Abstract
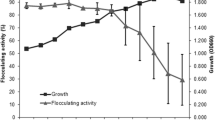
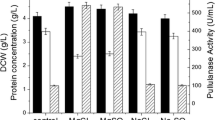
Biosynthesis of extracellular inulinase by bacteria Bacillus polymyxa 29,B. polymyxa 722, and B. subtilis 68 was studied. The optimal parameters for the producer growth were as follows: pH 7.0, 33–35°C, growth duration 72 h. The presence of reduced mineral nitrogen or organic nitrogen was necessary for the enzyme biosynthesis. The inulinase biosynthesis was sharply activated in the presence of carbohydrates. B. polymyxa 722 and B. polymyxa 29 displayed the maximum activities on a starch-containing culture medium; the maximum activity of B. subtilis 68 was in the presence of sucrose. Inulin did not induce inulinase biosynthesis by the strains studied. The time course of bacteria growth and enzyme biosynthesis was studied.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Pessoni, R.A.B., Figueiredo-Ribeiro, R.C.L., and Brada, M.R., J. Appl. Microbiol., 1999, vol. 87, no. 1, pp. 141–147.
Pavlova, N.M., Narsiya, T.A., Kalunyants, K.A., Shapenko, E.F., Krimentsova, V.P., Zueva, R.V., and Slobodkina, G.B., USSR Inventor's Certificate no. 1 631 070, Byull. Izobret., 1991, no. 12, pp. 10–15.
Gupta, A.K., Singh, D.P., and Kaur, N., Phytochemistry, 1998, vol. 49, no. 1, pp. 55–58.
Vullo, D.L., Coto, C.E., and Sineriz, F., Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1991, vol. 57, no. 8, pp. 2392–2394.
Gupta, A.K., Singh, D.P., Kaur, N., and Singh, R., J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol., 1994, vol. 59, no. 4, pp. 377–385.
Gupta, A.K., Gill, A., Kaur, N., and Singh, R., Biotechnol. Lett., 1994, vol. 16, no. 7, pp. 733–734.
Gern, R.M.M., Furlan, S.A., Ninow, J.L., and Jonas, R., Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2001, vol. 55, no. 5, pp. 632–635.
Metody biokhimicheskogo issledovaniya rastenii (Methods for Biochemical Study of Plants), Ermakova, A.I., Ed., Leningrad: Agropromizdat, 1987.
Manual of Methods for General Bacteriology, Gerhardt, F., et al., Eds., Washington: Am. Soc. Microbiol., 1981, vol. 1.
Bezborodov, A.M., Biokhimicheskie osnovy mikrobiologicheskogo sinteza (Boichemical Principles of Microbiological Synthesis), Moscow: Legkaya i Pishchevaya Promyshlennost', 1984.
Mikrobnye fermenty i biotekhnologiya (Microbial Enzymes and Biotechnology), Fogarti, V.M., Ed., Moscow: Agropromizdat, 1986.
Pirt, S.J., Principles of Microbe and Cell Cultivation, Oxford: Blackwell, 1975.
Korneeva, O.S., Zherebtsov, N.A., Shuvaeva, G.P., et al., Biotekhnologiya, 1993, no. 7, pp. 31–35.
Gracheva, I.M. and Krivova, A.Yu., Tekhnologiya fermentnykh preparatov (Technology of Enzymatic Preparations) Moscow: Elevar, 2000.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zherebtsov, N.A., Shelamova, S.A. & Abramova, I.N. Biosynthesis of Inulinases by Bacillus Bacteria. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology 38, 544–548 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020722510374
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020722510374