Abstract
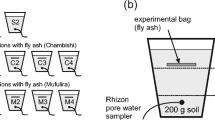
The effectiveness of lignite fly ash for stabilization of Pb,Zn and Cd in tailings and contaminated soils was examined. Flyash was mixed with the contaminated soil or oxidic tailingssamples at various doses and pot experiments were performed.The effectiveness of stabilization was mainly evaluated by thestandard US EPA TCLP toxicity test. The 5-stage sequentialextraction procedure was also applied to determine the form ofcontaminants in the fly ash amended soil or tailings samples.Complementary EDTA extraction tests were also carried out. Thefly ash treatment resulted in the reduction of TCLP solubilityof Pb, Zn and Cd to below the respective regulatory limits at5 and 10% w/w fly ash addition rates in tailings and soil,respectively. Speciation of lead, in the treated soil andtailings samples indicated that there was a significanttransition of the heavy metals form from the exchangeable andcarbonate fractions to reducible and residual, suggesting thatthe potential mechanisms of heavy metals retention are, apartfrom increase of pH, sorption on the oxides and hydroxidessurfaces and binding with the hydrated fly ash compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano, D. C., Page, A. L., Elseewi, A. A., Chang, A. C. and Straughan, I.: 1980, ‘Utilization and disposal of fly ash and other coal residues in terrestrial ecosystems: A review’, J. Environ. Qual. 9, 333–344.
Albanis, T. and Danis, T.: 1997, ‘Applications and Uses of Fly Ash and Other Adsorbents in Fixation and Removal of Toxic Organic Substances from Water’, Proceedings of the Conference on Uses of Fly Ash in Construction, Kozani, Greece, 3-4 October 1997, pp. 33–42, (in Greek).
American Society for Testing and Materials, ASTM C-618: 1988, ‘Standard specification for fly ash and raw or calcinated natural pozzolan for use as a mineral admixture in Portland cement concrete’, Philadelphia (PA).
Apak, R., Tütem, E., Hügül, M. and Hizal, J.: 1998, ‘Heavy metal cation retention by unconventional sorbents (red muds and fly ashes)’, Wat. Res. 32(2), 430–440.
Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME): 1999, ‘Canadian Soil Quality Guidelines for the Protection of Environmental and Human Health: Summary Tables’, in Canadian Environmental Quality Guidelines, 1999, Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg.
Chuan, M., Shu, G. and Liu, J.: 1996, ‘Solubility of Heavy Metals in a Contaminated Soil: Effects of Redox Potential and pH’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 90, 543–556.
Conner, J. R.: 1990, Chemical Fixation and Solidification of Hazardous Wastes, Van Nostrad Reinhold, New York, 692 pp.
Dessi, R., Boi, M., Persod, P. and Ullu, F.: 1999, ‘Environmental Characterization and Rehabilitation Proposals of Montevecchio Mine District’, in J. Gaballah, J. Hager and R. Solozabal (eds), Proceedings of the Global Symposium on Recycling Waste Teratment and Clean Technology REWAS’ 99, San Sebastian, SPAIN, 5-9 September 1999, pp. 2541–2550.
Duchesne, J. and Reardon, E. J.: 1999, ‘Lime treatment of fly ash: characterization of leachate composition and solid/water reactions’, Waste Manage. 19, 221–231.
Eriksson, J. E.: 1989, ‘The influence of pH, soil type and time of adsorption and uptake by plants of Cd added to the soil’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 48, 317–335.
Fang, M., Wong, J. W. C., Ma, K. K. and Wong, M. H.: 1999, ‘Co-composting of sewage sludge and coal fly ash: Nutrient transformations’, Bioresour. Technol. 67, 19–24.
Furr, A. K., Kelly, W. C., Bache, C. A., Gutemann, W. H. and Lisk, D. J.: 1976, ‘Multielement uptake by vegetables and millet grown in pots on fly ash amened soil’, J. Agric. Food Chem. 24, 885–888.
Dutch Soil Standards: 1994, Intervention Values and Target Values, Ministry of Housing, Spatial Planning and Environment.
Kilinckale, F., Ayhan, S. and Apak, R.: 1997, ‘Solidification/stabilization of heavy metal-loaded red mudsand fly ashes’,J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 69(2), 240–246.
Lindsay, W. L.: 1979, Chemical Equilibria in Soils, John Wiley & Sons, New York, Chichester.
Mishra, L. C. and Shukla, K. N.: 1986, ‘Elemental composition of corn and soyabean grown on fly ash amended soil’, Environ. Pollut. (Series B) 12, 313–321.
Papahristou, E.: 1982, ‘Contributions to the Research on the Utilization of Fly Ashes for the Remediation of Lead-Containing Industrial Wastes’, Ph.D. Thesis, Aristotele University of Thessalonika, pp. 154 (in Greek).
Quevauviller, P., Lachia, M., Barahona, E., Rauret, G., Ure, A., Gomez, A. and Muntau, H.: 1996, ‘Interlaboratory comparison of EDTA and DTPA procedures prior to certification of extractable trace elements in calcareous soil’, Sci. Total Environ. 178, 127–132.
Scotti, I. A., Silva, S. and Botteschi, G.: 1999, ‘Effect of fly ash on the availability of Zn, Cu, Ni and Cd to chicory’, Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 72, 159–163.
Shende, A., Juwarkar, A. S. and Dara, S. S.: 1994, ‘Use of fly ash in reducing heavy metal toxicity to plants’, Resour. Conserv. Recycling 12, 221–228.
Song, Y., Wilson, M., Moon, H., Bacon, J. and Bain, D.: 1999, ‘Chemical and mineralogical forms of lead, zinc and cadmium in particle size fractions of some wastes, sediments and soils in Korea’, Appl. Geochem. 14, 621–633.
Stamatakis, M., Fragoulis, D. and Papageorgiou, A.: 1997, ‘Variation in Quality of the Greek Fly Ashes and the Effect on the Cement Production’, Proceedings of the Conference on Uses of fly ash in construction, Kozani, Greece, 3-4 October 1997, pp. 213–228, (in Greek).
Tessier, A., Campbell, P. and Bisson, M.: 1979, ‘Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals’, Anal. Chem. 51, 844–850.
US EPA: 1990, Part 261, Appendix II - Method 1311 Toxicity Characteristic Leaching Procedure (TCLP), Federal Register, Vol. 55, No. 61, March 29, 1990, Rules and Regulations, pp. 11863–11877.
Wong, J. W. C. and Su, D. C.: 1997, ‘Reutilization of coal fly-ash and sewage sludge as an artificial soil-mix: Effects of preincubation on soil physico-chemical properties’, Bioresour. Technol. 59, 97–102.
Wright, R. J., Coding, E. E. and Wright, S. F.: 1998, ‘Root growth and trace element uptake in acid soils treated with coal combustion by-products’, Chemosphere 36(6), 1463–1474.
Xenidis, A., Stouraiti, C. and Paspaliaris, I.: 1999, ‘Stabilization of oxidic tailings and contaminated soils by calcium oxyphosphate addition: The case of Montevecchio (Sardinia, Italy)’, J. Soil Contam. 8(6), 681–697.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stouraiti, C., Xenidis, A. & Paspaliaris, I. Reduction of Pb, Zn and Cd Availability from Tailings and Contaminated Soils by the Application of Lignite Fly Ash. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 137, 247–265 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015507017799
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015507017799