (in Russian). Also Pergamon Press (1966).
P.B. Benham and D. McCammond, Studies of creep and contraction ratio in thermoplastics. Plastics and Polymers 39(1971) 130–136.
A.M. Freudenthal and L.A. Henry, On “Poisson's ratio” in linear visco-elastic propellants. In: M. Summerfield (ed.), American Rocket Society Solid Propellant Rocket Conference, Princeton University (1960), pp. 33–66.
A.M. Freudenthal, One-dimensional response and coefficient of thermal expansion in timesensitive materials. Acta Technica 41(1962) 415–449.
D. Göritz, Messung der Volumenänderung bei uniaxialen Dehnen. Colloid and Polymer Sci. 260(1982) 193–197.
W.G. Gottenberg and R.M. Christensen, Some interesting aspects of general linear viscoelastic deformation. Trans. Soc. Rheology 7(1963) 171–180.
I.H. Hwang, Thermo-viscoelastic behavior of composite materials. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Washington, Seattle (1990).
Y.K. Kim and S.R. White, Stress relaxation during cure of 3501-6 epoxy resin. In: Proc. Symp. Design and Manufacture of Composites, 1995 ASME Annual Winter Meeting, MID-69-1 (1995), pp. 43–56.
R.S. Lakes, The time dependent Poisson's ratio of viscoelastic cellular materials can increase or decrease. Cellular Polymers 10(1991) 466–469.
L.E. Nielsen, Stress dependence of Poisson's ratio and the softening temperature of plastics. Trans. Soc. Rheology 9(1965) 243–254.
L.E. Nielsen and R.F. Landel, Mechanical Properties of Polymers and Composites, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York (1994).
D.J. O'Brien, P.T. Mather and S.R. White, Viscoelastic properties of an epoxy resin during cure. J. Comp. Mat. 35(2001) 883–904.
K.G. Popov and K.B. Khadzhov, Relationships between relaxation characteristics and creep for isotropic materials. Mech. Comp. Mat. 16(1980) 6–10.
J.M. Powers and R.M. Caddell, The macroscopic volume changes of selected polymers subjected to uniform tensile deformation. Polymer Eng. Sci. 12(1972) 432–436.
Z. Rigbi, The value of Poisson's ratio of viscoelastic materials. Appl. Polymer Symp. 5(1967) 1–7.
F. Schwarzl, Linear viscoelastic behaviour of isotropic materials – transient measurements. Kolloid Zeitschrift 148(1956) 47–57.
A.J. Staverman and F. Schwarzl, Linear deformation behaviour of high polymers. In: H.A. Stuart (ed.), Die Physik der Hochpolymeren4, Springer-Verlag, New York (1956), pp. 1–95.
V.K. Stokes and H.F. Nied, Lateral strain effect during the large extension of thermoplastics. Polymer Eng. Sci. 28(1988) 1209–1218.
P.S. Theocaris, Creep and relaxation contraction ratio of linear viscoelastic materials, J. Mech. Phys. Solids 12(1964) 125–138.
P.S. Theocaris, Influence of plasticizer on Poisson's ratio of epoxy polymers. Polymer 20(1979) 1149–1152.
G.V. Vinogradov and A.Ya. Malkin, Rheology of Polymers – Viscoelasticity and Flow of Polymers. Mir, Moscow (1980).
S.R. White and A.B. Hartman, Effect of cure state on stress relaxation in 3501-6 epoxy resin. ASME J. Eng. Mat. Technology 119(1997) 262–265.
J.G. Williams, Stress Analysis of Polymers, 2nd edn. Ellis Horwood, Chichester (1980).
R. de Prony, Essai experimental et analytique. J. l'École Polytechnique de Paris 1(1795) 24–76.
H.H. Hilton and S.B. Dong, An analogy for anisotropic, nonhomogeneous, linear viscoelasticity including thermal stresses. In: Development in Mechanics, Pergamon Press, New York (1964), pp. 58–73.
M.A. Biot, Linear thermodynamics and the mechanics of solids. In: Proc. Third US Nat. Congr. Appl. Mech.(1958), pp. 1–18.
H.S. Tsien, A generalization of Alfrey's theorem in viscoelastic media. Quart. Appl. Math. 8(1950) 104–106.
H.H. Hilton, Thermal distributions without thermal stresses in nonhomogeneous media. ASME J. Appl. Mech. E 26(1959) 137–138.
H.H. Hilton and H.G. Russell, An extension of Alfrey's analogy to thermal stress problems in temperature dependent linear viscoelastic media. J. Mech. Phys. Sol. 9(1961) 152–164.
H.H. Hilton and J.R. Clements, Formulation and evaluation of approximate analogies for temperature-dependent linear viscoelastic media. In: Thermal Loading and Creep, Institution of Mechanical Engineers, London (1964), pp. 6-17–6-24.
A.E. Green and W. Zerna, Theoretical Elasticity. Oxford Univ. Press, New York (1968).
S. Yi, H.H. Hilton and M.F. Ahmad, Nonlinear thermoviscoelastic analysis of interlaminar stresses in laminated composites. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 63(1966) 218–224.
A.D. Drozdov, Finite Elasticity and Viscoelasticity – A Course in the Nonlinear Mechanics of Solids. World Scientific, Singapore.
Z. Li, Effective creep Poisson's ratio for damaged concrete. Int. J. Fract. 66(1994) 189–196.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hilton, H.H. Implications and Constraints of Time-Independent Poisson Ratios in Linear Isotropic and Anisotropic Viscoelasticity. Journal of Elasticity 63, 221–251 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014457613863
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014457613863