Abstract
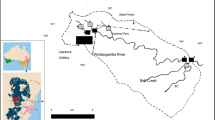
The history of heavy metal pollution in southern Sydney was reconstructed from wetland sediments using chemical analysis. Seven wetlands along the Pacific coast were examined for present day concentrations of acid-extractable Cd, Cu, Fe, Pb and Zn. Additionally, four of these sites were cored in order to assess past levels of these metal contaminants, changes in organic content and magnetic susceptibility variations. The low nutrient status and closed catchments of the study sites suggested that the pollutants were predominantly derived from atmospheric sources. Surficial sediments were enriched with Cd, Cu, Fe, Pb and Zn levels 5.0, 16.4, 22.7, 8.2 and 22.5 times baseline levels, respectively. In some cases, the concentrations of trace metals were in excess of environmentally acceptable levels. The results show a strong spatial association between sources and levels of pollutants, and the increase in metals levels in sedimentary records corresponds well to documentary historical evidence.This study demonstrates the utility of coastal wetlands in the reconstruction of atmospheric pollution histories, and their particular vulnerability to contamination from airborne pollutants in urban areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aaby, B.: 1986, ‘Palaeoecological Studies of Mires’, in B. E. Berglund (ed.), Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp. 145-164.
Alloway, B. J.: 1990, ‘Soil Processes and the Behaviour of Metals’, in B. J. Alloway (ed.), Heavy Metals in Soils, Blackie and Son, Glasgow, pp. 7-28.
ANZECC: 1992, Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for the Assessment and Management of Contaminated Sites, Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council, National Health and Medical Research Council, Australia.
Åström, M. and Nylund, K.: 2000, ‘Impact of historical metalworks on the concentrations of major and trace elements in sediments: A case study in Finland’, Appl. Geochem. 15, 807-817.
Bengtsson, L. and Enell, M.: 1986, ‘Chemical Analysis’, in B. E. Berglund (ed.), Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp. 423-451.
Bennett, K. D.: 1998, Psimpoll 3.01, Quaternary Geology, Institute of Earth Sciences, Uppsala Universitet, Sweden, http://www.kv geo.uu.se/psimpoll.html.
Benson, D. and Howell, J.: 1995, Taken for Granted: The Bushland of Sydney and its Suburbs, Kangaroo Press, Kenthurst, NSW.
Birch, G. F., Evenden, D. and Teutsch, M. E.: 1996, ‘Dominance of point source in heavy metal distributions in sediments of a major Sydney estuary (Australia)’, Environ. Geol. 28, 169-174.
Bruland, K. W., Bertine, K., Koide, M. and Goldberg, E. D.: 1974, ‘History of metal pollution in Southern California coastal zone’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 8, 425-432.
Buchanan, R. A.: 1980, ‘The Lambert Peninsula, Ku-ring-gai Chase National Park: Physiography and the Distribution of Podzols, Shrublands and Swamps, with Details of the Swamp Vegetation and Sediments’, Proceedings of the Linnean Society of New South Wales 104, 73-94.
Bureau of Meteorology: 1979, Climatic Survey - Sydney, Region 5, New South Wales, Australian Government Publishing Service, Canberra.
Bureau of Meteorology: 2001, Bureau of Meteorology Climate Averages: Sydney Airport,http://www.bom gov.au/climate/averages/tables/cw_066037.shtml.
Butlin, N. G. (ed.): 1976, Sydney's Environmental Amenity 1970-1975, Botany Bay Project, Australian National University Press, Canberra.
Chant, J. J.: 1993, ‘Past Cultural Changes and their Effects on Trenerry Reserve, Coogee, New South Wales’, Unpublished B.Sc. Thesis, School of Geography, University of New South Wales.
Chenhall, B. E., Batley, G. E., Yassini, I., Deepers, A. M. and Jones, B. G.: 1994, ‘Ash distribution and metal contents of Lake Illawarra bottom sediments’, Austr. J. Marine Freshw. Res. 45, 977-992.
Chenhall, B. E., Yassini, I. and Jones, B. G.: 1992, ‘Heavy metal concentrations in lagoonal saltmarsh species, Illawarra region, southeastern Australia’, Sci. Total Environ. 125, 203-225.
Clymo, R. S.: 1983, ‘Peat’, in A. J. P. Gore (ed.), Mires: Swamp, Bog, Fen and Moor, General Studies, Ecosystems of the World 4A, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 159-224.
Cridland, F.: 1950, The Story of Port Hacking, Cronulla and Sutherland Shire, Angus and Robertson, Sydney.
Croudace, I.W. and Cundy, A. B.: 1995, ‘Heavy metal and hydrocarbon pollution in recent sediments from Southampton Water, southern England: A geochemical and isotopic study’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 1288-1296.
Cundy, A. B., Croudace, I.W., Cearreta, A. and Irabien, M. J.: 2003, ‘Reconstructing historical trends in metal input in heavily-disturbed, contaminated estuaries: studies from Bilbao, Southampton Water and Sicily’, Appl. Geochem. 18, 311-325.
Daly, J. R. C.: 1993, ‘Human Impact on the Vegetation and Fire Regime, Trenerry Reserve, Coogee, New South Wales’, Unpublished B.Sc. Thesis, School of Geography, University of New South Wales.
Damman, A. W. H.: 1990, ‘Nutrient status of ombrotrophic peat bogs’, Aquilo Ser. Bot. 28, 5-14.
Dearing, J. A. and Foster, I. D. L.: 1986, ‘Lake Sediments and Palaeohydrological Studies’, in B. E. Berglund (ed.), Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp. 67-90.
Dickson, F. P.: 1973, ‘Aboriginal Prehistory of Botany Bay’, in D. J. Anderson (ed.), The Botany Bay Project - A Handbook of the Botany Bay Region - Some Preliminary Background Papers, Botany Bay Project Committee, Sydney, pp. 44-50.
Dodson, J. R., Chant, J. and Daly, J.: 1995, ‘Human impact recorded in an urban wetland's sediments in Sydney, Australia’, Man and Culture in Oceania 11, 113-124.
Doyle, M. O. and Otte, M. L.: 1997, ‘Organism-induced accumulation of iron, zinc and arsenic in wetland soils’, Environ. Pollut. 96, 1-11.
Eades, L. J., Farmer, J. G., MacKenzie, A. B., Kirika, A. and Bailey-Watts, A. E.: 2002, ‘Stable lead isotopic characterisation of the historical record of environmental lead contamination in dated freshwater lake sediment cores from northern and central Scotland’, Sci. Total Environ. 292, 55-67.
Emmerson, R. H. C., O’Reilly-Weise, S. B., Macleod, C. L. and Lester, J. N.: 1997, ‘A multivariate assessment of metal distribution in inter-tidal sediments of the Blackwater Estuary, U.K.’, Marine Pollut. Bull. 34, 960-968.
Engelmann, L.: 1996, ‘Discriminant Analysis’, in Statistics: SYSTAT 6.0, SPSS Inc., pp. 361-407.
EPA: 1997, State of the Environment 1997, NSW Environment Protection Authority, Sydney,http://www.epa.nsw gov.au/soe/97/ch1/6_2.htm.
Evans, L. J.: 1989, ‘Chemistry of metal retention by soils’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 23, 1046-1056.
FAC: 1990, Proposed Third Runway, Sydney (Kingsford-Smith) Airport: Draft Environmental Impact Statement, Kinhill Engineers P/L for the Federal Airports Corporation, Mascot.
Farmer, J. G., Mackenzie, A. B., Sugden, C. L., Edgar, P. J. and Eades, L. J.: 1997, ‘A comparison of the historical lead pollution records in peat and freshwater lake sediments from central Scotland’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 100, 253-270.
Gilbertson, D. D., Grattan, J. P., Cressey, M. and Pyatt, F. B.: 1997, ‘An air pollution history of metallurgical innovation in iron-and steel-making: a geochemical archive of Sheffield’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 100, 327-341.
Gittins, R.: 1980, Canonical Analysis: A Review with Applications in Ecology, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Goodman, G. T. and Roberts, T. M.: 1971, ‘Plants and soils as indicators of metal in air’, Nature 231, 287-292.
Gorrez, M. and Frenzel, B.: 1997, ‘Ash and metal concentrations in peat bogs as indicators of anthropogenic activity’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 100, 355-365.
Griffin, R. J.: 1963, ‘The Botany Basin’, Geological Survey of New South Wales Bulletin 18, Department of Mines, Sydney.
Hong, S., Candelone, J.-P., Patterson, C. C. and Boutron, C. F.: 1996, ‘History of ancient copper smelting pollution during Roman and Medieval times recorded in Greenland ice’, Science 272, 246-249.
Hunt, A., Jones, J. and Oldfield, F.: 1984, ‘Magnetic measurements and heavy metals in atmospheric particulates of anthropogenic origin’, Sci. Total Environ. 33, 129-139.
Irvine, I. and Birch, G. F.: 1998, ‘Distribution of heavy metals in surficial sediments of Port Jackson, Sydney, New South Wales’, Austr. J. Earth Sciences 45, 297-304.
Jeans, D. N.: 1973, ‘Nineteenth Century Botany Bay’, in D. J. Anderson (ed.), The Botany Bay Project - A Handbook of the Botany Bay Region - Some Preliminary Background Papers, Botany Bay Project Committee, Sydney, pp. 51-58.
Johnson, A. G.: 1994, ‘Late Holocene Environmental Canges on Kurnell Peninsula, NSW’, Proceedings of the Linnaean Society of New South Wales 114, 119-132.
Kempter, H. and Frenzel, B.: 2000, ‘The impact of early mining and smelting on the local tropospheric aerosol detected in ombrotrophic peat bogs in the Harz, Germany’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 121, 93-108.
Kuster, H. and Rehfuess, K.-E.: 1997, ‘Pb and Cd concentrations in a southern Bavarian bog profile and the history of vegetation as recorded by pollen analysis’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 100, 379-386.
Ligero, R. A., Barrera, M., Casas-Ruiz, M., Sales, D. and López-Aguayo, F.: 2002, ‘Dating of marine sediments and time evolution of heavy metal concentrations in the Bay of Cádiz, Spain’, Environ. Pollut. 118, 97-108.
Mackereth, F. J. H.: 1965, ‘Chemical Investigation of Lake Sediments and their Interpretation’, Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B161, 295-309.
Mann, S. S. and Ritchie, G. S. P.: 1995, ‘Forms of cadmium in sandy soils after amendment with soils of higher fixing capacity’, Environ. Pollut. 87, 23-29.
Martin, A. R. H.: 1994, ‘Kurnell Fen: An eastern Australian coastal wetland, its Holocene vegetation, relevant to sea-level change and aboriginal land use’, Rev. Palaeobot. Palynol. 80, 311-332.
Martínez Cortizas, A.M., García-Rodeja, E., Pontevedra Pombal, X., Nóvoa Muñoz, J. C., Weiss, D. and Cheburkin, A.: 2002a, ‘Atmospheric Pb deposition in Spain during the last 4600 yr recorded by two ombrotrophic peat bogs and implications for the use of peat as archive’, Sci. Total Environ. 292, 33-44.
Martínez Cortizas, A.M., Gayoso, E. G.-R. and Weiss, D.: 2002b, ‘Peat bog archives of atmospheric metal deposition’, Sci. Total Environ. 292, 1-5.
Martínez-Cortizas, A., Pontevedra-Pombal, X., Nóvoa Muñoz, J. C. and García-Rodeja, E.: 1997, ‘Four thousand years of atmospheric Pb, Cd, and Zn deposition recorded by the ombrotrophic peat bog of Penido Vello (northwestern Spain)’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 100, 387-403.
Monna, F., Lancelot, J., Croudace, I. W., Cundy, A. B. and Lewis, J. T.: 1997, ‘Pb isotopic composition of airborne particulate material from France and the southern United Kingdom: Implications for Pb pollution souces in urban areas’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 2277-2286.
Mooney, S. D., Radford, K. L. and Hancock, G.: 2001, ‘Clues to the ‘burning question’: Pre-European fire in the Sydney coastal region from sedimentary charcoal and palynology’, Ecolog. Manage. Restor. 2, 203-212.
01_inv_levels.pdf.
Nriagu, J. O.: 1979, ‘Global inventory of natural and anthropogenic emissions of trace metals to the atmosphere’, Nature 279, 409-411.
Nriagu, J. O. (ed.): 1984, Toxic Contaminants in the Great Lakes, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Nriagu, J. O.: 1996, ‘A history of global metal pollution’, Science 272, 223-224.
Ohmsen, G. S., Chenhall, B. E. and Jones, B. G.: 1995, ‘Trace metal distributions in two saltmarsh substrates, Illawarra region, New South Wales, Australia’, Wetlands (Australia) 14, 19-31.
Oldfield, F.: 1977, ‘Lakes and their drainage basins as units of sediment-based ecological study’, Progress in Physical Geography 1, 460-504.
Perkins, S. M., Filippelli, G. M. and Souch, C. J.: 2000, ‘Airborne trace metal contamination of wetlands sediments at Indiana Dunes National Lakeshore’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 122, 231- 260.
Peters, J.: 1994, ‘A Preliminary Investigation of Heavy Metal Pollution at the Botany Wetlands’, Unpublished B.Sc. Thesis, School of Geography, University of New South Wales.
Pickard, J.: 1972, ‘Rate of movement of transgressive dunes at Cronulla, New South Wales’, J. Geolog. Soc. Austr. 19, 213-216.
Prentice, I. C.: 1986, ‘Multivariate Methods for Data Analysis’, in B. E. Berglund (ed.), Handbook of Holocene Palaeoecology and Palaeohydrology, John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp. 775-797.
Randwick Municipal Council: 1986, Randwick: A Social History, New SouthWales University Press, Kensington, NSW.
Renberg, I., Brännvall, M.-L., Bindler, R. and Emeteryd, O.: 2002, ‘Stable lead isotopes and lake sediments-a useful combination for the study of atmospheric lead pollution history’, Sci. Total Environ. 292, 45-54.
Richardson, N.: 1986, ‘The mineral magnetic record in recent ombrotrophic peat synchronised by fine resolution pollen analysis’, Physics Earth Planet. Interiors 42, 48-56.
Roy, P. S. and Crawford, E. A.: 1981, ‘Holocene geological evolution of the southern Botany Bay - Kurnell region, central New South Wales coast’, New South Wales Geological Survey Records 20, 159-250.
Ruiz-Fernández, A. C., Hillaire-Marcel, C., Páez-Osuna, F., Ghaleb, B. and Soto-Jiménez, M.: 2003, ‘Historical trends of metal pollution recorded in the sediments of the Culiacan River Estuary, Northwestern Mexico’, Appl. Geochem. 18, 577-588.
Santschi, P. H., Presley, B. J., Wade, T. L., Garcia-Romero, B. and Baskaran, M.: 2001, ‘Historical contamination of PAHs, PCBs, DDTs, and heavy metals in Mississippi River Delta, Galveston Bay and Tampa Bay sediment cores’, Marine Environ. Res. 52, 51-79.
SPCC: 1984, Annual Report 1983-1984, State Pollution Control Commission, Sydney.
Steinnes, E.: 1997, ‘Trace element profiles in ombrogenous peat cores from Norway: Evidence of long range atmospheric transport’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 100, 405-413.
Stewart, C. and Fergusson, J. E.: 1994, ‘The use of peat in the historical monitoring of trace metals in the atmosphere’, Environ. Pollut. 86, 243-249.
Thompson, R., Bloemendal, J., Dearing, J. A., Oldfield, F., Rummery, T. A., Stober, J. C. and Turner, G. M.: 1980, ‘Environmental applications of magnetic measurements’, Science 207, 481-486.
Tolonen, K. and Oldfield, F.: 1986, ‘The record of magnetic-mineral and heavy metal deposition at Regent Street Bog, Fredricton, New Brunswick, Canada’, Physics Earth Planet. Interiors 42, 57-66.
Tuncer, G., Tuncel, G. and Robert, M.: 2001, ‘Evolution of metal pollution in the Golden Horn (Turkey) sediments between 1912 and 1987’, Marine Pollut. Bull. 42, 350-360.
Van den Berg, G. A., Buykx, S. E. J., Van den Hoop, M. A. G. T., Van der Heijdt, L. M. and Zwolsman, J. J. G.: 2001, ‘Vertical profiles of trace metals and acid-volatile sulphide in a dynamic sedimentary environment: Lake Ketel, The Netherlands’, Appl. Geochem. 16, 781-791.
Von Gunten, H. R., Sturm, M. and Moser, R. N.: 1997, ‘200-Year record of metals in lake sediments and natural background concentrations’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 31, 2193-2197.
Wallace, I.: 1973, ‘Extractive Resources of the Botany Bay Region: Construction Materials and Coal’, in D. J. Anderson (ed.), The Botany Bay Project - A Handbook of the Botany Bay Region - Some Preliminary Background Papers, Botany Bay Project Committee, Sydney, pp. 95-100.
Warwick, P., Hall, A., Pashley, V., Van der Lee, J. and Maes, A.: 1998, ‘Zinc and cadmium mobility in sand: Effects of pH, speciation, cation exchange capacity (CEC), humic acid and metal ions’, Chemosphere 36, 2283-2290.
West, S., Charman, D. J., Grattan, J. P. and Cherburkin, A. K.: 1997, ‘Heavy metals in Holocene peats from south west England: Detecting mining impacts and atmospheric pollution’, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 100, 343-353.
Wilkinson, L. and Coward, M.: 1996, ‘Analysis of Variance’, in Statistics: SYSTAT 6.0, SPSS Inc., pp. 119-223.
Zwolsman, J. J. G., Berger, G. W. and Van Eck, G. T. M.: 1993, ‘Sediment accumulation rates, historical input, postdepositional mobility and retention of major elements and trace metals in salt marsh sediments of the Scheldt estuary, SW Netherlands’, Marine Chem. 44, 73-94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Connor, S.E., Thomas, I. Sediments as Archives of Industrialisation: Evidence of Atmospheric Pollution in Coastal Wetlands of Southern Sydney, Australia. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 149, 189–210 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025626104164
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1025626104164