Abstract
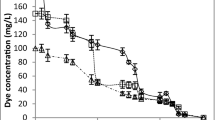
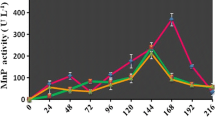
Although a non-sterile, undiluted carpet dye effluent (containing two anthraquinone dyes) did not support growth of Trametes versicolor, the pre-grown fungus removed 95% of its color in shake-flasks after 10 h of incubation. After decoloration, the COD of the cell-free supernatant increased and the toxicity was unchanged as determined by the Microtox assay using Vibrio fischeri. Decoloration rates decreased when either glucose alone or Mn2+ and glucose were added. T. versicolor, immobilized on jute twine in a rotating biological contacting reactor, also decolorized four successive batches of the effluent. There was no decoloration in any of the uninoculated, non-sterile controls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clesceri LS, Greenberg AE, Eaton AD, eds. (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edn. Washington, D.C.: American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, Water Environment Association.
Coleman RN, Qureshi AA (1985) Microtox and Spirillum volutans tests for assessing toxicity of environmental samples. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 35: 443–451.
Fu Y, Viraraghavan T (2001) Fungal decolorization of dye wastewaters: a review. Bioresour. Technol. 79: 251–262.
Giffron F (2000) Fungal pyranose oxidases: occurrence, properties and biotechnical applications in carbohydrate chemistry. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 54: 727–740.
Ramsay JA, Nguyen T (2002) Decoloration of textile dyes by Trametes versicolor and its effect on dye toxicity. Biotechnol. Lett. 24: 1757–1761.
Reddy A (1995) The potential for white-rot fungi in the treatment of pollutants. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 6: 320–328.
Robinson T, McMullan G, Marchant R, Nigam P (2001) Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative. Bioresour. Technol. 77: 247–255.
Scheel T, Höfer M, Ludwig S, Hölker U (2000) Differential expression of manganese peroxidase and laccase in white rot fungi in the presence of manganese or aromatic compounds. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 54: 686–691.
Schliephake K, Mainwaring DE, Lonergan GT, Jones IK, Baker WL (2000) Transformation and degradation of the disazo chicago sky blue by a purified laccase from Pycnoporus cinnabarinus. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 27: 100–107.
Shahvali M, Assadi MM, Rostami K (2000) Effect of environmental parameters on decolorization of textile wastewater using Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Bioprocess Eng. 23: 721–726.
Shin M, Nguyen T, Ramsay J (2002) Evaluation of support materials for the surface immobiliztion and decoloration of amaranth by Trametes versicolor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 60: 218–223.
Soares GMB, Costa-Ferreira M, Pessoa de Amorim MT (2001) Decolorization of an anthraquinone-type dye using a laccase formulation. Bioresour. Technol. 79: 171–177.
Swamy J, Ramsay J (1999a) Effects of Mn2+ and NH4+ concentrations on laccase and manganese peroxidase production and amaranth decoloration by Trametes versicolor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 51: 391–396.
Swamy J, Ramsay J (1999b) Effects of glucose and NH4+ concentrations on sequential dye decoloration by Trametes versicolor. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 25: 278–284.
Vandevivere PC, Bianchi R, Verstraete W (1998) Treatment and reuse of wastewater from the textile wet-processing industry: review of emerging technologies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 72: 289–302.
Wesenberg D, Buchon F, Agathos SN (2002) Degradation of dye-containing textile effluent by the agaric white-rot fungus Clitocybula dusenii. Biotechnol. Lett. 24: 989–993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramsay, J.A., Goode, C. Decoloration of a Carpet Dye Effluent Using Trametes Versicolor . Biotechnology Letters 26, 197–201 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000013711.32890.5d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000013711.32890.5d