Abstract
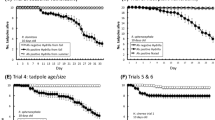
Declines of amphibians have been attributed to many factors including habitat degradation. The introduction of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) as a biological agent for aquatic plant control in ponds and lakes managed narrowly for human recreation has likely contributed to amphibian declines through massive plant removal and associated habitat simplification and thus degradation. This research examined the interactions among grass carp and three Midwestern aquatic plants (Jussiaea repens, Ranunculus longirostris, and R. flabellaris) that may be of value in rehabilitation of habitats needed by amphibians. The feeding preference study found that C. idella avoided eating both J. repens and R. longirostris. Ranunculus species studied to date contain a vesicant toxin called ranunculin that is released upon mastication. The study that compared the effects of R. flabellaris, J. repens and a control food administered by tube feeding to C. idella found significant lesions only in the mucosal epithelium of the individuals exposed to R. flabellaris. The avoidance by C. idella of J. repens and R. longirostris in the feeding preference study, and the significant toxicity of R. flabellaris demonstrated by the dosing study, indicate these plants warrant further examination as to their potential effectiveness in aquatic amphibian habitat rehabilitation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, K. (1992). Herpetology: Current Research on Amphibians and Reptiles from the World Congress, Oxford, OH: Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles.
AOAC, (1990). Official Methods of Analysis (15th edn) Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA.
Anderson, R.J., Luu, H.A., Chen, D.Z.X., Holmers, C.F.B.R., Kent, M.L., LeBlanc, M., Taylor, F.J.R.M. and Williams, D.E. (1993). Chemical and biological evidence links microcystins to salmon netpen liver disease. Toxicon. 31, 1315–23.
Arnold, S.J. and Wassersug, R.J. (1978). Differential predation on metamorphic anurans by garter snakes (Thamnophis): social behavior as a possible defense. Ecology 59, 1014–22.
Balon, E.K. (1974). Domestication of the carp (Cyprinus carpio) L, Royal Ontario Museum. p. 37.
Beasley, V.R., Dahlem, A.M., Cook, W.O., Valentine, W.M., Lovell, R.A., Hooser, S.B., Harada, K.-I., Suzuki, M. and Carmichael, W.W. (1989). Diagnostic and clinically important aspects of cyanobacterial (blue-green algae) toxicoses. J. Vet. Diag. Invest. 1, 359–65.
Beasley, V.R., Faeh, S.A., Wikoff, B., Eisold, J., Nichols, D., Cole, R., Schotthoefer, A.M., Staehle, C., Greenwell, M. and Brown, L.E. (2002). Risk factors and the decline of the cricket frog, Acris crepitans: Evidence for involvement of herbicides, parasitism, and habitat modification. In Lannoo, M. (ed.) Status and Conservation of North American Amphibians. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press, (in press).
Bonar, S.A., Vecht, S.A., Bennett, C.R., Pauley, G.B. and Thomas, G.L. (1993). Capture of grass carp from vegetated lakes. J. Aquat. Plant Man. 31, 168–74.
Brady, P. (1982). White Amur (Grass Carp). USDA, SCS, Little Rock AR.
Brodman, R. and Kilmurry, M. (1998). Status of amphibians in northwestern Indiana. In Lannoo, M.J. (ed.) Status and Conservation of Midwestern Amphibians. Iowa City, IA: University of Iowa Press, pp. 125–36.
Brooker, M.P. and Edwards, R.W. (1975). Review paper: Aquatic herbicides and the control of water weeds. Water Res. 9, 1.
Buckingham, G.R. and Habeck, D.H. (1990). Aquatic Weeds: Classical Biological Control in the Southern U.S., pp. 167–73.
Center, T., Sutton, D.L., Ramney, V.A. and Langeland, K.A. (1991). Other Methods of Aquatic Plant Management. Aquatic Pest Control Applicator Manual, Gainesville, FL: University of Florida, pp. 61–7.
Cooke, G.D., Welch, E.B., Peterson, S.A. and Newroth, P.R. (1986). Lake and Reservoir Restoration. Storeham, MA: Butterworth Publishers.
Cooper, M.R. and Johnson, A.W. (1994). Poisonous Plants and Fungi: An Illustrated Guide. Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food, London, England: HMSO.
Fajt, J.R. and Grizzle, J.M. (1993). Oral toxicity of rotenone for common carp. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 122, 302–4.
Foster, A.B. (1973). Approved Practices in Soil Conservation. Danville, IL: The Interstate Printers and Publishers Inc..
Green, B.D., Dixon, J.R., Mueller, J.M., Whiting, M.J. and Thornton, O.W. (1994). Feeding ecology of the concho water snake, Nerodia harteri paucimaculata. J. Herpetol. 28, 165–72.
Greenwell, M., Beasley, V. and Brown, L.E. (1996). Cricket frog research: The mysterious decline of the cricket frog. Aquaticus 26, 48–54.
Hargeby, A. (1990). Macrophyte associated invertebrates and the effect of habitat permanence. Oikos. 57, 338.
Hay, R. (1998). Blanchard's cricket frogs in Wisconsin: A status report. In Lannoo, M.J. (ed.) Status and Conservation of Midwestern Amphibians. Iowa City, IA: University of Iowa Press, pp. 19–82.
Illinois-DNR, (1994). Aquatic Plants Their Identification and Their Management. Springfield, IL: Illinois Department of Conservation.
Jeraci, J.L., Hernandez, T., Robertson, J.B. and Van Soest, P.J. (1988). New and improved procedure for neutral-detergent fiber. J. Anim. Sci. 66(Suppl. 1): 351.
Johnson, P.T., Lunde, K.B., Ritchie, E.G. Launer, A.E. (1999). The effect of trematode infection on amphibian limb development and survivorship. Science 284, 802–4.
Jung, R.E. (1993). Blanchard's cricket frogs (Acris crepitans blanchardi) in southwest Wisconsin. Transactions of the Wisconsin Academy of Sciences. Arts and Letters 81, 79–87.
Klussman, W.K., Noble, R.L., Martyn, R.D., Clark, W.J., Betsill, R.K., Bettoli, P.W., Cichra, M.F. and Campbell, J.M. (1988). Control of Aquatic Grass Carp in Lake Conroe, Texas, and the Effects on the Reservoir Ecosystem. College Station, TX: Texas Agricultural Experiment Station.
Lannoo, M.J. (1998). Amphibian conservation and wetland management in the Upper Midwest: A catch-22 for the cricket frog? In Lannoo, M.J. (ed.) Status and Conservation of Midwestern Amphibians. Iowa City, IA: University of Iowa Press, 330–9.
Leslie, A.J. and Kobylinski, G.J. (1985). Benthic macroinvertebrates response to aquatic vegetation removal by grass carp in North-Florida Reservoir. Florida Scientist 48, 220.
Mitzner, L. (1980). Biological Control of Nuisance Aquatic Vegetation by Grass Carp. Iowa Conservation Commission Fisheries Section.
Oldham, M.J. (1992). Declines in the Blanchard's cricket frog in Ontario. In Bishop, C.A. and Pettit, K.E. (eds) Declines in Canadian Amphibian Populations: Designing a National Monitoring Strategy. Occasional Paper No. 76, Ottawa Canada: Canadian Wildlife Service, pp. 30–1.
Opuszynski, K. and Shireman, J.V. (1995). Herbivorous Fishes Culture and Use for Weed Management. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Ramus, E. (1998). 1998–1999 Directory: The Herpetology Sourcebook. Reptiles and Amphibian Magazine, Pottsville, PA.
Ruijgrok, H.W.L. (1966). Distribution of ranunculin and cyanogenetic compounds in the Ranunculaceae, In Swain, T. (ed.) Comparative Phytochemistry. New York: Academic Press, pp. 175–86.
Schramm, H.L., Jirka, L.J. and Hiyer, M.V. (1987). Epiphytic macroinvertebrates on dominant macrophytes in two central Florida lakes. Journal of Freshwater Ecology. 4, 151.
Shireman, J.V. and Smith, C.R. (1983). Synopsis of biological data on the grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (Cuvier and Valenciennes, 1844). FAO Fisheries Synopsis. 135, 86.
Sterner, R.W. (1989). Resource competition during seasonal succession toward dominance by cyanobacteria. Ecology 70, 229–45.
Theriot, R.F. and Sanders, D.R. (1975). Food preferences of yearling hybrid carp. Hyacinth Con. J. 13, 51.
Wassersug, R.J. and Sperry, D.G. (1977). The relationship of locomotion to differential predation on Pseudacris triseriata (Anura: Hylidae). Ecology 58, 830–9.
Watkins, C.E., Shireman, J.V. and Haller, W.T. (1983). The influence of aquatic vegetation upon zooplankton and benthic macroinvertebrates in Orange Lake, Florida. J. Aquat. Plant Man. 21, 78.
Westbrooks, R.G. Preacher, J.W. (1986). Poisonous Plants of Eastern North America. University of South Carolina Press.
Whitwell, T. and Bayne, D.R. (1980). Weed Control in Lakes and Farm Ponds. Auburn, AL: Alabama Cooperative Extension Service, Auburn University.
Wiley, M.J. and Wike, L.D. (1986). Energy balances of diploid, triploid, and hybrid grass carp. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 115, 853.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murphy, J.E., Beckmen, K.B., Johnson, J.K. et al. Toxic and Feeding Deterrent Effects of Native Aquatic Macrophytes on Exotic Grass Carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Ecotoxicology 11, 243–254 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016344103565
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016344103565