Abstract
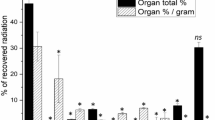
After intravenous injection of a low dose (25 µg/kg) in rats, the anti HIV-1 compound succinylated human serum albumin (Suc-HSA) is taken up mainly in the liver and spleen and is proteolytically degraded. Ten minutes after injection of 125I-Suc-HSA, 72 and 14% of the dose were found in the liver and spleen, respectively. With immunohistochemistry we demonstrated that in both organs, Suc-HSA was specifically endocytosed in endothelial cells. In the isolated perfused rat liver preparation, liver uptake was shown to be saturable, with a K m of 2.9 10−8 M and a V max of 2.4 µg/inin/100 g body weight. The apparent K m and V max in vivo were 2.2 10−7 M and 10.3 µg/min/100 g, respectively. Uptake in liver and spleen was inhibited by preadministration of an excess of formaldehyde-treated albumin and with polyinosinic acid, indicating the involvement of the scavenger receptor, as anticipated for such polyanionic compounds. Suc-HSA is not absorbed intact from the colon and the ileum. After injecting (i.v.) rats with a high dose of Suc-HSA (10 mg/kg), the elimination t 1/2 was 3 hr, and therefore, sustained plasma levels above the concentration needed for in vitro anti-HIV-1 activity can be achieved.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
R. W. Jansen, G. Molema, R. Pauwels, D. Schols, E. De Clercq, and D. K. F. Meijer. Potent in vitro anti-HIV-1 activity of modified human serum albumins. Mol. Pharmacol. 39:818–823 (1991).
R. W. Jansen, R. Pauwels, D. Schols, E. De Clercq, and D. K. F. Meijer. Novel negatively charged human serum albumins are highly potent and selective anti-HIV-1 agents in vitro. Mol. Pharmacol. (in press) (1993).
M. Ito, M. Baba, A. Sato, R. Pauwels, E. De Clercq, and S. Shigeta. Inhibitory effect of dextran sulfate and heparin on the replication of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in vitro. Antivir. Res. 7:361–367 (1987).
V. A. Johnson, M. A. Barlow, T.-C. Chou, R. A. Fisher, B. D. Walker, M. S. Hirsch, and R. T. Schooley. Synergistic inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) replication in vitro by recombinant soluble CD4 and 3′-azi-do-3′-dexythymidine. J. Infect. Dis. 159:837–844 (1989).
J. M. Huraux, D. Ingrand, and H. Agut. Perspectives in Antiviral Chemotherapy. Fund. Clin. Pharmacol. 4:357–372 (1990).
C. Flexner, P. A. Barditchcrovo, D. M. Kornhauser, H. Farzadegan, L. J. Nerhood, R. E. Chaisson, K. M. Bell, K. J. Lorentsen, C. W. Hendrix, B. G. Petty, and P. S. Lietman. Pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and activity of intravenous dextran sulfate in human immunodeficiency virus infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 35:2544–2550 (1991).
R. Yarchoan, H. Mitsuya, and S. Broder. Immunological issues in anti-retroviral therapy. Immunol. Today 11:327–333 (1990).
N. R. Hartman, D. G. Johns, and H. Mitsuya. Pharmacokinetic analysis of dextran sulfate in rats as pertains to its clinical usefulness for therapy of HIV infection. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 6:805–812 (1990).
O. H. Lowry, N. J. Rosebrough, A. L. Farr, and R. J. Randall. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193:265–275 (1951).
M. M. Bradford. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254 (1976).
A. F. S. A. Habeeb. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal. Biochem. 14:328–336 (1966).
R. W. Jansen, G. Molema, T. L. Ching, R. Oosting, G. Harms, F. Moolenaar, M. J. Hardonk, and D. K. F. Meijer. Hepatic endocytosis of various types of mannose-terminated albumins. What is important, sugar recognition, net charge or the combination of these features. J. Biol. Chem. 266:3343–3348 (1991).
R. W. Jansen, G. Molema, G. Harms, J. K. Kruijt, T. J. C. Van Berkel, M. J. Hardonk, and D. K. F. Meijer. Formaldehyde treated albumin contains monomeric and polymeric forms that are differently cleared by endothelial and Kupffer cells of the liver: Evidence for scavenger receptor heterogeneity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 180:23–32 (1991).
F. C. Greenwood, W. M. Hunter, and J. S. Glover. The preparation of 131I labeled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Biochem. J. 89:114–123 (1963).
D. K. F. Meijer, K. Keulemans, and G. J. Mulder. Isolated perfused rat liver technique. In W. B. Jakoby (ed.), Methods in Enzymology, Academic Press, New York, 1981, pp. 81–94.
G. Harms, C. D. Dijkstra, Y. C. Lee, and M. J. Hardonk. Glycosyl receptors in macrophage subpopulations of rat spleen and lymph node. A comparative study using neoglycoproteins and monoclonal antibodies ED1, ED2 and ED3. Cell Tissue Res. 262:35–40 (1990).
D. I. Abrams, S. Kuno, R. Wong, K. Jeffords, M. Nash, J. B. Molahan, R. Gorter, and R. Ueno. Oral dextran sulfate (UA001) in the treatment of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. Ann. Intern. Med. 110:183–188 (1989).
K. J. Lorentsen, C. W. Hendrix, J. M. Collins, D. M. Kornhauser, B. G. Petty, R. W. Klecker, C. Flexner, R. H. Eckel, and P. S. Lietman. Dextran sulfate is poorly absorbed after oral administration. Ann. Intern. Med. 111:561–566 (1989).
D. J. Capon, S. M. Chamow, J. Mordenti, S. A. Marsters, T. Gregory, H. Mitsuya, R. A. Byrn, C. Lucas, F. M. Wurm, J. E. Groopman, S. Broder, and D. H. Smith. Designing CD4 immunoadhesins for AIDS therapy. Nature 337:525–531 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jansen, R.W., Olinga, P., Harms, G. et al. Pharmacokinetic Analysis and Cellular Distribution of the Anti-HIV Compound Succinylated Human Serum Albumin (Suc-HSA) in Vivo and in the Isolated Perfused Rat Liver. Pharm Res 10, 1611–1614 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018972603494
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018972603494