Abstract
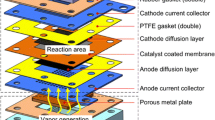
A five-cell 150 W air-feed direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) stack was demonstrated. The DMFC cells employed Nafion 117® as a solid polymer electrolyte membrane and high surface area carbon supported Pt-Ru and Pt catalysts for methanol electrooxidation and oxygen reduction, respectively. Stainless steel-based stack housing and bipolar plates were utilized. Electrodes with a 225 cm2 geometrical area were manufactured by a doctor-blade technique. An average power density of about 140 mW cm−2 was obtained at 110 °C in the presence of 1 M methanol and 3 atm air feed. A small area graphite single cell (5 cm2) based on the same membrane electrode assembly (MEA) gave a power density of 180 mW cm−2 under similar operating conditions. This difference is ascribed to the larger internal resistance of the stack and to non-homogeneous reactant distribution. A small loss of performance was observed at high current densities after one month of discontinuous stack operation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Kordesch and G. Simader, ‘Fuel Cells and their Applications’ (VCH, Weinheim, 1996).
A. Hamnett, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A354 (1996) 1653.
M.P. Hogarth and G.A. Hards, Platinum Metal Rev. 40 (1996) 150.
C. Lamy and J-M. Léger, in O. Savadogo and P.R. Roberge (Eds), Proc. 2nd International Symp. on ‘New Materials for Fuel Cells and Modern Battery Systems’, Montréal, Canada (1997), pp. 477–487.
A.K. Shukla, P.A. Christensen, A. Hamnett and M.P. Hogarth, J. Power Sources 55 (1995) 87.
L. Liu, C. Pu, R. Viswanathan, Q. Fan, R. Liu and E.S. Smotkin, Electrochim. Acta 43 (1998) 3657.
X. Ren, M.S. Wilson and S. Gottesfeld, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143 (1996) L12.
A.S. Aricò, P. Creti, P.L. Antonucci and V. Antonucci, Electrochem. Solid State Lett. 1 (1998) 4.
S.R. Narayanan, W.Chun, T.I. Valdez, B. Jeffries-Nakamura, H. Frank, S. Surampudi, G. Halpert, J. Kosek, C. Cropley, A.B. LaConti, M. Smart, Q. Wang, G. Surya Prakash and G.A. Olah, Program and Abstracts, Fuel Cell Seminar (1996), pp. 525–8.
M. Baldauf and W. Preidel, J. Power Sources 84 (1999) 161.
S. Wasmus and A. Kuver, J. Electroanal. Chem. 461 (1999) 14.
A.S. Aricò, A.K. Shukla, K.M. el-Khatib, P. Cretì and V. Antonucci, J. Appl. Electrochem. 29 (1999) 671.
A. Hamnett and B.J. Kennedy, Electrochim. Acta 33 (1988) 1613.
K. Scott, W.M. Taama, P. Argyropoulos and K. Sundmacher, J. Power Sources 83 (1999) 204.
S. Cleghorn, X. Ren, S. Thomas and S. Gottesfeld, ‘Book of Extended Abstracts’, 1997 ISE-ECS Joint Symposium, Paris, Sept. (1997), Abstract 182, pp. 218–219.
A.S. Aricò, P. Creti, H. Kim, R. Mantegna, N. Giordano and V. Antonucci, J. Electrochem. Soc. 143 (1996) 3950.
S. C. Thomas, X. Ren and S. Gottesfeld, in S. Gottesfeld and T.F. Fuller (Eds), ‘Proton Conducting Fuel Cells in Proton Conducting Membrane Fuel Cells’ (Second International Symposium), Proc. 98–27, (Electrochemical Society, Pennington, NJ, 1999), pp. 267–272.
T.J. Schmidt, H.A. Gasteiger and R.J. Behm, Electrochem. Commun. 1 (1998) 1.
M. Gotz and H. Wendt, Electrochim. Acta 43 (1998) 3637.
K. Lasch, L. Jorissen and J. Garche, in C. Lamy and H. Wendt (Eds), Proceedings of the Workshop ‘Electrocatalysis in Indirect and Direct Methanol PEM Fuel Cells’, 12–14 Sept. (1999), Portoroz, Slovenia, p. 104.
H. Kim and A. Wieckowski, in O. Savadogo (Ed), Third International Symposium. on ‘New Materials for Fuel Cells and Modern Battery Systems’, Montrèal, Canada (1999), pp. 125–126.
R.M. Moore, S. Gottesfeld and P. Zelenay, in S. Gottesfeld and T.F. Fulles (Eds), ‘Proton Conducting Fuel Cells in Proton Conducting Membrane Fuel Cells’ (Second International Symposium), Proceedings, 98–27, (1999), pp. 365–379.
B.D. McNicol, D.A.J. Rand and K.R. Williams, J. Power Sources 83, (1999) 15.
M. Watanabe and S. Motoo, J. Electroanal. Chem. 60 (1975) 275.
P.S. Kaurenan and E. Skou, J. Electroanal. Chem. 408 (1996) 189.
P.L. Antonucci, A.S. Aricò, P. Cretì, E. Ramunni and V. Antonucci, Solid State Ionics 125 (1999) 431.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buttin, D., Dupont, M., Straumann, M. et al. Development and operation of a 150 W air-feed direct methanol fuel cell stack. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry 31, 275–279 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017526214805
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017526214805