Abstract
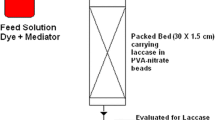
Reactive Black 5 industrial dyeing effluent was decolourized by free and immobilized laccase. The stability of the enzyme (194 h free and 79 h immobilized) depended on the dyeing liquor composition and the chemical structure of the dye. In the decolourization experiments with immobilized laccase, two phenomenons were observed – decolourization due to adsorption on the support (79%) and dye degradation due to the enzyme action (4%). Dyeing in the enzymatically recycled effluent provided consistency of the colour with both bright and dark dyes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abadulla E, Tzanov T, Costa G, Robra KH, Cavaco-Paulo A, Gubitz G (2000) Decolourization and detoxification of textile dyes with a laccase from Trametes hirsuta. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 3357–3362.
Bourbonnais R, Paice MG (1990) Oxidation of non-phenolic substrates. An expanded role for laccase in lignin biodegradation. FEBS Lett. 267: 99–102.
Carpenter JF, Crowe JH (1988) The mechanism of cryoprotection of proteins by solutes. Cryobiology 25: 244–55.
Cho YK, Bailey JE (1979) Immobilization of enzymes on activated carbon: selection and preparation of the carbon support. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 21: 461–476.
Churchley JH, Greaves AJ, Hutchings MG, Phillips DAS, Taylor JA (2000) A chemometric approach to understanding the bioelimination of anionic, water-soluble dyes by a biomass - Part 4: Reactive Dyes. J. Soc. Dyers Colourists 116: 323–329.
Costa S, Tzanov T, Carneiro AF, Paar A, Gübitz GM, Cavaco-Paulo A (2002) Kinetics and stabilization study of catalase immobilized on alumina for treatment of bleaching liquors. Biotechnol. Lett. 24: 173–176.
Davis S, Burns RG (1992) Covalent immobilization of laccase on activated carbon for phenolic effluent treatment. Microb. Biotechnol. 37: 474–479.
Dötsch V, Wider G, Siegal G, Wüthrich K (1995) Salt-stabilized Globular Protein Structure in 7 M Aqueous Urea Solution. FEBS Lett. 372: 288–290.
Emine A, Leman T (1995) Characterization of immobilized catalases and their application in pasteurization of milk with H2O2. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 50: 291–303.
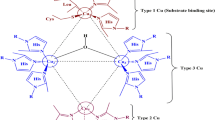
Gianfreda L, Xu F, Bollag JM (1999) Laccases: a useful group of oxidoreductive enzymes. Bioremed. J. 3: 1–25.
Göller K, Galinski EA (1999) Protection of a model enzyme (lactate dehydrogenase) against heat, urea and freeze-thaw treatment by compatible solute additives. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enz. 7: 37–45.
Harold RW (1987) Textiles: appearance analysis and shade sorting. Text. Chem. Color 19: 23–31.
Leonowicz A, Sarkar JM, Bollag JM (1988) Improvement in the stability and reusability of a fungal laccase by immobilization on porous glass. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29: 129–135.
Matulis D, Wu C, Van Pham T, Guy C, Lovrien R (1999) Protection of enzymes by aromatic sulfonates from inactivation by acid and elevated temperatures. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enz. 7: 21–36.
Pierce J (1994) Color in textile effluents: the origins of the problem. J. Soc. Dyers Colorists 110: 131–134.
Robles A, Lucas R, De Cienfuegos AG, Galvez A (2000) Phenoloxidase (laccase) activity in strain of the hyphomycete Chalara paradoxa isolated from olive mill wastewater disposal ponds. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 26: 484–490.
Rogalski J, Jozwik E, Hatakka A, Leonowicz A (1995) Immobilization of laccase from Phlebia radiata on controlled porosity glass. J. Mol. Catal. 95: 99–108.
Spadaro JT, Lorne I, Renganathan V (1994) Hydroxyl radical mediated degradation of azo dyes: evidence for benzene generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 28: 1389–1393.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zille, A., Tzanov, T., Gübitz, G.M. et al. Immobilized laccase for decolourization of Reactive Black 5 dyeing effluent. Biotechnology Letters 25, 1473–1477 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025032323517
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025032323517