Abstract
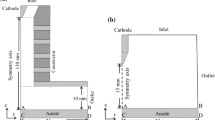
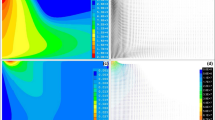
The present modeling of a free-burning argon arc accounts for copper vapor contamination from the anode. Simulations are made for an atmospheric arc that has a length of 10 mm and an electric current of 200 amps. Predicted results for two different anode evaporation rates are compared to those from a pure argon arc with no copper vapor contamination. Copper vapor concentration, temperature, electric potential, and current density profiles are presented. Included in this analysis are radiation losses from both the argon and copper by using recently calculated net emission coefficients. It was found that evaporation of copper from the anode results in a cooling of the arc in a region close to the anode, but has an insignificant influence on the arc close to the cathode. Due to the arc flow characteristics most of the copper vapor tends to be confined to the anode region.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
K. Etemadi and E. Pfender, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 5, 175 (1985).
B. Cheminat and P. Andanson, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 18, 2183 (1985).
A. Farmer, G. Haddad, and L. Cram, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 19, 1723 (1986).
M. Razafinimanana, L. El Hamidi, A. Gleizes, and S. Vacquie, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 4, 501 (1995).
J. Gonzalez, M. Bouaziz, M. Razafinimanana, and A. Gleizes, Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 6, 20 (1997).
A. Gleizes, M. Bouaziz, J. Gonzalez, and M. Razafinimanana, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 24, 891 (1997).
G. Y. Zhao, M. Dassanayake, and K. Etemadi, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 10, 87 (1990).
J. J. Gonzalez, A. Gleizes, P. Proulx, and M. Boulos, J. Appl. Phys. 74, 3065 (1992).
D. Evans and R. Tankin, Phys. Fluids 10, 1137 (1967).
J. Menart, J. Heberlein, and E. Pfender, Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 16, 245 (1996) (Suppl.).
J. J. Lowke, P. Kovitya, and H. P. Schmidt, J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 25, 1600 (1992).
J. Menart and L. Lin, J. Thermophys. Heat Transfer, 12, 500 (1998).
C. R. Wilke, J. Chem. Phys. 14, 517 (1950).
J. Menart, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN (1996).
Y. Chyou, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN (1984).
S. V. Patankar, Numerical Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow, McGraw-Hill, New York (1980).
X. Zhou, D. Berns, and J. Heberlein, 30th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conf., Indianapolis, IN (1994).
K. C. Hsu, K. Etemadi, and E. Pfender, J. Appl. Phys. 54, 1293 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menart, J., Lin, L. Numerical Study of a Free-Burning Argon Arc with Copper Contamination from the Anode. Plasma Chemistry and Plasma Processing 19, 153–170 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021635507382
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021635507382