Abstract
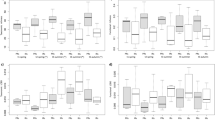
The diversity of benthic macrofaunal assemblages in the eastern English Channel is described from 707 samples collected with a Rallier-du-Baty dredge during 1971–1975. Four assemblages were primarily defined by means of multivariate data analyses and clustering methods: the ‘Abra alba community’, the ‘Ophelia borealis community’, the ‘pebbles community’ and a ‘mixed assemblage’ of the first three communities. Spatial heterogeneity of these communities is significantly correlated with sedimentary characteristics, although local variability appears to be controlled by both physical and biological processes. Ecological diversity of these communities was analysed considering species richness (S), the Shannon diversity index (H′), and rank-frequency diagrammes (RFD). These analyses were performed at two spatial scales: for a single sample, and for a 'site’ of 10 pooled samples. Thus, several sites were chosen in order to compare diversity patterns and species quantitative structure among and within the communities. The greatest species richness was recorded for the pebbles (57–69) and the A. alba (63–79) communities. In the former, high values may be due to the complexity of microhabitats and the large flux of food related to strong currents. In the latter, both organic matter and terrestrial inputs associated with the mud favour the presence of deposit-feeder organisms. No clear trend was observed among and within the community sites in terms of the species quantitative structure. Thus, convex RFD shapes were observed in three assemblages: the ‘mixed assemblage’ (offshore site), the A. alba (North Sea), and the pebbles (Normandy coast). ‘Sigmoid’ shapes were observed in the pebbles (Dover Strait) and A. alba (English coast) communities. Presumably, these shapes can be caused by the combined action of physical (strong currents, substrate stability, mud content in the sediments) and biological factors (co-occurrence of species from different communities, strong species recruitment, relative dominance of carnivorous species).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angermeier PL and Winston MR (1999) Characterizing fish community diversity across Virginia landscapes prerequisite for conservation. Ecological Applications 9: 335-349
Cabioch L (1984) Groupe de recherche coordonnés Manche (Greco 19). Rapport d'activité No. 3,188 p
Cabioch L and Glaçon R (1975) Distribution des peuplements benthiques en Manche Orientale, de la Baie de Somme au Pas-de-Calais. Comptes Rendus de la Académie des Sciences de Paris 280, serie D, 491-494
Cabioch L and Glaçon R (1977) Distribution des peuplements benthiques en Manche Orientale, du Cap d'Antifer à la Baie de Somme. Comptes Rendus de la Académie des Sciences de Paris 285, serie D, 209-212
Cabioch L, Dauvin JC, Mora-Bermúdez J and Rodríguez-Babio C (1980) Effects de la marée noire de l'Amoco Cadiz sur le benthos supralittoral du nord de la Bretagne. In: Kinne O and Bulnheim HP (eds) 14th European Marine Biological Symposium on Protection of Life in the Sea, Vol 33, pp 192-208. Helgoland, Germany
Chardy P and Dauvin JC (1992) Carbon flows in a subtidal fine sand community from the western English Channel: a simulation analysis. Marine Ecology Progress Series 81: 147-161
Clique PM and Lepetit JP (1987) Catalogue sédimentologique des cótes françaises. Cótes de la Mer du Nord et de la Manche. De la frontière belge a la Baie de Somme. Collection Direction des Études et des Recherches, Electricité de France 61: 12-133
Culver SJ and Buzas MA (2000) Global latitudinal species diversity gradient in deep-sea benthic foraminifera. Deep-Sea Research 47: 259-275
Dauvin JC (1997) Les biocenoses marines et littorales françaises des cótes Atlantique, Manche et Mer du Nord. Synthèse, menaces et perspectives. Museum National d'Histoire Naturelle, Paris, 359 pp
Dauvin JC (1999) Mise à jour de la liste des espèces d'Amphipodes (Crustacea: Peracarida) presents en Manche. Cahiers de Biologie Marine 2: 165-183
Dauvin JC, Kendall M, Paterson G, Gentil F, Jirkov I, Sheader M and de Lange M (1996) An initial assessment of polychaete diversity in the northeastern Atlantic Ocean. Biodiversity Letters 2: 171-181
Davoult D (1990) Biofacies et structure trophique du peuplement des cailloutis du Pas-de-Calais (France). Oceanologica Acta 13: 335-348
Davoult D (1992) Choix raisonné de l'effort d'echantillonnage lors de l'étude spatiale de peuplements macrobenthiques. Comptes Rendus de la Académie des Sciences de Paris 285, serie III, 279-315
Davoult D and Gounin F (1995) Suspension feeding of a dense Ophiothrix fragilis (Abildgaard) population at the water-sediment interface: time coupling of food availability and the feeding behavior of the species. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 41: 567-577
Dewarumez JM, Davoult D and Frontier S (1990) Examples of reponses of benthic communities to environmental stress (Dover Strait, France). Oceanologica Acta Vol. Sp. 11: 191-196
Dewarumez JM, Davoult D, Sanvicente-Añorve L and Frontier S (1992) Is the ‘muddy heterogeneous sediment assemblage’ an ecotone between the pebbles community and the Abra alba community in the Southern Bight of the North Sea? Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 30: 229-238
Eleftheriou A and Holme NA (1984) Macrofauna techniques. In: Holme NA and McIntyre MC (eds) Methods for the Study of Marine Benthos, 2nd Edition, pp 140-216. Blackwell Scientific, Oxford
Frontier S (1985) Diversity and structure in aquatic ecosystems. Oceanography and Marine Biology an Annual Review 23: 253-312
Frontier S (1976) Utilisation des diagrammes rangs-fréquences dans l'analyse des ecosystèmes. Journal de Recherche Océanographique 1: 35-48
Gage JD (1996) Why are there so many species in deep-sea sediments? Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 200: 257-286
Gee JM and Warwick RM (1994) Metazoan community structure in relation to the fractal dimension of marine macroalgae. Marine Ecology Progress Series 103: 141-150
Grassle JF and Maciolek NJ (1992) Deep-sea species richness: regional and local diversity estimates from quantitative bottom samples. American Naturalist 139: 313-341
Hicks GR (1980) Structure of phytal harpacticoid copepod assemblages and the influence of habitat complexity and turbidity. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 44: 157-192
Hixon MA and Menge BA (1991) Species diversity: prey refuges modify the interactive effects of predation and competition. Theoretical Population Biology 39: 178-200
Holme NA (1966) The bottom fauna of the English Channel, part II. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 46: 401-493
Jambu M (1978) Classification automatique pour l'analyse des données. Paris, Dunod, 310 p
Juan J (1982) Programme HIVOR de classification ascendante hierarchique selon les voisins reciproques et le critère de la variance. Les Cahiers de l'Analyse des Données 7: 173-184
Kobayashi S (1981) Diversity indices: relations to sample size and spatial distribution. Japanese Journal of Ecology 31: 231-236
Larsonneur C, Bouysse P and Auffret JP (1982) The superficial sediments of the English Channel and its western approaches. Sedimentology 29: 851-864
MacArthur RA and MacArthur JW (1961) On the bird species diversity. Ecology 42: 594-598
Magurran AE (1983) Ecological Diversity and Its Measurement. Croom Helm, London, 179 pp
May RM (1993) Reply to Poore and Wilson. Nature 361: 598
Michel P and Averty B (1999) Contamination of French coastal waters by organotin compounds: 1997 update. Marine Pollution Bulletin 38: 268-275
Migne A and Davoult D (1997) Distribution quantitative de la macrofaune benthique du peuplement des cailloutis dans le détroit du Pas de Calais (Manche orientale, France). Oceanologica Acta 20: 453-460
Moore PG (1974) The kelp fauna of northeast Britain. III. Qualitative and quantitative ordinations, and the utility of a multivariate approach. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 16: 257-300
Parker RH (1975) The Study of Benthic Communities. A Model and a Review. Elsevier Oceanographic Series, Oxford, 279 pp
Pielou EC (1975) Ecological Diversity. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 286 pp
Pingree RD and Maddock L (1977) Tidal residuals in the English Channel. Journal of theMarine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 57: 339-354
Prygiel J, Davoult D, Dewarumez JM, Glaçon R and Richard A (1988) Description et richesse des peuplements benthiques de la partie française de la Mer du Nord. Comptes Rendus de la Académie des Sciences de Paris (III) 306: 5-10
Rees HL, Pendle MA, Waldock R, Limpenny DS and Boyd SE (1999) A comparison of benthic biodiversity in the North Sea, English Channel, and Celtic Seas. ICES Journal of Marine Science 56: 228-246
Rex MA, Stuart CT and Coyne G (2000) Latitudinal gradients of species richness in the deep-sea benthos of the north Atlantic. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 97: 4082-4085
Salomon JC and Breton M (1991) Courants residuels de marée dans la Manche. Oceanologica Acta Vol. Sp. 11: 47-53
Sanvicente-Añorve L (1991) Caractérisation par des methodes numériques de l'évolution pluriannuelle de deux peuplements benthiques dans la partie française de la Mer du Nord. D. E. A. University of Paris, 50 pp
Sanvicente-Añorve L and Leprêtre A (1995) Typologie des stations océanographiques en Manche Orientale: comparaison des méthodes d'interpolation spatiale. Journal de Recherche Oceanographique 20: 27-32
Sanvicente-Añorve L, Leprêtre A and Davoult D (1996) Large scale spatial pattern of the macrobenthic diversity in the eastern English Channel. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 76: 153-160
Service Hydrographique et Océanographique de la Marine (S.H.O.M.) (1968) Courants de marée dans la Manche et les cótes françaises de l'Atlantique. Paris, 287 pp
Shannon CE and Weaver W (1963) The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press, Illinois 117 p
Snelgrove PVR (1998) The biodiversity of macrofaunal organisms in marine sediments. Biodiversity and Conservation 7: 1123-1132
Snelgrove PVR, Grassle JF and Petrecca RF (1992) The role of food patches in maintaining high deepsea diversity: field experiments with hydrodynamically unbiased colonization trays. Limnology and Oceanography 37: 1543-1550
Souplet A, Glaçon R, Dewarumez JM and Smigielski F (1980) Distribution des peuplements benthiques littoraux en Mer du Nord du Cap blanc-Nez à la frontière de Belgique. Comptes Rendus de la Académie des Sciences de Paris 290: 627-630
Stoner AW and Lewis FG (1985) The influence of the quantitative and qualitative aspects of habitat complexity in tropical seagrass meadows. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 94: 19-40
Vanosmael C, Willems KA, Claeys D, Vincx Mand Heip C (1982) Macrobenthos of a sublittoral sandbank in the Southern bight of the North Sea. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 62: 521-534
Vinchon C, Dupont P, Lafite R and Matthews A (1993) Turbidity in French coastal waters of the Dover Strait illustrated by satellite imagery. Annales de la Societé Géologique du Nord, (2nd serie), T. 2., 179-188
Volle M (1985) Analyse des données. Economica, Paris, 324 p
Warwick RM (1993) Environmental impact studies on marine communities: pragmatical considerations. Australian Journal of Ecology 18: 63-80
Warwick RM and Clarke KR (1995) New ‘biodiversity’ measures reveal a decrease in taxonomic distinctness with increasing stress. Marine Ecology Progress Series 129: 301-305
Warwick RM and Ruswahyuni (1987) Comparative study of the structure of some tropical and temperate marine soft-bottom macrobenthic communities. Marine Biology 95: 641-649
Wiens JA (1989) Spatial scaling in ecology. Functional Ecology 3: 385-397
Withers RG and Thorp CM (1978) The macrobenthos inhabiting sandbanks in Langstone Harbour, Hampshire. Journal of Natural History 12: 445-455
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanvicente-Añorve, L., Leprêtre, A. & Davoult, D. Diversity of benthic macrofauna in the eastern English Channel: comparison among and within communities. Biodiversity and Conservation 11, 265–282 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014583122765
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014583122765