Abstract
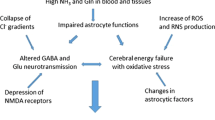
The ammonia and GABAergic neurotransmission hypotheses of the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) have appeared to be unrelated and perhaps mutually exclusive. Observations in animal models of fulminant hepatic failure, that are consistent with increased GABAergic inhibitory neurotransmission contributing to the manifestations of HE, include: (i) abnormal visual evoked potential waveforms that resemble those induced by GABAA/benzodiazepine (BZ) receptor complex agonists; (ii) GABAA/BZ receptor complex antagonist-induced ameliorations of encephalopathy; (iii) increased resistance to drugs which decrease GABAergic tone; and (iv) hypersensitivity of CNS neurons to depression by GABAA/BZ receptor complex agonists. Mechanisms of increased GABAergic tone in HE may include the following: (i) increased brain concentrations of natural BZs; and (ii) increased GABA concentrations in synaptic clefts, possibly due to increased blood-brain-barrier permeability to GABA and a decrease in GABAB receptor density. Both neuroelectrophysiological and behavioral data indicate that ammonia concentrations in the range 0.75-2 mM induce increased excitatory neurotransmission. In contrast, recently, ammonia concentrations in the range 0.15-0.75 mM, i.e. concentrations that commonly occur in plasma in precoma HE, have been shown: (i) to increase GABA-induced chloride current in cultured neurons; and (ii) to enhance synergistically the binding of GABAA/BZ receptor agonists. In addition, increased ammonia concentrations enhance synthesis of neurosteroids in astrocytes, and some neurosteroids potently augment GABAergic neurotransmission. Thus, the modestly elevated concentrations of ammonia, that commonly occur in liver failure, may contribute to the manifestations of HE by enhancing GABAergic inhibitory neurotransmission. This concept appears to unify the ammonia and GABAergic neurotransmission hypotheses.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Akwa, Y., Sananes, N., Gouezou, M., Robel, P., Baulieu, E.E. and Le Goascogne, C. (1993). Astrocytes and neurosteroids: metabolism of pregnenolone and dehydro-epiandrosterone. Regulation by cell density. J. Cell. Biol. 12:135–143.
Bakti, G., Fisch, H.U., Karlaganis, G., Minder, C. and Bircher, J. (1987). Mechanism of the excessive sedative response of cirrhotics to benzodiazepines: model experiments with triazolam. Hepatology 7:629–638.
Bansky, G., Meier, P.J., Ziegler, W.H., Walser, H., Schmid, M. and Huber, M. (1985). Reversal of hepatic coma by benzodiazepine antagonist (Ro 15-1788). Lancet 1: 1324–1325.
Basile, A.S. and Skolnick, P. (1986). Subcellular localization of “peripheral-type” binding sites for benzodiazepines in rat brain. J. Neurochem. 46:305–308.
Basile, A.S., Gammal, S.H., Mullen, K.D., Jones, E.A. and Skolnick, P. (1988). Differential responsiveness of cerebellar Purkinje neurons to GABA and benzodiazepine receptor ligands in an animal model of hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurosci. 8:2414–2421.
Basile, A.S., Gammal, S.H., Jones, E.A. and Skolnick, P. (1989). The GABAA receptor complex in an experimental model of hepatic encephalopathy: evidence for elevated levels of an endogenous benzodiazepine receptor ligand. J. Neurochem. 53:1057–1063.
Basile, A.S., Ostrowski, N.L., Gammal, S.H., Jones, E.A. and Skolnick, P. (1990a). The GABAA receptor complex in hepatic encephalopathy: autoradiographic evidence for the presence of an endogenous benzodiazepine receptor ligand. Neuropsychopharmacology 3:61–71.
Basile, A.S., Pannell, L., Jaouni, T., Gammal, S.H., Fales, H., Jones, E.A. and Skolnick, P. (1990b). Brain concentrations of benzodiazepines are elevated in an animal model of hepatic encephalopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:5263–5267.
Basile, A.S. (1991). The contribution of endogenous benzodiazepine receptor ligands to the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Synapse 7:141–150.
Basile, A.S., Hughes, R.D., Harrison, P.M., Murata, Y., Pannell, L., Jones, E.A. et al. (1991). Elevated brain concentrations of 1,4-benzodiazepines in fulminant hepatic failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 325:473–478.
Basile, A.S. and Jones, E.A. (1997). Ammonia and GABA-ergic neurotransmission: interrelated factors in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 25:1303–1305.
Bassett, M.L., Mullen, K.D., Skolnick, P. and Jones, E.A. (1987). Amelioration of hepatic encephalopathy by pharmacologic antagonism of the GABAA-benzodiazepine receptor complex in a rabbit model of fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology 93:1069–1077.
Bassett, M.L., Mullen, K.D., Scholz, B., Fenstermacher, J. and Jones, E.A. (1990). Increased brain uptake of gamma-aminobutyric acid in a rabbit model of hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 98: 47–757.
Braestrup, C., Schmiechen, R., Neef, G., Nielsen, M. and Petersen E.N. (1982). Interaction of convulsive ligands with benzodiazepine receptors. Science 216:1241–1243.
Butterworth, R.F., Giguère, J.-F., Michaud, J., Lavoie, J. and Pomier Layrargues, G. (1987). Ammonia: Key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:1–12.
Conn, H.O. (1993). Hepatic encephalopathy. In: (L. Schiff and E.R. Schiff, eds). Diseases of the Liver. Lippincott, Philadelphia: 1036–1061.
Ferenci, P., Herneth, A. and Steindl, P. (1996). Newer approaches to therapy of hepatic encephalopathy. Semin. Liver Dis. 16:329–338.
Ferreira, M.R., Gammal, S.H. and Jones, E.A. (1997). Resistance to 3-mercaptopropionic acid-induced seizures in hepatic encephalopathy. Hepato-Gastroenterol. 44:766–769.
Flannery, D.B., Hsia, Y.E. and Wolf, B. (1982). Current status of hyperammonaemia syndromes. Hepatology 2:495–506.
Gammal, S.H., Basile, A.S., Geller, D., Skolnick, P. and Jones EA. (1990). Reversal of the behavioural and electrophysiological abnormalities of an animal model of hepatic encephalopathy by benzodiazepine receptor ligands. Hepatology 11:371–378.
Ha, J.-H. and Basile, A.S. (1996). Modulation of ligand binding to components of the GABAA receptor complex by ammonia: implications for the pathogenesis of hyperammonemic syndromes. Brain Res. 720:35–44.
Itzhak, Y., Roig-Cantisano, A., Dombro, R.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1995). Acute liver failure and hyperammonaemia increase peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor binding and pregnenolone synthesis in mouse brain. Brain Res. 705:345–348.
Itzhak, Y. and Norenberg, M.D. (1994a). Ammonia-induced upregulation of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in cultured astrocytes labeled with [3H]PK 11195. Neurosci. Lett. 177:35–38.
Itzhak, Y. and Norenberg, M.D. (1994b). Attenuation of ammonia toxicity in mice by PK 11195 and pregnenolone sulfate. Neurosci. Lett. 182:251–254.
Jones, D.B., Mullen, K.D., Roessle, M., Maynard, T. and Jones, E.A. (1987). Hepatic encephalopathy: application of visual evoked responses to test hypotheses of its pathogenesis in rats. J. Hepatol. 4:118–126.
Jones, E.A., Yurdaydin, C. and Basile, A.S. (1994). The GABA hypothesis — State-of-the-art. Adv. Exp. Biol. Med. 368: 89–101.
Lambert, J.J., Belelli, D., Hill-Venning, C. and Peters, J.A. (1995). Neurosteroids and GABAA receptor function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 6:295–303.
Maddison, J.E., Dodd, P.R., Morrison, M., Johnson, G.A.R. and Farrell, G.C. (1987). Plasma GABA, GABA-like activity and the brain GABA-benzodiazepine receptor complex in rats with chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 7:621–628.
Majewska, M.D., Harrison, N.L., Schwartz, R.D, Barker, J.L. and Paul, S.M. (1986). Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science 232:1004–1007.
Majewska, M.D. and Schwartz R.D. (1987). Pregnenolone-sulfate: an endogenous antagonist of the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor complex in brain? Brain Res. 404:355–360.
Oja, S.S., Saransaari, P., Wysmyk, U. and Albrecht, J. (1993). Loss of GABAB binding sites in the cerebral cortex of rats with acute hepatic encephalopathy. Brain Res. 629:355–357.
Olasmaa, M., Rothstein, J.D., Guidotti, A., Weber, R.J., Paul, S.M., Spector, S. et al. (1990). Endogenous benzodiazepine receptor ligands in human and animal hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurochem. 55:2015–2033.
Pappas, S.C., Ferenci, P., Schafer, D.F. and Jones, E.A. (1984). Visual evoked potentials in a rabbit model of hepatic encephalopathy. II. Comparison of hyperammonaemic encephalopathy, postictal coma, and coma induced by synergistic neurotoxins. Gastroenterology 86:546–551.
Raabe, W.A. (1989). Neurophysiology of ammonia intoxication. In: (R.F. Butterworth and G. Pomier Layrarques, eds). Hepatic encephalopathy. Pathophysiology and Treatment. Humana, Clifton NJ, 49–77.
Rossle, M., Deckert, J. and Jones, E.A. (1989a). Autoradiographic analysis of GABA/ benzodiazepine receptors in an animal model of acute hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 10:143–147.
Rossle, M., Mullen, K.D. and Jones, E.A. (1989b). Cortical benzodiazepine receptor binding in a rabbit model of hepatic encephalopathy: the effect of Triton X-100 on receptor solubilization. Metab. Brain Dis. 4:203–212.
Roy, S., Pomier Layrargues, G., Butterworth, R.F. and Huet, P.-M. (1988). Hepatic encephalopathy in cirrhotic and portacaval shunted dogs: Lack of changes in brain GABA uptake, brain GABA levels, brain glutamic acid decarboxylase activity and brain postsynaptic GABA receptors. Hepatology 8:845–849.
Rzepczynski, D., Zieve, L., Lindblad, S. and LaFontaine, D. (1986). In vivo studies of GABAergic effects in experimental hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 5:902–905.
Schafer, D.F., Fowler, J.M., Brody, L.E. and Jones, E.A. (1980). Hepatic coma and inhibitory neurotransmission: the enteric bacterial flora as a source of gamma-aminobutyric acid. Gastroenterology 79:1052.
Schafer, D.F. and Jones, E.A. (1982). Hepatic encephalopathy and the gamma-aminobutyric acid neurotransmitter system. Lancet 1:18–20.
Schafer, D.F., Fowler, J.M., Munson, P.J., Thakur, A.K., Waggoner, J.G. and Jones, E.A. (1983). Gamma-aminobutyric acid and benzodiazepine receptors in an animal model of fulminant hepatic failure. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 102:870–880.
Schafer, D.F., Pappas, S.C., Brody, L.E., Jacobs, R. and Jones, E.A. (1984). Visual evoked potentials in a rabbit model of hepatic encephalopathy. I. Sequential changes and comparisons with drug-induced comas. Gastroenterology 86:540–545.
Scollo-Lavizzari, G. and Steinmann, E. (1985). Reversal of hepatic coma by benzodiazepine antagonist (Ro 15-1788). Lancet 1:1324.
Study, R. and Barker, J. (1981). Diazepam and (−)-pentobarbital: fluctuation analysis reveals different mechanisms for potentiation of gamma-aminobutyric acid responses in cultured central neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77:7486–7472.
Takahashi, K., Kameda, H., Kataoka, M., Sanjou, K., Harata, N. and Akaike, N. (1993). Ammonia potentiates GABAA response in dissociated rat cortical neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 151:51–54.
Willow, M. and Johnson, G.A.R. (1981). Dual action of pentobarbitone on GABA binding: role of binding site integrity. J. Neurochem. 37:1291–1294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jones, E.A., Basile, A.S. Does Ammonia Contribute to Increased GABA-ergic Neurotransmission in Liver Failure?. Metab Brain Dis 13, 351–360 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020693026810
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020693026810