Abstract
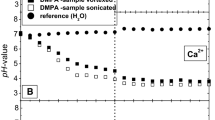
The partitioning of six phenothiazines was determined between phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) and the lipid phases of cyclohexane, n-octanol and dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine (DMPC). For DMPC liposomes studies were carried out both below and above the phase transition temperature (Tc) of the liposomes. The partitioning of chlorpromazine hydrochloride between n-octanol and phosphate buffer was both pH and concentration-dependent. A linear relationship between the absolute temperature (T−1) and the logarithm of the equilibrium partition coefficient (ln K) was derived. The temperature dependence of the partition coefficient (K) over the temperature range 20–40° C in cyclohexane and n-octanol, and 5–40° C in DMPC liposomes, permitted the calculation of free-energy (G), enthalpy (H) and the entropy (S) of partitioning. Both the entropy and the enthalpy of partitioning of phenothiazines were positive in the three systems studied. In general, the partitioning of phenothiazines in cyclohexane, n-octanol and DMPC liposomes (both above and below the phase transition temperature (Tc)) is entropically controlled. Correlation was not however found between the free-energy of oil-water partitioning and liposome-water partitioning which may be attributed to the formation of surface associated phenothiazine in high concentrations at the liposome water interface. The concentration dependent partitioning of chlorpromazine in DMPC liposomes may be attributed to the adsorbed fraction of drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bingham, A. D. (1968) Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol., 18, 29–95.
Papahadjopoulos, D., Kimelberg, K. K. (1973) Prog. Surface Sci., 4, 141–232.
Meyer, H. (1899) Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol., 42, 110.
Overton, E. (1901) Studien über die Narkose, Fischer, Jena, Germany.
Collander, R. (1954) Physiol. Plant., 7, 420.
Burton, D. E., Clark, K., Gray, G. W. (1964) J. Chem. Soc., 1315.
Hansch, C., Quinlan, J. E., Lawrence, G. L. (1968) J. Org. Chem., 33, 347.
Smith, R. N., Hansch, C., Ames, M. (1975) J. Pharm. Sci., 64, 599–606.
Leo, A., Hansch, C., Elkins, D. (1971) Chem. Rev., 71, 525–554.
Hansch, C., Leo, A. (1979) “Substituent Constants for Correlation Analysis in Chemistry and Biology”, Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Murthy, K. S., Zografi, G. (1970) J. Pharm. Sci., 59, 1281–1285.
Vezin, W. R., Florence, A. T. (1979) Int. J. Pharm., 3, 231–237.
Leterrier, F., Kersante, R. (1975) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 63, 515–521.
Maoi, M., Suzuki, T., Yagi, K. (1979) Biochem. Pharmac., 28, 295–299.
Schwendener, R. T., Weder, H. G. (1978) Biochem. Pharmac., 27, 2721–2727.
Spooner, P. J. R., Olliff, C. J. (1978) J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 30, 38P.
Jain, M. K., Wu, N. M. (1978) Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun., 81, 1412–1417.
Ahmed, M., Burton, J. S., Hadgraft, J., Kellaway, I. W. (1980) Biochem. Pharmacol., 29, 2361–2363.
Ahmed, M., Burton, J. S., Hadgraft, J., Kellaway, I. W. (1981) J. Memb. Biol., 58, 181–189.
Ahmed, M., Burton, J. S., Hadgraft, J., Kellaway, I. W. (1981) Chem. Phys. Lipids, 27, 251–262.
Stahl, E. (1969) “Thin-Layer Chromatography”, Second Ed., pp. 508–517. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Tinoco, I., Sauer, K., Jr., Wang, J. C. (1978) Physical Chemistry: Principles and Application in Biological Sciences. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N. J.
Melchior, D. L., Steim, J. M. (1976) Ann. Rev. Biophys. Bioeng., 5, 205–238.
Cohen, B. E., (1975) J. Memb. Biol., 20, 205–234.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmed, A.M.S., Farah, F.H. & Kellaway, I.W. The Thermodynamics of Partitioning of Phenothiazines between Phosphate Buffer and the Lipid Phases of Cyclohexane, n-Octanol and DMPC Liposomes. Pharm Res 2, 119–124 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016359215869
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016359215869