Abstract
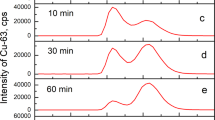
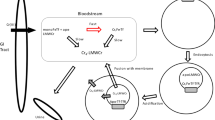
Serum albumin (human, bovine) has a specific Cu(II)-ion binding site, and is proposed to act as a copper transport protein in blood plasma. Human transferrin, normally about 30% saturated with iron in vivo, has two sites/molecule capable of complexing Cu(II); one more strongly than the other (Hirose et al. 1996). The present study shows that this binding site has a slightly stronger affinity for Cu(II) than that on the albumins. However, both human- and bovine albumin could take up part of the transferrin bound Cu(II), the second order rate constant for the reaction estimated to 12 mM−1 min−1 for both species. In vivo the albumin concentration is considerably higher than that of iron-free transferrin, and it seems unlikely that the latter can compete with albumin for non-ceruloplasmin cupric ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breslow E. 1964 Comparison of cupric ion-binding sites in myoglobin derivatives and serum albumin. J Biol Chem 239, 3252-3259.
Chasteen ND, White LK, Campbell RF. 1977 Metal site conformational states of vanadyl(IV) human serotransferrin complexes. Biochemistry 16, 363-365.
Gordon DT, Leinart AS, Cousins JR. 1987 Portal copper transport in rat by albumin. Am J Physiol 252, E327-333.
Giroux E, Schoun J. 1981 Copper and zinc ion binding by bovine, dog and rat serum albumins. J Inorg Biochem 14, 359-362.
Hirose J, Fujiwara H, Magarifuchi T, Iguti Y, Iwamoto H, Kominami S, Hiromi K. 1996 Copper binding selectivity of N-and C-sites in serum (human)-and ovo-transferrin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1296, 103-111.
Lau S-J, Sarkar B. 1971 Ternary coordination complex between human serum albumin, copper(II), and L-histidine. J Biol Chem 246, 5938-5943.
Marceau N, Aspin N. 1973 The intracellular distribution of radiocopper derived from ceruloplasmin and from albumin. Biochim Biophys Acta 328, 338-350.
Masuoka J, Hegenauer J, Van Dyke BR, Saltman P. 1993 Intrinsic stoichiometric equilibrium constants for the binding of zinc(II) and copper(II) to the high affinity site of serum albumin. J Biol Chem 268, 21533-21537.
Owen CA. 1965 Metabolism of radiocopper (Cu64) in the rat. Am J Physiol 209, 900-904.
Syvertsen C, Gaustad R, SchrØder K, Ljones T. 1986 Studies on the binding of copper to dopamine beta-monooxygenase and other proteins using the Cu2+ ion selective electrode. J Inorg Biochem 26, 63-76.
Wirth PL, Linder MC. 1985 Distribution of copper among components of human serum. J Natl Cancer Inst 75, 277-284.
Zgirski A, Frieden E. 1990 Binding of Cu(II) to non-prosthetic sites in ceruloplasmin and bovine serum albumin. J Inorg Biochem 39, 137-148.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Løvstad, R.A. A kinetic study on the distribution of Cu(II)-ions between albumin and transferrin. Biometals 17, 111–113 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOM.0000018362.37471.0b
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BIOM.0000018362.37471.0b