Abstract
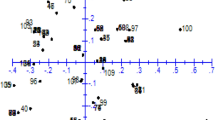
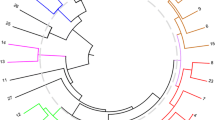
Microsatellite markers were used to characterize 35 banana (Musa spp.)genotypes cultivated in Brazil, including triploid cultivars and tetraploid hybrids. A total of 33 Musa-specific primers were tested, and 11 produced clear ,reproducible and discrete bands. The average number of alleles amplified per primer was 6.1, ranging from 4 to 8, with a total of 67 alleles identified. Phenetic analysis based on Jaccard similarity index derived from presence or absence of the alleles agreed with the morphological classification. Bootstrap analysis divided the genotypes into four clusters, according to genomic group and subgroup classification. The first cluster contained the majority of cultivars which have ‘A’ genome alone; while the second contained all triploid cultivars of the subgroup Prata (Pome) and their tetraploid hybrids. The third cluster contained cultivar ‘Maçã’ together with other genotypes considered for breeding purposes as similar to the Silk subgroup. These last two clusters formed a larger group including the majority of genotypes that resulted from hybridization between M. acuminata and M. balbisiana. The microsatellite loci were highly informative, with some pair of primers generating an unique finger printing for each genomic group and discriminating a genotype of doubtful classification, although somatic mutants from a subgroup were seldom distinguished from their original clone. Tetraploid hybrids exhibited distortion in the proportion of alleles donated by their triploid female parent. For a few primers, some genotypes exhibited a higher number of alleles than expected from their ploidy level, suggesting the occurrence of duplicated alleles or duplicated chromosomal regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhat, K.V. & R.L. Jarret, 1995. Random amplified polymorphic DNA and genetic diversity in Indian Musa germplasm. Genet Res Crop Evol 42: 107-118.
Carreel, F., D.G. Leon, P.J.L. Lagoda, C. Lanaud, C. Jenny, J.P. Horry & H.T. du Montcel, 2002. Ascertaining maternal and paternal lineage within Musa by chloroplast and mitochondrial DNA RFLP analyses. Genome 45: 679-692.
Creste, S., A. Tulmann-Neto & A. Figueira, 2001. Detection of single sequence repeat polymorphisms in denaturing polyacrylamide sequencing gels by silver staining. Plant Mol Biol Rep 19: 299-306.
Crouch, H.K., J.H. Crouch, R.L. Jarret, P.B. Cregan & R. Ortiz, 1998. Segregation at microsatellite loci in haploid and diploid gametes of Musa. Crop Sci 38: 211-217.
Crouch, J.H., H.K. Crouch, A. Tenkouano & R. Ortiz, 1999a. VNTR-based diversity analysis of 2x and 4x full-sib Musa hybrids. Eletron J Biotechn 2: 99-108.
Crouch, J.H., H.K. Crouch, H. Constandt, A. Van Gysel, P. Breyne, M.V. Montagu, R.L. Jarret & R. Ortiz, 1999b. Comparison of PCR-based molecular marker analyses of Musa breeding populations. Mol Breeding 5: 233-244.
Dantas, J.L.L., K. Shepherd, S.O. Silva & W.S. Soares-Filho, 1997. Classificação botânica, origem, evolução e distribuição geográfica. In: E.J. Alves (Ed.), A Cultura da Banana: aspectos técnicos, socioeconômicos e agroindustriais, pp. 27-34. Brasília, Embrapa.
Doyle, J.J. & J.L. Doyle, 1990. Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12: 13-15.
Fauré, S., J.L. Noyer, F. Carreel, J.P. Horry, F. Bakry & C. Lanaud, 1994. Maternal inheritance of chloroplast genome and paternal inheritance of mitochondrial genome in bananas (Musa acuminata). Curr Genet 25: 265-269.
Gawel, N.J., R.L. Jarret & A.P. Whittemore, 1992. Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-based phylogenetic analysis of Musa. Theor Appl Genet 84: 286-290.
Grapin, A., J.L. Noyer, F. Carreel, D. Dambier, F.-C. Baurens, C. Lanaud & P.J.L. Lagoda, 1998. Diploid Musa acuminata genetic diversity assayed with sequence-tagged microsatellite sites. Electrophoresis 19: 1374-1380.
Jenny, C., F. Carreel, K. Tomekpe, X. Perrier, C. Dubois, J.P. Horry & H.T. Montcel, 1999. Les bananiers. In: P. Hamon, M. Seguin, X. Perrier & J.C. Glaszman (Eds.), Centre de Coopération Internationale en Recherche Agronomique pour le Développement. Diversité Génétique des Plantes Tropicales, pp. 113-139. Montpellier, CIRAD.
Kaemmer, D., D. Fisher, R.L. Jarret, F.-C. Baurens, A. Grapin, D. Dambier, J.L. Noyer, C. Lanaud, G. Khal & P.J.L. Lagoda, 1997. Molecular breeding in the genus Musa: a strong case for STMS marker technology. Euphytica 96: 49-63.
Lagoda, P.J.L., D. Dambier, A. Grapin, F.-C. Baurens, C. Lanaud & J.L. Noyer, 1998a. Nonradioactive sequence-tagged microsatellite site analyses: A method transferable to the tropics. Electrophoresis 19: 152-157.
Lagoda, P.J.L., J.L. Noyer, D. Dambier, F.-C. Baurens, A. Grapin & C. Lanaud, 1998b. Sequence tagged microsatellite site (STMS) markers in the Musaceae. Mol Ecol 7: 657-666.
Loh, J.P., R. Kiew, O. Set, L.H. Gan & Y.Y. Gan, 2000. Amplified fragment length polymorphism fingerprinting of 16 bananas cultivars (Musa cvs.). Mol Phylogenet Evol 17: 360-366.
Ortiz, R., 1995. Musa genetics. In: S. Gowen (Ed.), Bananas and Plantains, pp. 84-109, Chapman & Hall, London.
Pillay, M., D.C. Nwakanma & A. Tenkouano, 2000. Identification of RAPD markers linked to A and B genome sequences in Musa L. Genome 43: 763-767.
Pillay M., E. Ogundiwin, D.C. Nwakanma, G. Ude & A. Tenkouano, 2001. Analysis of genetic diversity and relationships in East African banana germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 102: 965-970.
Provan, J., W. Powell & R. Waugh, 1996. Microsatellite analysis of relationships within cultivated potato (Solanum tuberosum). Theor Appl Genet 92: 1078-1084.
Sánchez-Escribano, E.M., J.P. Martin, J. Carreño & J.L. Cenis, 1999. Use of sequence-tagged microsatellite site markers for characterizing table grape cultivars. Genome 42: 87-93.
Silva, S.O., E.J. Alves, K. Shepherd & J.L.L. Dantas, 1997. Cultivares. In: E.J. Alves (Ed.), A Cultura da Banana: aspectos técnicos, socioeconômicos e agroindustriais, pp. 85-105. Brasília, Embrapa.
Silva, S.O., A.P. Matos & E.J. Alves, 1998. Melhoramento genético da bananeira. Pesqui Agropecuária Brasileira 33: 693-703.
Silva, S.O, M.T. Souza-Junior, E.J. Alves, J.R.S. Silveira & M.B. Lima, 2001. Banana breeding program at Embrapa. Crop Breed Appl Biotechn 1: 399-436.
Simmonds, N.W. & K. Shepherd. 1955. The taxonomy and origins of the cultivated bananas. Bot J Linn Soc 55: 302-312.
Simmonds, N.W., 1973. Los plátanos: técnicas agrícolas y producciones tropicales. Editorial Blume, Barcelona, Spain.
Simmonds, N.W., 1995. Bananas. In: J. Smartt & N.W. Simmonds (Eds.), Evolution of Crop Plants, pp. 370-375. Longman, Essex, UK.
Stover, R.H. & N.W. Simmonds, 1987. Bananas. 3rd Edn. Longman Scientific & Technical. New York, USA.
Tautz, D., 1989. Hypervariability of simple sequences as a general source of polymorphic markers. Nucl Acids Res 17: 6463-6471.
Testolin, R., T. Marrazzo, G. Cipriani, R. Quarta, I. Verde, M.T. Dettori, M. Pancaldi & S. Sansavini, 2000. Microsatellite DNA in peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch) and its use in fingerprinting and testing the genetic origin of cultivars. Genome 43: 512-520.
Ude, G., M. Pillay, D. Nwakanma & A. Tenkouano, 2002. Genetic diversity in Musa acuminata Colla and Musa balbisiana Colla and some of their natural hybrids using AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 104: 1246-1252.
Wang, Z., J.L. Weber, G. Zhong & S.D. Tanksley, 1994. Survey of plant short tandem repeats. Theor Appl Genet 88: 1-6.
Yap, I.V. & R.J. Nelson, 1996.WinBoot: A Program for Performing Bootstrap Analysis of Binary Data to Determine the Confidence Limits of UPGMA-based Dendrograms. Manila: International Rice Research Institute-IRRI, 22 pp. (Discussion paper series, 14).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Creste, S., Tulmann Neto, A., de Oliveira Silva, S. et al. Genetic characterization of banana cultivars (Musa spp.) from Brazil using microsatellite markers. Euphytica 132, 259–268 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025047421843
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025047421843