Abstract
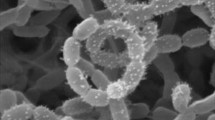
The taxonomic position of an actinomycete isolated from an ultramafic soil in New Caledonia was examined using a polyphasic approach. The organism, which was designated SFOCin 76, was found to have chemical and morphological properties typical of streptomycetes and formed a distinct phyletic line in the Streptomyces violaceusniger clade of the 16S rDNA tree. It also showed a unique pattern of phenotypic properties that distinguished it from representatives of all of the validly described species classified in this clade. It is, therefore, proposed that strain SFOCin 76 be classified in the genus Streptomyces as Streptomyces yatensis sp. nov.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Tai A., Kim B., Kim S.B., Manfio G.P. and Goodfellow M. 1999. Streptomyces malaysiensis sp. nov., a new streptomycete species with rugose, ornamented spores. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49: 1395–1402.
Ambrosio M., Guerriero A., Ripamonti M., Debitus C., Waikedre J. and Pietra F. 1996. The active centers of agelastatin A, a strongly cytotoxic alkaloid of the Coral Sea axinellid sponge with semi-synthetic derivatives. Helv. Chim. Acta 79: 727–735.
Atalan E., Manfio G.P., Ward A.C., Kroppenstedt R.M. and Goodfellow M. 2000. Biosystematic studies on novel streptomycetes from soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 77: 337–353.
Bérdy J. 1995. Are actinomycetes exhausted as a source of secondary metabolites? Biotechnologia 7–8: 13–34.
Chun J. 1995. Computer-assisted classification and identification of actinomycetes, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Newcastle, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK.
Chun J. and Goodfellow M. 1995. A phylogenetic analysis of the genus Nocardia with 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 45: 240–245.
Felsenstein J. 1981. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 17: 368–376.
Felsenstein J., University of Washington, Department of Genetics, Seattle,WA, USA 1993. PHYLIP (Phylogenetic Inference Package), version 3c.
Fitch W.M. and Margoliash E. 1967. Construction of phylogenetic trees: a method based on mutation distances as estimated from cytochrome C sequences is of general applicability. Science 155: 279–284.
Gordon R.E. and Mihm J.M. 1962. Identification of Nocardia caviae (Erikson) nov. comb. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 98: 628–636.
Jaffré T. 1976. Composition clinique et conditions de l'alimentation minérale des plantes sur roches ultrabasiques. Cah ORSTOM, Ser. Biol. 11: 53–63.
Jukes T.H. and Cantor C.R. 1969. Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro H.N. (ed.), Mammalian Protein Metabolism Vol. 3. Academic Press, New York, NY, pp. 21–132.
Kim B., Sahin N., Minnikin D.E., Zakrzewska-Czerwinska J., Mordarski M. and Goodfellow M. 1999. Classification of thermophilic streptomycetes, including the description of Streptomyces thermoalcalitolerans sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49: 7–17.
Kim B., Al-Tai A.M., Kim S.B., Somasundaram P. and Goodfellow M. 2000. Streptomyces thermocoprophilus sp. nov., a cellulose-free endo-xylanase-producing streptomycete. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 50: 505–509.
Kim D., Chun J., Sahin N., Hah Y.-C. and Goodfellow M. 1996. Analysis of thermophilic clades within the genus Streptomyces by 16S ribosomal DNA sequence comparisons. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46: 581–587.
Kim S.B., Falconer C., Williams E. and Goodfellow M. 1998. Streptomyces thermocarboxydovorans sp. nov and Streptomyces thermocarboxydus sp. nov., two moderately thermophilic carboxydotrophic species from soil. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48: 59–68.
Kluge A.G. and Farris F.S. 1969. Quantitative phyletics and the evolution of anurans. Syst. Evol. 18: 1–32.
Küster E. 1959. Outline of a comparative study of criteria used in characterization of the actinomycetes. Int. Bull. Bact. Nomencl. Taxon. 9: 97–104.
Labeda D.P. 1993. DNA relatedness among strains of the Streptomyces lavendulae phenetic cluster group. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 43: 822–825.
Labeda D.P. 1996. DNA relatedness among verticil-forming Streptomyces species (formerly Streptoverticillium species). Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 46: 699–703.
Labeda D.P. 1998. DNA relatedness among the Streptomyces fulvissimus and Streptomyces griseoviridis phenotypic cluster groups. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 48: 829–832.
Labeda D.P. and Lyons A.J. 1991. The Streptomyces violaceusniger cluster is heterogeneous in DNA relatedness among strains: Emendation of the descriptions of Streptomyces violaceusniger and Streptomyces hygroscopicus. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 41: 398–401.
Labeda D.P. and Lyons A.J. 1992. DNA relatedness among strains of the sweet pea potato pathogen Streptomyces ipomoea (Person and Martin 1940) Waksman and Henrici. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 532–535.
Labeda D.P., Lechevalier M.P. and Testa R.T. 1997. Streptomyces stramineus sp. nov., a new species of the verticillate streptomycetes. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47: 747–753.
Lane D.J. 1991. 16/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E. and Goodfellow M. (eds), Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp. 115–175.
Manfio G.P., Zakrzewska-Czerwinska J., Atalan E. and Goodfellow M. 1995. Towards minimal standards for the description of Streptomyces species. Biotechnologia 7–8: 242–253.
Minnikin D.E., O'Donnell A.G., Goodfellow M., Alderson G., Athalye M., Schaal A. et al. 1984. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 2: 233–241.
O'Donnell A.G., Falconer C., Goodfellow M., Ward A.C. and Williams E. 1993. Biosystematics and diversity amongst novel carboxydotrophic actinomycetes. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 64: 325–340.
Saitou N. and Nei M. 1987. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4: 406–425.
Sanglier J.J., Haag H., Huck T.A. and Fehr T. 1996. Review of actinomycetes compounds 1990–1995. Exp. Opin. Invest. Drugs 5: 207–223.
Sembiring L., Ward A.C. and Goodfellow M. 2000. Selective isolation and characterisation of members of the Streptomyces violaceusniger clade associated with the roots of Paraserianthes falcataria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 78: 353–366.
Sembiring L., Goodfellow M., Saintpierre D. and Ward A.C. 2002. The Streptomyces violaceusniger clade: a home for streptomycetes with rugose ornamented spores. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. (accepted).
Shirling E.B. and Gottlieb D. 1966. Methods for characterisation of Streptomyces species. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 16: 313–340.
Stackebrandt E., Rainey F.A. and Rainey N.L. 1997. Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, Actinobacteria classis nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47: 479–491.
Staneck J.L. and Roberts G.D. 1974. Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl. Microbiol. 28: 225–231.
Vobis G. 1992. The genus Actinoplanes and related genera. In: Balows A., Trüper H.G., Dworkin M., Harder W. and Schleifer K.-H. (eds), The Prokaryotes. 2nd edn. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp. 1029–1060.
Wayne L.G., Brenner D.J. and Colwell R.R. (9 other authors) 1987. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 37: 463–464.
Williams S.T., Goodfellow M., Alderson G., Wellington E.M.H., Sneath P.H.A. and Sackin M.J. 1983. Numerical classification of Streptomyces and related genera. J. Gen. Microbiol. 129: 1743–1813.
Williams S.T., Goodfellow M. and Alderson G. 1989. Genus Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici, 1943, 339AL. In: Williams S.T., Sharpe M.E. and Holt J.G. (eds), Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology Vol. 4. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD, pp. 2452–2492.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saintpierre, D., Amir, H., Pineau, R. et al. Streptomyces yatensis sp. nov., a novel bioactive streptomycete isolated from a New-Caledonian ultramafic soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 83, 21–26 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022906325397
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022906325397