Abstract
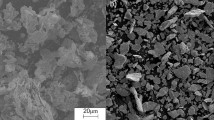
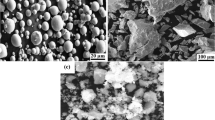
The homogenous distribution of the reinforcement phase is an essential condition for a composite material to achieve its superior performance. Powder metallurgy (PM) can produce metal matrix composites in a wide range of matrix reinforcement compositions without the segregation phenomena typical of casting processes. Particularly, mechanical alloying can be used to mix the matrix and reinforcement particles, enhancing the homogeneity of the reinforcement distribution. This work investigates the production of aluminium 6061 reinforced with zirconium diboride by mechanical alloying followed by cold pressing and hot extrusion, and compares the results with the same composite produced by conventional PM and hot extrusion. The incorporation of the ZrB2 particles produces only a small increase in the material hardness, but a small decrease in the UTS when conventional PM is employed. Mechanical alloying breaks the reinforcement particle clusters, eliminates most of the cracks present in the surface of the reinforcement particles, decreases its size and improves its distribution. This enhancement of the composite structure, in addition to the metallurgical aspects promoted by mechanical alloying in the matrix, brings approximately 100% improvements in the composite UTS and hardness, compared with the composites obtained by PM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. V. Foltz, Adv. Mater. Process 154 (1998) 19.
J. Boselli, P. D. Pitcher, P. J. Gregson and I. Sinclair, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 300 (2001) 113.
V. V. Bhanuprasad, R. B. V. Bhat, A. K. Kuruvilla, K. S. Prasad, A. B. Pandey and Y. Mahajan, Int. J. Powder Metall. 27 (1991) 227.
M. K. Jain, V. V. Bhanuprasad, S. V. Kamat, A. B. Pandey, V. K. Varma, B. V. R. Bhat and Y. R. Mahajan, ibid. 29 (1993) 267.
K. Hanada, Y. Murakoshi, H. Negishi and T. Sano, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 63 (1997) 405.
M. J. Tan and X. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 244 (1998) 80.
A. N. Tiwari, V. Gopinathan and P. Ramakrishnan, Mater. Manuf. Process. 6 (1991) 621.
J. Lee, S. Kim, C. Park and C. Bae, J. Mater. Process. Manuf. 4 (1995) 55.
L. Lu, M. O. Lai and S. Zhang, Key Eng. Mater. 104–107 (1995) 111.
K. Hanada, K. A. Khor, M. J. Tan, Y. Murakoshi, H. Negishi and T. Sano, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 67 (1997) 8.
L. Lu, M. O. Lai and C. W. Ng, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 252 (1998) 203.
E. M. Ruiz-Navas, C. E. Costa, J. M. Ruizroman, L. E. G. Cambronero and J. M. Ruizprieto, in Proceedings of the Powder Metallurgy World Congress and Exhibition (Granada, Spain, 1998) Vol. 5, p. 146.
O. Gingu, M. Rosso and G. Ubertalli, in Proceedings of the Powder Metallurgy World Congress and Exhibition (Granada, Spain, 1998) Vol. 5, p. 162.
L. Lu and M. O. Lai, in “Mechanical Alloying” (Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1998) p. 165.
C. Suryanarayana, Prog. Mater. Sci. 46 (2001) 1.
J. M. Torralba, C. E. Da Costa and F. Velasco, J. Mater. Process. Tech. 133 (2003) 203.
M. Lieblich, J. L. GonzÁlez-Carrasco and G. Caruana, Intermetallics 5 (1997) 515.
V. AmigÓ and V. J. L. Ortiz, Scripta Mater. 42 (2000) 383.
J. B. Fogagnolo, F. Velasco, M. H. Robert and J. M. Torralba, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 342 (2003) 131.
J. B. Fogagnolo, E. M. Ruiz-Navas, M. H. Robert and J. M. Torralba, Scripta Mater. 47 (2002) 243.
S. K. M. Pathak, S. Das, S. K. Das and P. Ramachandrarao, J. Mater. Res. 15 (2000) 2499.
F. Monteverde, S. Guicciardi and A. Bellosi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 346 (2003) 310.
J. S. Benjamin and T. E. Volin, Metall. Trans. 5 (1974) 1929.
J. B. Fogagnolo, E. M. Ruiz-Navas, M. H. Robert and J. M. Torralba, J. Mater. Sci. 37 (2002) 4603.
E. Hochreiter, C. Kowanda and B. Orter, in Proceedings of the 3rd European Association for Composite Materials and Processes, Editions de Physique Les Ulis (1993) Vol. 3, p. 1829.
Y. L. Shen, E. Fishencord and N. Chawla, Scripta Mater. 42 (2000) 427.
C. H. CÁceres and W. J. Poole, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 332 (2002) 311.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fogagnolo, J.B., Robert, M.H., Ruiz-Navas, E.M. et al. 6061 Al reinforced with zirconium diboride particles processed by conventional powder metallurgy and mechanical alloying. Journal of Materials Science 39, 127–132 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000007736.03608.e5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JMSC.0000007736.03608.e5