Abstract
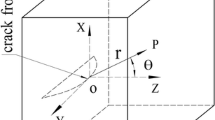
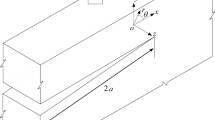
The sign of the T-stress has been widely used for deciding whether directional stability prevails for straight cracks subjected to mode I loading under small scale yielding. However, there is little evidence for the reliability of such a criterion. On the contrary, it is shown that a local criterion is not applicable and that directional stability generally depends on body and load geometry as well as on material parameters, whereas the sign of the T-stress is totally irrelevant in most cases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AlFalou, A.A., Larralde, H. and Ball, R.C. (1997). Effect of T-stresses on the path of a three-dimensional crack propagating quasistsically under type I loading. International Journal of Solids and Structures 34, 569–580.
Broberg, K.B. (1975). On the theory of wedging. Reports of the Research Institute of Strength and Fracture of Materials, Tohoku University 11, 1–27.
Broberg, K.B. (1999). Cracks and Fracture. Academic Press, London.
Broberg, K.B. (2001). Private communication.
Cotterell, B. and Rice, J.R. (1980). Slightly curved or kinked cracks. International Journal of Fracture 16, 155–169.
Fleck, N.A., Hutchinson, J.W. and Sou, Z. (1991). Crack path selection in a brittle adhesive layer. International Journal of Solids and Structures 27, 1683–1703.
Gao, H. and Chiu, C. (1992). Slightly curved or kinked cracks in anisotropic elastic solids. International Journal of Solids and Structures 29, 947–972.
Gol'dstein, R.V. and Salganik, R.L. (1974). Brittle fracture of solids with arbitrary cracks. International Journal of Fracture 10, 507–523.
Melin, S. (1983). Why do cracks avoid each other? International Journal of Fracture 23, 37–45.
Melin, S. (1986). When does a crack grow under mode II conditions? International Journal of Fracture 30, 103–114.
Melin, S. (1991). On the directional stability of wedging. International Journal of Fracture 50, 293–300.
Melin, S. (1992). Directional stability of an originally straight crack. International Journal of Fracture 53, 121-128.
Movchan, A.B., Gao, H. and Willis, J.R. (1998). On pertubations of plane cracks. International Journal of Solids and Structures 35, 3419–3453.
Sladek, J., Sladek, V. and Fedelinski, P. (1997). Contour integrals for mixed-mode crack analysis; effect of nonsingular terms. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics 27, 115–127.
Williams, M.L. (1957). On the stress distribution at the base of a stationary crack. Journal of Applied Mechanics 24, 109–114.
Yang B. and Ravi-Chandar, K. (2001). Crack path instabilities in a quenched glass plate. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 49, 91–130.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Melin, S. The influence of the T-stress on the directional stability of cracks. International Journal of Fracture 114, 259–265 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015521629898
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1015521629898