Abstract
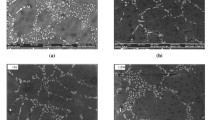
In this investigation, an attempt has been made to examine the effect of Ni on the wear response of a high-aluminum zinc alloy. The alloy has been modified with 0.3 and 0.9 wt% Ni, and wear tests have been carried out at sliding speeds of 3.925 and 6.54 m/s. The wear characteristics have been correlated with their microstructural features. The unmodified alloy exhibits inferior wear behavior with the increase in sliding speed. The improved wear response of the modified alloys is due to the presence of Ni3Al phase formed throughout the matrix. Moreover, the improvement of the modified alloy is more significant at the higher speed of sliding and also with the increase in Ni content. This study indicates that it is possible to develop modified versions of high-aluminum zinc-based alloys having much improved wear characteristics; the information gains special attention in view of the high speed of sliding used in this study.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
E. J. KUBEL JR., Adv. Mater. Proc. 132 (1987) 51.
B. K. PRASAD, A. K. PATWARDHAN and A. H. YEGNESWARAN, Met. & Mat. Trans. A 27A (1996) 3513.
T. CALAYAG and D. FERREA, Soc. of Automotive Engineers 90 (1982) 40.
B. K. PRASAD, A. K. PATWARDHAN and A. H. YEGNESWARAN, Scripta Mat. 37 (1997) 323.
Y. CHEN and M. TU, Mat. Sci. & Tech. 14 (1998) 473.
K. H. ZUM GAHR, Tribology Intl. 31 (1998) 587.
J. T. BURWELL and C. D. STRANG, Proc. R. Soc. A 212 (1952) 470.
J. F. ARCHARD, J. Appl. Phys. 24 (1953) 981.
E. RABINOWICZ, in“Friction & Wear of Materials” (JohnWiley, New York, 1965).
I. M. HUTCHINGS, in “Tribology: Friction & Wear of Engg. Materials” (Edward Arnold, London, 1992).
K. HOKKIRIGAWA, in Proceedings of Surface Modification Technology VIII, edited by T. S. Sudarshan and M. Jeandin (Inst. of Materials, London, 1995) p. 93.
J. H. TYLCZAK and A. OREGON, “ASM Handbook,” Vol. 18, 8th ed. (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1973) p. 186.
P. P. BANDOPADHYAY, S. DAS, S. MADHUSUDAN and A. B. CHATTOPADHYAY, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 18 (1999) 727.
J. L. MURRAY, “Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams,” Vol. 1, 2nd ed. (ASM International, Materials Park, Ohio, 1990) p. 239.
P. J. BLAU, “ASMHandbook,”Vol. 18, 8th ed. (American Society for Metals, Metals Park, Ohio, 1973) p. 774.
M. YAMAGUCHI and Y. UMAKOSHI, Prog. In Mat. Sci. 34 (1990) 37.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhury, P., Das, S. & Datta, B.K. Effect of Ni on the wear behavior of a zinc-aluminum alloy. Journal of Materials Science 37, 2103–2107 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015297904125
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015297904125