Abstract
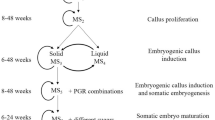
The aminoglycoside antibiotic kanamycin was evaluated for its effects on callus initiation from hypocotyl and cotyledon explants, proliferation of non-embryogenic and embryogenic calli, initiation and development of somatic embryos in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). On this basis, the potential use of kanamycin as a selective agent in genetic transformation with the neomycin phosphotransferase II gene as the selective marker gene was evaluated. Cotton cotyledon and hypocotyl explants, and embryogenic calluses were highly sensitive to kanamycin. Kanamycin at 10 mg/L or higher concentrations reduced callus formation, with complete inhibition at 60 mg/L. Kanamycin inhibited embryogenic callus growth and proliferation, as well as the initiation and development of cotton somatic embryos. The sensitivity of embryogenic callus and somatic embryos to kanamycin was different during the initiation and development stages. Kanamycin was considered as a suitable selective agent for transformed callus formation and growth of non-embryogenic callus. Forty to sixty mg/L was the optimal kanamycin concentration for the induction and proliferation of transformed callus. The concentration of kanamycin must be increased (from 50 to 200 mg/L) for the selection of transformation embryogenic callus and somatic embryos. A scheme for selection of transgenic cotton plants when kanamycin is used as the selection agent is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayley C, Trolinder N, Ray C, Morgan M, Quisenberry JE and Ow DW (1992) Engineering 2,4-D resistance into cotton. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 83(5): 645–649
Beck E, Ludwig G, Auerswald EA, Reiss R and Schaller H (1982) Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene 19: 327–336
Chen ZM, Schnurr JA and Kapaun (1998) Timentin as an alternative antibiotic for supression of Agrobacterium tumefaciens in genetic transformation. Plant Cell Reports 17: 646–649
Chen ZX, Li SJ and Trolider NL (1987) Some characteristics of somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in cotton cell suspension culture. Scientia Agricultura Sinica 20: 6–11
Chlan CA, Lin JM, Cary JW and Cleveland TE (1995) A procedure for biolistic transformation and regeneration of transgenic cotton from meristematic tissue. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter 13: 31–37
Colby SM and Meredith CP (1990) Kanamycin sensitivity of cultured tissue of Vitis. Plant Cell Reports 9: 237–240
Cousins YL, Lyon BR and Llewell DJ (1991) Transformation of an Australian cotton cultivar: prospects for cotton improvement through genetic engineering. Austalian Journal of Plant Physiology 18(5): 481–494
Davidonis GH and Hamilton RH (1983) Plant regeneration from callus tissue of Gossypium hirsutum L. Plant Science Letters 32: 89–93
Davies J, Gorini L and Davis BD (1965) Misreading of RNA codewords induced by aminoglycoside antibiotics. Mol Pharmacol 1: 93–106
DeBlock M, Herrera-Estrella L, Van Montagu M, Schell J and Zambryski P (1984) Expression of foreign gene in regenerated plants and their progeny. EMBO J 3: 1681–1689
Finer JJ and McMullen MD (1990) Transformation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) via particle bombardment. Plant Cell Reports 8: 586–589
Firoozabady E, DeBoer DL, Merlo DJ, Halls E, Halk EL, Amerson LN, Rashka KE and Murray EE (1987) Transformation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) by Agrobacterium tumefaciens and regeneration of transgenic plants. Plant Molecular Biology 10: 105–106
Flavell RB, Dart E, Fuchs RL and Fraley RT (1992) Selectable marker genes: safer for plants? Bio/Technology 10: 141–144
Fraley RT, Roger SG and Horsch RB (1986) Genetic transformation in higher plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Science 4: 1–46
Gamborg O, Miller R and Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Experimental Cell Research 50: 151–158
Gimenez CA, MenendezYuffa A and deGarcia E (1996) Effect of the antibiotic kanamycin in different explants of Catimor, a hybrid coffee plant (Coffea species). Phyton-International Journal of Experimental Botany 59: 39–46
Holford P and Newbury HJ (1992) The effect of antibiotics and their breakdown products on the in vitro growth of Antirrhinum majus. Plant Cell Reports 11: 93–96
Humara JM and Ordas RJ (1999) The toxicity of antibiotics and herbicides on in vitro adventitious shoot formation on Pinus pinea L. cotyledons. In Vitro Cellular and Developmental Biology - Plant 35: 339–343
International Advisory Committee (1996) Cotton: Review of World Situation, Monogram by International Advisory Committee, Washington, DC
John ME (1997) Cotton crop improvement through genetic engineering. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology 17: 185–208
John ME and Crow LJ (1992) Gene expression in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) fiber: cloning of the messenger RNAs. P. Natl Acad Sci USA 89(13): 5769–5773
Jorgensen RA, Rothstein SJ and Reznikoff WS (1979) A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Molecular and General Genetics 177: 65–72
Kapaun JA and Cheng ZM (1999) Aminoglycoside antibiotics inhibit shoot regeneration from Siberian elm leaf explants. Hortsciences 34: 727–729
Keller G, Spatola L, McCabe D, Martinell B, Swain W and John ME (1997) Transgenic cotton resistant to herbicide bialaphos. Transgenic Research 6: 385–392
Kolganova TV, Srivastava DK and Mett VL (1992) Callusogenesis and regeneration of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. cv 108-F). Sov Plant Physiol 39: 232–236
Kumar S and Pental D (1998) Regeneration of Indian cotton variety MCU-5 through somatic embryogenesis. Current Science 74: 538–540
Luo JH and Gould JH (1999) In vitro shoot-tip grafting improves recovery of cotton plants from culture. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 57: 211–213
Lyon BR, Cousins YL, Llewell DJ and Dennis ES (1993) Cotton plants transformed with a bacterial degradation gene are protected from accidental spray drift damage by the herbicide 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Transgenic Research 2(3): 162–169
Mazodier P, Cossart P, Giraud E and Gasser F (1985) Completion of the nucleotide sequence of the central region of Tn 5 confirms the presence of three resistance genes. Nucleic acids Research 13: 195–205
McCabe DE and Martinell BJ(1993) Transformation of elite cotton cultivars via particle bombardment of meristems. Biotechnology 11: 596–598
Moazed D and Noller HF (1987) Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites 16s ribosomal RNA. Nature 327: 389–394
Murashige T and Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 80: 662–668
Perlak FJ, Deaton RW, Armstrong TA, Fuchs RL, Sims SR, Greenplate JT and Fishhoff DA (1990) Insect resistant cotton plants. Bio/technology 8: 939–943
Rajasekaran K, Hudspeth RL, Cary JW, Anderson DM and Cleveland TE (2000) High-frequency stable transformation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) by particle bombardment of embryogenic cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Reports 19: 539–545
Rajasekraran K, Grula JW, Hudspeth RL, Pofelis S and Anderson DM (1996) Herbicide-resistant Acala and Coker cotton transformed with a native gene encoding mutant forms of acetohydroxy acid syntheses. Molecular Breeding 2: 307–317
Recht MI, Douthwaite S and Puglisi JD (1999) Basis for prokaryotic specificity of action of aminoglycoside antibiotics. EMBO J 18: 3133–3138
Sarma KS, Evans NE and Selby C (1995) Effects of carbenicillin and cefotaxime on somatic embryogenesis of Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis Carr). Journal of Experimental Botany 46: 1779–1781
Shaw CH, Leemans J, Shaw CH, Van Montagu M and Schell J (1983) A general method for the transfer of cloned genes to plant cells. Gene 23: 315–330
Shoemaker RC, Couche IJ and Galbraith DW (1986) Characterization of somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in cotton(Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Reports 3: 178–181
Thomas JC, Adams DG, Keppenne VD, Wasmann CC, Brown JK, Kanost MR and Bohnert HJ (1995) Protease inhibitors of Manduce sexta expressed in transgenic cotton. Plant Cell Reports 14(12): 758–762
Trolider NL and Goodin JR (1986) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Plant Cell Reports 6: 231–234
Umbeck P, Swain W and Yang NS (1989) Inheritance and expression of genes for kanamycin and chloramphenicol. Crop Science 29(1): 196–201
Umbeck P, Tohnson G, Barton K and Swain W (1987) Genetically transformed cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) plant. Biotechnology 5: 263–266
Voo KS, Rugh CL and Kamalay JC (1991) Indirect somatic embryogenesis and plant recovery from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 27P: 117–124
Wilmink A and Dons JJM (1993) Selective agents and mark genes for use in transformation of monocotyledonous plant. Plant Molecular Biology Reports 11: 165–185
Yepes LM and Aldwinckle HS (1994) Factors that affect leaf regeneration efficiency in apple and effect of antibiotics in morphogenesis. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 37: 257–269
Yepes LM and Aldwinckle HS (1994) Micropropagation of 13 malus cultivars and rootstocks, and effect of antibiotics on proliferation. Plant Growth Regulation 15: 55–67
Zapata C, Park SH, Ei-Zik KM and Smith RH (1999) Transformation of a Texas cotton cultivar by using Agrobacterium and the shoot apex. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 98: 252–256
Zhang BH (1997) Cotton biotechnology and its application. Beijing: China Agricultural Press
Zhang BH and Feng R (1998) Achievement, problems and strategies of transgenic insect-resistant cotton. Acta Agronomica Sinica 24: 238–246
Zhang BH, Feng R, Li XL and Li FL (1996) Anther culture and plant regeneration of cotton (Gossypium klotzschianum Anderss). Chinese Science Bulletin 41: 145–148
Zhang BH, Feng R, Liu F and Yao CB (1999) Direct induction of cotton somatic embryogenesis. Chinese Science Bulletin 44: 766–767
Zhang BH, Liu F and Yao CB (2000) Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in cotton. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 60: 89–94
Zhang BH, Liu F, Yao CB and Wang KB (2000) Recent progress in cotton biotechnology and genetic engineering in China. Current Science 79: 37–44
Zhang DL and Wang ZZ (1989) Tissue culture and embryogenesis of Gossypium hirsutum L. Acta Botanica Sinica 31: 161–163
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, BH., Liu, F., Liu, ZH. et al. Effects of kanamycin on tissue culture and somatic embryogenesis in cotton. Plant Growth Regulation 33, 137–149 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017563327264
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017563327264