Abstract
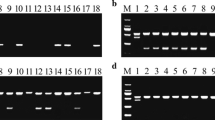
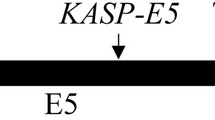
The Pi-ta gene from indica introgressed into japonica rice has been used to control the blast disease caused by the fungal pathogen Magnaporthe grisea (Herbert) Barr. (anamorph Pyricularia oryzae Cav.) worldwide. A single nucleotide length polymorphism (SNLP) was identified at the intron region of the Pi-ta gene to develop a codominant Pi-ta gene marker suitable for genotyping with an automated machine. The DNA primer specific to the resistant Pi-taallele was labeled with blue dye (FAM, 6-carboxyfluorescein) as a forward primer, the DNA primer specific to the susceptible pi-ta allele was labeled with green dye (HEX, 4,7,2′,4′,5′,7′-hexachloro-6-carboxyfluorescein) as another forward primer and the DNA primer identical to both Pi-ta/pi-ta alleles was unlabeled as the reverse primer for polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Using these three primers, a 181-bp blue peak in homozygous resistant and a green peak of 182–183 bp in homozygous susceptible, and both peaks in heterozygous plants were produced by PCR. The utility of marker was verified using a segregating F2 population, inbred cultivated lines, dominant markers and pathogenicity testing. A codominant Pi-ta marker was thus developed for effective Pi-ta assisted selection for crop improvement. Using highly homologous competitive primers for allele detection by PCR can benefit the study of genome organization of the complex locus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bent, A.F., 2002. Crop diseases and strategies for their control. In: M.J. Chrispeels & D.E. Sadava (Eds.), Plants, Genes, and Crop Biotechnology, pp. 390-412. Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Inc, Sudbury, MA.
Brar, D.S. & G.S. Khush, 1997. Alien introgression in rice. Plant Mol Biol 35: 35-47.
Bryan, G.T., K. Wu, L. Farrall, Y. Jia, H.P. Hershey, S. McAdams, R. Tarchini, G. Donaldson, K. Faulk & B. Valent, 2000. A sin-gle amino acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 12: 2033-2045.
Chao, C.T., K.A.K. Moldenhauer & A.H. Ellingboe, 1999. Genetic analysis of resistance/susceptibility in individual F3 families of rice against strains of Magnaporthe grisea containing different genes for avirulence. Euphytica 109: 183-190.
Chauhan, R.S., M.L. Farman, H.B. Zhang & S.A. Leong, 2002. Genetic and physical mapping of a rice blast resistance lo-cus, Pi-CO39(t), that corresponds to the avirulence gene AVR1-CO39 of Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Gen Genomics 267: 603-612.
Correll, J.C., T.L. Harp, J.C. Guerber, R.S. Zeigler, B. Liu, R.D. Cartwright & F.N. Lee, 2000. Characterization of Pyricularia grisea in the United States using independent genetic and molecular markers. Phytopathology 90: 1396-1404.
Eizenga, G.C. & Y. Jia, 2003. Molecular characterization of rice wild relatives and accelerating the development of disease resistant germplasm using microsatellite markers. In: The XI Congress of International Plant and Animal Genome, p. 151. January 11-15, 2003, San Diego, CA, USA.
Flor, H.H., 1971. Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopathol 9: 275-296.
Fjellstrom, R.G., A.M. McClung, R. Shank & T. Marchetti, 2003. Progress on development of microsatellite markers associated with rice blast resistance genes. In: The XI Congress of Inter-national Plant and Animal Genome, p. 154. January 11-15, San Diego, CA, USA.
Hittalmani, S., A. Parco, T.W. Mew, R. S. Zeigler & N. Huang, 2000. Fine mapping and DNA marker-assisted pyramiding of the three major genes for blast resistance in rice. Theor Appl Genet 100: 1121-1128.
Hulbert, S.H., C.A. Webb, S.M. Smith & Q. Sun, 2001. Resistance gene complexes: Evolution and utilization. Ann Rev Phytopathol 39: 285-312.
Imbe, T., 1997. Genetic studies on blast resistance. In: Stabilization of Rice Culture Under Water Stress in the Tropics Utilizing a Broader Spectrum of Genetic Resources, pp. 1-38. Progress Report (1995-1996), IRRI-Japan Collaboration Research Project.
Johnson, V.A., J.G. Gibbons, K.A.K., Moldenhauer & Y. Jia, 2003. Rice variety improvement using maker-assisted selection. In: Abstracts of the XI Congress of International Plant and Animal Genome, p. 149. January 11-15, 2003, San Diego, CA, USA.
Jia, Y., S.A. McAdams, G.T. Bryan, H.P. Hershey & B. Valent, 2000. Direct interaction of resistance gene and avirulence products confers rice blast resistance. Eur Mol Biol Org J 19: 4004-4014.
Jia, Y., Z. Wang & P. Singh, 2002a. Development of dominant rice blast Pi-ta resistance gene markers. Crop Sci. 42: 2145-2149.
Jia, Y., Z. Wang, P. Singh, F.N. Lee, R. Fjellstrom, J. Correll, G.C. Eizenga, D.R. Gealy, J. Gibbons, K.A.K. Moldenhauer, J.N. Rutger, A. McClung & T. Marchetti, 2002b. Opportunities of the development of rice blast resistant germplasm. In: The 3rd International Rice Blast Conference, p. 65. September 11-14, 2002. Ibaraki, Japan.
Jia, Y., G.T. Bryan, L. Farrall & B. Valent, 2003. Natural variation at the Pita rice blast resistance locus. Phytopathology 93: 1452-1459.
Jia, Y., 2003. Marker-assisted selection for the control of rice blast disease. Pesticide Outlook 14: 150-152.
Jia, Y., Z. Wang, R.G. Fjellstrom, K.A.K. Moldenhauer, M.A. Azam, J. Correll, F.N. Lee, Y. Xia & J.N. Rutger, 2004. Rice Pi-ta gene confers resistance to two major pathotypes of the rice blast fungus in the US. Phytopathology 94: 296-301.
Jiang, J., J.W. Gibbons & K.A.K. Moldenhauer, 2002. Developing an efficient haploid rice breeding system at UARREC. In: The 29th Rice Technical Working Group Meeting, p. 50. February 24-27, Little Rock, AR, USA.
Kiyosawa, S., 1967. Genetic studies on host-pathogen relationship in the rice blast disease. In: Proceedings of the Symposium on Rice Disease and Their Control by Growing Resistant Varieties and Other Measures, pp. 137-153. Tokyo, Japan.
Khush, G.S. & D.S. Brar, 1998. The application of biotechnology to rice. In: C.L. Ives, B.M. Bedford (Eds.), Agricultural Biotechnology in International Development, pp. 97-121. Wallingford, CAB International UK.
Mackill, D.J. & J.M. Bonman, 1992. Inheritance of blast resistance in near-isogenic lines of rice. Phytopathology 82: 746-749.
McCouch, S.R., R.J. Nelson, J. Tohme & R.S. Zeigler, 1994. Mapping of blast resistance genes in rice. In: R.S. Zeigler, S.A. Leong & P.S. Teng (Eds.), Rice Blast Disease, pp. 167-186. CAB Internationa1 and IRRI, Wallingford, Oxon, UK.
Moldenhauer, K.A.K., F.N. Lee, R.J. Norman, R.S. Helms, R.H. Well, R.H. Dilday, P.C. Rohman & M.A. Marchetti, 1990. Registration of 'Katy' rice. Crop Sci 30: 747-748.
Ni, J., P.M. Colowit & D. Mackill, 2002. Evaluation of genetic diversity in rice subspecies using microsatellite markers. Crop Sci. 42: 601-607.
Rybka, K., M. Miyamoto, I. Ando, A. Saito & S. Kawasaki, 1997. High resolution mapping of the indica-derived rice blast resistance gene II. Pi-ta 2 and Pi-ta and a consideration of their origin. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 10: 517-524.
Shigemura, S. & E. Kitamura, 1954. Breeding of blast resistant cul-tivars with crossing of japonica and indica rice. J Agric Sci Tokyo Nogyo Daigaku 9: 321-323 (in Japanese, English abstract).
Silue, D., J.L. Notteghem & D. Tharreau, 1992. Evidence for a gene-for-gene relationship in the Oryza sativa-Magnaporthe grisea pathosystem. Phytopathology 82: 577-580.
Tian, D., H. Araki, E. Stahl, J. Bergelson & M. Kreitman, 2002. Signature of balancing selection in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99: 11525-11530.
Valent, B., 1997. The rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea. In: G.C. Carroll, P. Tudzynoski (Eds.), Plant Relationships, The Mycota V Part B, pp. 37-54. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg.
Valent, B., L. Farrall & F.G. Chumley, 1991. Magnaporthe grisea genes for pathogenicity and virulence identified through a series of backcrosses. Genetics 127: 87-101.
Wang, Z.-X., M. Yano, U. Yamanouchi, M. Iwamoto, L. Monna, H. Hayasaka, Y. Katayose & T. Sasaki, 1999. The Pib gene for rice blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J 19: 55-64.
Wang, Z., 2003. Development of molecular markers of the rice blast resistance gene Pi-ta and its application. Ph.D. Disserta-tion, pp. 106. Institute of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, Zhejiang, University, P.R. China (in Chinese, English abstract).
Xu, Y., 2002. Global view of QTLs: Rice as a model. In: M.S. Kang (Ed.), Quantitative, Genomics and Plant Breeding, pp. 109-134. CAB International, Wallingford, UK.
Young, N.D., 1999. A cautiously optimistic vision for marker-assisted breeding. Mol Breed 5: 505-510.
Yu, Z.H., D.J. Mackill, J.M. Bonman & S.D. Tanksley, 1991. Molecular mapping of genes for resistance to rice blast (Pyricularia grisea Sacc.). Theor Appl Genet 81: 471-476.
Yu, Z.H., D.J. Mackill, J.M. Bonman, S.R. McCouch, E. Guideroni, J.L. Notteghem & S.D. Tanksley, 1996. Molecular mapping of genes for resistance to rice blast (Pyricularia grisea Sacc.). Theor Appl Genet 93: 859-863.
Zeigler, R.S., J. Tohme, J. Nelson, M. Levy & F. Correa, 1994. Link-ing blast population analysis to resistance breeding: A proposed strategy for durable resistance. In: R.S. Ziegler, S. Leoung & P.S. Teng (Eds.), Rice Blast Disease, pp. 267-292. CAB International, Wallingford, UK.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Redus, M., Wang, Z. et al. Development of a SNLP marker from the Pi-ta blast resistance gene by tri-primer PCR. Euphytica 138, 97–105 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EUPH.0000047079.42768.4d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:EUPH.0000047079.42768.4d