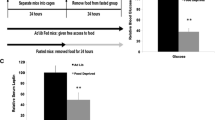
Abstract
DNA microarray analysis has been used to investigate relative changes in the level of gene expression in the CNS, including changes that are associated with disease, injury, psychiatric disorders, drug exposure or withdrawal, and memory formation. We have used oligonucleotide microarrays to identify hypothalamic genes that respond to nutritional manipulation. In addition to commonly used microarray analysis based on criteria such as fold-regulation, we have also found that simply carrying out multiple t tests then sorting by P value constitutes a highly reliable method to detect true regulation, as assessed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), even for relatively low abundance genes or relatively low magnitude of regulation. Such analyses directly suggested novel mechanisms that mediate effects of nutritional state on neuroendocrine function and are being used to identify regulated gene products that may elucidate the metabolic pathology of obese ob/ob, lean Vgf-/Vgf-, and other models with profound metabolic impairments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bondjers, C., Kalen, M., Hellstrom, M., Scheidl, S. J., Abramsson, A., Renner, O., Lindahl, P., Cho, H., Kehrl, J., and Betsholtz, C. 2003. Transcription profiling of platelet-derived growth factor-B-deficient mouse embryos identifies RGS5 as a novel marker for pericytes and vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Pathol. 162:721–9.
Cao, Y. and Dulac, C. 2001. Profiling brain transcription: neurons learn a lesson from yeast. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11:615–20.
Elliott, R. C., Miles, M. F., and Lowenstein, D. H. 2003. Overlapping microarray profiles of dentate gyrus gene expression during development-and epilepsy-associated neurogenesis and axon outgrowth. J. Neurosci. 23:2218–27.
Ginsberg, S. D. and Che, S. 2002. RNA amplification in brain tissues. Neurochem. Res. 27:981–92.
Kotlyar, M., Fuhrman, S., Ableson, A., and Somogyi, R. 2002. Spearman correlation identifies statistically significant gene expression clusters in spinal cord development and injury. Neurochem. Res. 27:1133–40.
Linnarsson, S., Mikaels, A., Baudet, C., and Ernfors, P. 2001. Activation by GDNF of a transcriptional program repressing neurite growth in dorsal root ganglia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:14681–6.
Mody, M., Cao, Y., Cui, Z., Tay, K. Y., Shyong, A., Shimizu, E., Pham, K., Schultz, P., Welsh, D., and Tsien, J. Z. 2001. Genome-wide gene expression profiles of the developing mouse hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:8862–7.
Balasubramaniam, J. and Del Bigio, M. R. 2002. Analysis of age-dependent alteration in the brain gene expression profile following induction of hydrocephalus in rats. Exp. Neurol. 173:105–13.
Colantuoni, C., Jeon, O. H., Hyder, K., Chenchik, A., Khimani, A. H., Narayanan, V., Hoffman, E. P., Kaufmann, W. E., Naidu, S., and Pevsner, J. 2001. Gene expression profiling in postmortem Rett syndrome brain: differential gene expression and patient classification. Neurobiol. Dis. 8:847–65.
Cooper, J. D. 2003. Progress towards understanding the neurobiology of Batten disease or neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 16:121–8.
Johnston, M. V., Jeon, O. H., Pevsner, J., Blue, M. E., and Naidu, S. 2001. Neurobiology of Rett syndrome: a genetic disorder of synapse development. Brain. Dev. 23 (Suppl. 1):S206–13.
Tudor, M., Akbarian, S., Chen, R. Z., and Jaenisch, R. 2002. Transcriptional profiling of a mouse model for Rett syndrome reveals subtle transcriptional changes in the brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:15536–41.
Araki, T., Nagarajan, R., and Milbrandt, J. 2001. Identification of genes induced in peripheral nerve after injury. Expression profiling and novel gene discovery. J. Biol. Chem. 276:34131–41.
Bowler, R. P., Sheng, H., Enghild, J. J., Pearlstein, R. D., Warner, D. S., and Crapo, J. D. 2002. A catalytic antioxidant (AEOL 10150) attenuates expression of inflammatory genes in stroke. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 33:1141–52.
Fan, M., Mi, R., Yew, D. T., and Chan, W. Y. 2001. Analysis of gene expression following sciatic nerve crush and spinal cord hemisection in the mouse by microarray expression profiling. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 21:497–508.
Ginsberg, M. D. 2003. Adventures in the pathophysiology of brain ischemia: penumbra, gene expression, neuroprotection: the 2002 Thomas Willis Lecture. Stroke 34:214–23.
Hu, J., Fink, D., and Mata, M. 2002. Microarray analysis suggests the involvement of proteasomes, lysosomes, and matrix metalloproteinases in the response of motor neurons to root avulsion. Eur. J. Neurosci. 16:1409–16.
Jin, K., Mao, X. O., Eshoo, M. W., Nagayama, T., Minami, M., Simon, R. P., and Greenberg, D. A. 2001. Microarray analysis of hippocampal gene expression in global cerebral ischemia. Ann. Neurol. 50:93–103.
Ko, J., Na, D. S., Lee, Y. H., Shin, S. Y., Kim, J. H., Hwang, B. G., Min, B. I., and Park, D. S. 2002. cDNA microarray analysis of the differential gene expression in the neuropathic pain and electroacupuncture treatment models. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 35:420–7.
Kobori, N., Clifton, G. L., and Dash, P. 2002. Altered expression of novel genes in the cerebral cortex following experimental brain injury. Brain. Res. Mol. Brain. Res. 104:148–58.
Long, Y., Zou, L., Liu, H., Lu, H., Yuan, X., Robertson, C. S., and Yang, K. 2003. Altered expression of randomly selected genes in mouse hippocampus after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 71:710–20.
Marciano, P. G., Eberwine, J. H., Ragupathi, R., Saatman, K. E., Meaney, D. F., and McIntosh, T. K. 2002. Expression profiling following traumatic brain injury: a review. Neurochem. Res. 27:1147–55.
Matzilevich, D. A., Rall, J. M., Moore, A. N., Grill, R. J., and Dash, P. K. 2002. High-density microarray analysis of hippocampal gene expression following experimental brain injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 67:646–63.
Tachibana, T., Noguchi, K., and Ruda, M. A. 2002. Analysis of gene expression following spinal cord injury in rat using complementary DNA microarray. Neurosci. Lett. 327:133–7.
Tang, Y., Nee, A. C., Lu, A., Ran, R., and Sharp, F. R. 2003. Blood genomic expression profile for neuronal injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 23:310–9.
Whitney, L. W., Becker, K. G., Tresser, N. J., Caballero-Ramos, C. I., Munson, P. J., Prabhu, V. V., Trent, J. M., McFarland, H. F., and Biddison, W. E. 1999. Analysis of gene expression in mutiple sclerosis lesions using cDNA microarrays. Ann. Neurol. 46:425–8.
Bahn, S., Augood, S. J., Ryan, M., Standaert, D. G., Starkey, M., and Emson, P. C. 2001. Gene expression profiling in the postmortem human brain—no cause for dismay. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 22:79–94.
Bunney, W. E., Bunney, B. G., Vawter, M. P., Tomita, H., Li, J., Evans, S. J., Choudary, P. V., Myers, R. M., Jones, E. G., Watson, S. J., and Akil, H. 2003. Microarray technology: a review of new strategies to discover candidate vulnerability genes in psychiatric disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 160:657–66.
Hakak, Y., Walker, J. R., Li, C., Wong, W. H., Davis, K. L., Buxbaum, J. D., Haroutunian, V., and Fienberg, A. A. 2001. Genome-wide expression analysis reveals dysregulation of myelination-related genes in chronic schizophrenia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:4746–51.
Li, M. D., Konu, O., Kane, J. K., and Becker, K. G. 2002. Microarray technology and its application on nicotine research. Mol. Neurobiol. 25:265–85.
Mirnics, K., Middleton, F. A., Marquez, A., Lewis, D. A., and Levitt, P. 2000. Molecular characterization of schizophrenia viewed by microarray analysis of gene expression in prefrontal cortex. Neuron 28:53–67.
Mirnics, K., Middleton, F. A., Lewis, D. A., and Levitt, P. 2001. Analysis of complex brain disorders with gene expression microarrays: schizophrenia as a disease of the synapse. Trends Neurosci. 24:479–86.
Mirnics, K., Middleton, F. A., Stanwood, G. D., Lewis, D. A., and Levitt, P. 2001. Disease-specific changes in regulator of G-protein signaling 4 (RGS4) expression in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 6:293–301.
Pongrac, J., Middleton, F. A., Lewis, D. A., Levitt, P., and Mirnics, K. 2002. Gene expression profiling with DNA microarrays: advancing our understanding of psychiatric disorders. Neurochem. Res. 27:1049–63.
Vawter, M. P., Crook, J. M., Hyde, T. M., Kleinman, J. E., Weinberger, D. R., Becker, K. G., and Freed, W. J. 2002. Microarray analysis of gene expression in the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia: a preliminary study. Schizophr. Res. 58:11–20.
Williams, M. 2003. Genome-based drug discovery: prioritizing disease-susceptibility/disease-associated genes as novel drug targets for schizophrenia. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 4:31–6.
Wong, A. H., Macciardi, F., Klempan, T., Kawczynski, W., Barr, C. L., Lakatoo, S., Wong, M., Buckle, C., Trakalo, J., Boffa, E., Oak, J., Azevedo, M. H., Dourado, A., Coelho, I., Macedo, A., Vicente, A., Valente, J., Ferreira, C. P., Pato, M. T., Pato, C. N., Kennedy, J. L., and Van Tol, H. H. 2003. Identification of candidate genes for psychosis in rat models, and possible association between schizophrenia and the 14-3-3eta gene. Mol. Psychiatry 8:156–66.
Colangelo, V., Schurr, J., Ball, M. J., Pelaez, R. P., Bazan, N. G., and Lukiw, W. J. 2002. Gene expression profiling of 12633 genes in Alzheimer hippocampal CA1: transcription and neurotrophic factor down-regulation and up-regulation of apoptotic and proinflammatory signaling. J. Neurosci. Res. 70:462–73.
Beitner-Johnson, D., Seta, K., Yuan, Y., Kim, H., Rust, R. T., Conrad, P. W., Kobayashi, S., and Millhorn, D. E. 2001. Identification of hypoxia-responsive genes in a dopaminergic cell line by subtractive cDNA libraries and microarray analysis. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 7:273–281.
Grunblatt, E., Mandel, S., Maor, G., and Youdim, M. B. 2001. Gene expression analysis in N-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mice model of Parkinson's disease using cDNA microarray: effect of R-apomorphine. J. Neurochem. 78:1–12.
Hanzel, D. K., Trojanowski, J. Q., Johnston, R. F., and Loring, J. F. 1999. High-throughput quantitative histological analysis of Alzheimer's disease pathology using a confocal digital microscanner. Nat. Biotechnol. 17:53–7.
Hata, R., Masumura, M., Akatsu, H., Li, F., Fujita, H., Nagai, Y., Yamamoto, T., Okada, H., Kosaka, K., Sakanaka, M., and Sawada, T. 2001. Up-regulation of calcineurin Abeta mRNA in the Alzheimer's disease brain: assessment by cDNA microarray. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 284:310–6.
Ho, L., Guo, Y., Spielman, L., Petrescu, O., Haroutunian, V., Purohit, D., Czernik, A., Yemul, S., Aisen, P. S., Mohs, R., and Pasinetti, G. M. 2001. Altered expression of a-type but not b-type synapsin isoform in the brain of patients at high risk for Alzheimer's disease assessed by DNA microarray technique. Neurosci. Lett. 298:191–4.
Kim, S. H., Won, S. J., Sohn, S., Kwon, H. J., Lee, J. Y., Park, J. H., and Gwag, B. J. 2002. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor can act as a pronecrotic factor through transcriptional and translational activation of NADPH oxidase. J. Cell Biol. 159:821–31.
Loring, J. F., Wen, X., Lee, J. M., Seilhamer, J., and Somogyi, R. 2001. A gene expression profile of Alzheimer's disease. DNA Cell Biol. 20:683–95.
Mandel, S., Grunblatt, E., Maor, G., and Youdim, M. B. 2002. Early and late gene changes in MPTP mice model of Parkinson's disease employing cDNA microarray. Neurochem. Res. 27:1231–43.
Mandel, S., Grunblatt, E., Riederer, P., and Youdim, M. B. 2003. Genes and oxidative stress in parkinsonism: cDNA microarray studies. Adv. Neurol. 91:123–32.
Napolitano, M., Centonze, D., Calce, A., Picconi, B., Spiezia, S., Gulino, A., Bernardi, G., and Calabresi, P. 2002. Experimental parkinsonism modulates multiple genes involved in the transduction of dopaminergic signals in the striatum. Neurobiol. Dis. 10:387–95.
Pasinetti, G. M. 2001. Use of cDNA microarray in the search for molecular markers involved in the onset of Alzheimer's disease dementia. J. Neurosci. Res. 65:471–6.
Pasinetti, G. M. and Ho, L. 2001. From cDNA microarrays to high-throughput proteomics. Implications in the search for preventive initiatives to slow the clinical progression of Alzheimer's disease dementia. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 18:137–42.
Puskas, L. G., Kitajka, K., Nyakas, C., Barcelo-Coblijn, G., and Farkas, T. 2003. Short-term administration of omega 3 fatty acids from fish oil results in increased transthyretin transcription in old rat hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:1580–5.
Uryu, S., Tokuhiro, S., and Oda, T. 2003. Beta-Amyloid-specific upregulation of stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase-1 in macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 303:302–5.
Wada, R., Tifft, C. J., and Proia, R. L. 2000. Microglial activation precedes acute neurodegeneration in Sandhoff disease and is suppressed by bone marrow transplantation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97:10954–9.
Yao, P. J., Zhu, M., Pyun, E. I., Brooks, A. I., Therianos, S., Meyers, V. E., and Coleman, P. D. 2003. Defects in expression of genes related to synaptic vesicle trafficking in frontal cortex of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 12:97–109.
Yoo, M. S., Chun, H. S., Son, J. J., DeGiorgio, L. A., Kim, D. J., Peng, C., and Son, J. H. 2003. Oxidative stress regulated genes in nigral dopaminergic neuronal cells: correlation with the known pathology in Parkinson's disease. Brain. Res. Mol. Brain. Res. 110:76–84.
Yoshihara, T., Ishigaki, S., Yamamoto, M., Liang, Y., Niwa, J., Takeuchi, H., Doyu, M., and Sobue, G. 2002. Differential expression of inflammation-and apoptosis-related genes in spinal cords of a mutant SOD1 transgenic mouse model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurochem. 80:158–67.
Prolla, T. A. 2002. DNA microarray analysis of the aging brain. Chem. Senses 27:299–306.
Zhou, F. C., Duguid, J. R., Edenberg, H. J., McClintick, J., Young, P., and Nelson, P. 2001. DNA microarray analysis of differential gene expression of 6-year-old rat neural striatal progenitor cells during early differentiation. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 18:95–104.
Cavallaro, S., Schreurs, B. G., Zhao, W., D'Agata, V., and Alkon, D. L. 2001. Gene expression profiles during long-term memory consolidation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 13:1809–15.
Cavallaro, S., Dagata, V., and Alkon, D. L. 2002. Programs of gene expression during the laying down of memory formation as revealed by DNA microarrays. Neurochem. Res. 27:1201–7.
Cavallaro, S., D'Agata, V., Manickam, P., Dufour, F., and Alkon, D. L. 2002. Memory-specific temporal profiles of gene expression in the hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:16279–84.
D'Agata, V. and Cavallaro, S. 2002. Gene expression profiles—a new dynamic and functional dimension to the exploration of learning and memory. Rev. Neurosci. 13:209–19.
Dent, G. W., O'Dell, D. M., and Eberwine, J. H. 2001. Gene expression profiling in the amygdala: an approach to examine the molecular substrates of mammalian behavior. Physiol. Behav. 73:841–7.
Irwin, L. N. 2001. Gene expression in the hippocampus of behaviorally stimulated rats: analysis by DNA microarray. Brain. Res. Mol. Brain. Res. 96:163–9.
Leil, T. A., Ossadtchi, A., Cortes, J. S., Leahy, R. M., and Smith, D. J. 2002. Finding new candidate genes for learning and memory. J. Neurosci. Res. 68:127–37.
Luo, Y., Long, J. M., Spangler, E. L., Longo, D. L., Ingram, D. K., and Weng, N. P. 2001. Identification of maze learning-associated genes in rat hippocampus by cDNA microarray. J. Mol. Neurosci. 17:397–404.
Hernan, R., Fasheh, R., Calabrese, C., Frank, A. J., Maclean, K. H., Allard, D., Barraclough, R., and Gilbertson, R. J. 2003. ERBB2 up-regulates S100A4 and several other prometastatic genes in medulloblastoma. Cancer Res. 63:140–8.
Hui, A. B., Lo, K. W., Yin, X. L., Poon, W. S., and Ng, H. K. 2001. Detection of multiple gene amplifications in glioblastoma multiforme using array-based comparative genomic hybridization. Lab. Invest. 81:717–23.
Ljubimova, J. Y., Lakhter, A. J., Loksh, A., Yong, W. H., Riedinger, M. S., Miner, J. H., Sorokin, L. M., Ljubimov, A. V., and Black, K. L. 2001. Overexpression of alpha4 chain-containing laminins in human glial tumors identified by gene microarray analysis. Cancer Res. 61:5601–10.
Miettinen, H. E., Jarvinen, T. A., Kellner, U., Kauraniemi, P., Parwaresch, R., Rantala, I., Kalimo, H., Paljarvi, L., Isola, J., and Haapasalo, H. 2000. High topoisomerase IIalpha expression associates with high proliferation rate and poor prognosis in oligodendrogliomas. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 26:504–12.
Nishizuka, I., Ishikawa, T., Hamaguchi, Y., Kamiyama, M., Ichikawa, Y., Kadota, K., Miki, R., Tomaru, Y., Mizuno, Y., Tominaga, N., Yano, R., Goto, H., Nitanda, H., Togo, S., Okazaki, Y., Hayashizaki, Y., and Shimada, H. 2002. Analysis of gene expression involved in brain metastasis from breast cancer using cDNA microarray. Breast Cancer 9:26–32.
Rickman, D. S., Bobek, M. P., Misek, D. E., Kuick, R., Blaivas, M., Kurnit, D. M., Taylor, J., and Hanash, S. M. 2001. Distinctive molecular profiles of high-grade and low-grade gliomas based on oligonucleotide microarray analysis. Cancer Res. 61:6885–91.
Sallinen, S. L., Sallinen, P. K., Haapasalo, H. K., Helin, H. J., Helen, P. T., Schraml, P., Kallioniemi, O. P., and Kononen, J. 2000. Identification of differentially expressed genes in human gliomas by DNA microarray and tissue chip techniques. Cancer Res. 60:6617–22.
Schaefer, K. L., Wai, D., Poremba, C., Diallo, R., Boecker, W., and Dockhorn-Dworniczak, B. 2002. Analysis of TP53 germline mutations in pediatric tumor patients using DNA microarray-based sequencing technology. Med. Pediatr. Oncol. 38:247–53.
Tanwar, M. K., Gilbert, M. R., and Holland, E. C. 2002. Gene expression microarray analysis reveals YKL-40 to be a potential serum marker for malignant character in human glioma. Cancer Res. 62:4364–8.
Yeatman, T. J. 2003. The future of clinical cancer management: one tumor, one chip. Am. Surg. 69:41–4.
Zardo, G., Tiirikainen, M. I., Hong, C., Misra, A., Feuerstein, B. G., Volik, S., Collins, C. C., Lamborn, K. R., Bollen, A., Pinkel, D., Albertson, D. G., and Costello, J. F. 2002. Integrated genomic and epigenomic analyses pinpoint biallelic gene inactivation in tumors. Nat. Genet. 32:453–8.
Hoffman, P. L., Miles, M., Edenberg, H. J., Sommer, W., Tabakoff, B., Wehner, Jm, and Lewohl, J. 2003. Gene expression in brain: a window on ethanol dependence, neuroadaptation, and preference. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 27:155–68.
Lewohl, J. M., Wang, L., Miles, M. F., Zhang, L., Dodd, P. R., and Harris, R. A. 2000. Gene expression in human alcoholism: microarray analysis of frontal cortex. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 24:1873–82.
Mayfield, R. D., Lewohl, J. M., Dodd, P. R., Herlihy, A., Liu, J., and Harris, R. A. 2002. Patterns of gene expression are altered in the frontal and motor cortices of human alcoholics. J. Neurochem. 81:802–13.
Saito, M., Smiley, J., Toth, R., and Vadasz, C. 2002. Microarray analysis of gene expression in rat hippocampus after chronic ethanol treatment. Neurochem. Res. 27:1221–9.
Ang, E., Chen, J., Zagouras, P., Magna, H., Holland, J., Schaeffer, E., and Nestler, E. J. 2001. Induction of nuclear factor-kappaB in nucleus accumbens by chronic cocaine administration. J. Neurochem. 79:221–4.
Jayanthi, S., McCoy, M. T., Ladenheim, B., and Cadet, J. L. 2002. Methamphetamine causes coordinate regulation of Src, Cas, Crk, and the Jun N-terminal kinase-Jun pathway. Mol. Pharmacol. 61:1124–31.
Kontkanen, O., Toronen, P., Lakso, M., Wong, G., and Castren, E. 2002. Antipsychotic drug treatment induces differential gene expression in the rat cortex. J. Neurochem. 83:1043–53.
Konu, O., Kane, J. K., Barrett, T., Vawter, M. P., Chang, R., Ma, J. Z., Donovan, D. M., Sharp, B., Becker, K. G., and Li, M. D. 2001. Region-specific transcriptional response to chronic nicotine in rat brain. Brain Res. 909:194–203.
Lee, K. H., Ahn, J. I., Yu, D. H., Koh, H. C., Kim, S. H., Yang, B. H., and Lee, Y. S. 2003. Dextromethorphan alters gene expression in rat brain hippocampus and cortex. Int. J. Mol. Med. 11:559–68.
Loguinov, A. V., Anderson, L. M., Crosby, G. J., and Yukhananov, R. Y. 2001. Gene expression following acute morphine administration. Physiol. Genomics. 6:169–81.
Parmentier-Batteur, S., Jin, K., Xie, L., Mao, X. O., and Greenberg, D. A. 2002. DNA microarray analysis of cannabinoid signaling in mouse brain in vivo. Mol. Pharmacol. 62:828–35.
Sokolov, B. P., Polesskaya, O. O., and Uhl, G. R. 2003. Mouse brain gene expression changes after acute and chronic amphetamine. J. Neurochem. 84:244–52.
Toyooka, K., Usui, M., Washiyama, K., Kumanishi, T., and Takahashi, Y. 2002. Gene expression profiles in the brain from phencyclidine-treated mouse by using DNA microarray. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 965:10–20.
Uhl, G. R., Liu, Q. R., Walther, D., Hess, J., and Naiman, D. 2001. Polysubstance abuse-vulnerability genes: genome scans for association, using 1,004 subjects and 1,494 single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69:1290–300.
Xie, T., Tong, L., Barrett, T., Yuan, J., Hatzidimitriou, G., McCann, U. D., Becker, K. G., Donovan, D. M., and Ricaurte, G. A. 2002. Changes in gene expression linked to methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci. 22:274–83.
Yamada, M., Yamazaki, S., Takahashi, K., Nishioka, G., Kudo, K., Ozawa, H., Yamada, S., Kiuchi, Y., Kamijima, K., Higuchi, T., and Momose, K. 2000. Identification of a novel gene with RING-H2 finger motif induced after chronic antidepressant treatment in rat brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 278:150–7.
Cotman, C. W. and Berchtold, N. C. 2002. Exercise: a behavioral intervention to enhance brain health and plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 25:295–301.
Cotman, C. W. and Engesser-Cesar, C. 2002. Exercise enhances and protects brain function. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 30:75–9.
Molteni, R., Ying, Z., and Gomez-Pinilla, F. 2002. Differential effects of acute and chronic exercise on plasticity-related genes in the rat hippocampus revealed by microarray. Eur. J. Neurosci. 16:1107–16.
Tong, L., Shen, H., Perreau, V. M., Balazs, R., and Cotman, C. W. 2001. Effects of exercise on gene-expression profile in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiol. Dis. 8:1046–56.
Becker, A. J., Wiestler, O. D., and Blumcke, I. 2002. Functional genomics in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy: powerful new tools to identify molecular disease mechanisms of hippocampal damage. Prog. Brain Res. 135:161–73.
Li, J. Y., Lescure, P. A., Misek, D. E., Lai, Y. M., Chai, B. X., Kuick, R., Thompson, R. C., Demo, R. M., Kurnit, D. M., Michailidis, G., Hanash, S. M., and Gantz, I. 2002. Food deprivation-induced expression of minoxidil sulfotransferase in the hypothalamus uncovered by microarray analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 277:9069–76.
Bonaventure, P., Guo, H., Tian, B., Liu, X., Bittner, A., Roland, B., Salunga, R., Ma, X. J., Kamme, F., Meurers, B., Bakker, M., Jurzak, M., Leysen, J. E., and Erlander, M. G. 2002. Nuclei and subnuclei gene expression profiling in mammalian brain. Brain Res. 943:38–47.
Cho, Y., Gong, T. W., Stover, T., Lomax, M. I., and Altschuler, R. A. 2002. Gene expression profiles of the rat cochlea, cochlear nucleus, and inferior colliculus. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 3:54–67.
Zhao, X., Lein, E. S., He, A., Smith, S. C., Aston, C., and Gage, F. H. 2001. Transcriptional profiling reveals strict boundaries between hippocampal subregions. J. Comp. Neurol. 441:187–96.
Chen, B., Wang, J. F., Sun, X., and Young, L. T. 2003. Regulation of GAP-43 expression by chronic desipramine treatment in rat cultured hippocampal cells. Biol. Psychiatry 53:530–7.
Fortin, A., Cregan, S. P., MacLaurin, J. G., Kushwaha, N., Hickman, E. S., Thompson, C. S., Hakim, A., Albert, P. R., Cecconi, F., Helin, K., Park, D. S., and Slack, R. S. 2001. APAF1 is a key transcriptional target for p53 in the regulation of neuronal cell death. J. Cell Biol. 155:207–16.
Jin, K., Mao, X. O., Eshoo, M. W., del Rio, G., Rao, R., Chen, D., Simon, R. P., and Greenberg, D. A. 2002. cDNA microarray analysis of changes in gene expression induced by neuronal hypoxia in vitro. Neurochem. Res. 27:1105–12.
Luo, Y., Cai, J., Liu, Y., Xue, H., Chrest, F. J., Wersto, R. P., and Rao, M. 2002. Microarray analysis of selected genes in neural stem and progenitor cells. J. Neurochem. 83:1481–97.
Nagarajan, R., Svaren, J., Le, N., Araki, T., Watson, M., and Milbrandt, J. 2001. EGR2 mutations in inherited neuropathies dominant-negatively inhibit myelin gene expression. Neuron 30:355–68.
Nagarajan, R., Le, N., Mahoney, H., Araki, T., and Milbrandt, J. 2002. Deciphering peripheral nerve myelination by using Schwann cell expression profiling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:8998–9003.
Brown, V., Jin, P., Ceman, S., Darnell, J. C., O'Donnell, W. T., Tenenbaum, S. A., Jin, X., Feng, Y., Wilkinson, K. D., Keene, J. D., Darnell, R. B., and Warren, S. T. 2001. Microarray identification of FMRP-associated brain mRNAs and altered mRNA translational profiles in fragile X syndrome. Cell 107:477–87.
Chan, E. Y., Luthi-Carter, R., Strand, A., Solano, S. M., Hanson, S. A., DeJohn, M. M., Kooperberg, C., Chase, K. O., DiFiglia, M., Young, A. B., Leavitt, B. R., Cha, J. H., Aronin, N., Hayden, M. R., and Olson, J. M. 2002. Increased Huntington protein length reduces the number of polyglutamine-induced gene expression changes in mouse models of Huntington's disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11:1939–51.
D'Agata, V., Warren, S. T., Zhao, W., Torre, E. R., Alkon, D. L., and Cavallaro, S. 2002. Gene expression profiles in a transgenic animal model of fragile X syndrome. Neurobiol. Dis. 10:211–8.
Luthi-Carter, R., Strand A. D., Hanson, S. A., Kooperberg, C., Schilling, G., La Spada, A. R., Morry, D. E., Young, A. B., Ross, C. A., Borchelt, D. R., and Olson, J. M. 2002. Polyglutamine and transcription: gene expression changes shared by DRPLA and Huntington's disease mouse models reveal context-independent effects. Hum. Mol. Genet. 11:1927–37.
Maurer, M. H., Frietsch, T., Waschke, K. F., Kuschinsky, W., Gassmann, M., and Schneider, A. 2002. Cerebral transcriptome analysis of transgenic mice overexpressing erythropoietin. Neurosci. Lett. 327:181–4.
Mirjany, M., Ho, L., and Pasinetti, G. M. 2002. Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in neuronal cell cycle activity and glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 301:494–500.
Poguet, A. L., Legrand, C., Feng, X., Yen, P. M., Meltzer, P., Samarut, J., and Flamant, F. 2003. Microarray analysis of knockout mice identifies cyclin D2 as a possible mediator for the action of thyroid hormone during the postnatal development of the cerebellum. Dev. Biol. 254:188–99.
Wurmbach, E., Gonzalez-Maeso, J., Yuen, T., Ebersole, B. J., Mastaitis, J. W., Mobbs, C. V., and Sealfon, S. C. 2002. Validated genomic approach to study differentially expressed genes in complex tissues. Neurochem. Res. 27:1027–33.
Welle, S., Brooks, A. I., Delehanty, J. M., Needler, N., and Thornton, C. A. 2003. Gene expression profile of aging in human muscle. Physiol. Genomics 14:149–159.
Irizarry, R. A., Bolstad, B. M., Collin, F., Cope, L. M., Hobbs, B., and Speed, T. P. 2003. Summaries of Affymetrix GeneChip probe level data. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 31:e15.
Yuen, T., Zhang, W., Ebersole, B. J., and Sealfon, S. C. 2002. Monitoring G-protein-coupled receptor signaling with DNA microarrays and real-time polymerase chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 345:556–69.
Wurmbach, E., Yuen, T., Ebersole, B. J., and Sealfon, S. C. 2001. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor-coupled gene network organization. J. Biol. Chem. 276:47195–201.
Yen, K., Mastaitis, J. W., Isoda, F., Mizuno, T., Ngyuen, V., Sealfon, S. C., Wurmbach, E., Salton, S. R., and Mobbs, C. V. 2003. FKBP51 regulation by fasting and leptin. 63rd Scientific Sessions (ADA):1847-Poster.
Scammell, J. G., Denny, W. B., Valentine, D. L., and Smith, D. F. 2001. Overexpression of the FK506-binding immunophilin FKBP51 is the common cause of glucocorticoid resistance in three New World primates. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 124:152–65.
Davies, T. H., Ning, Y. M., and Sanchez, E. R. 2002. A new first step in activation of steroid receptors: hormone-induced switching of FKBP51 and FKBP52 immunophilins. J. Biol. Chem. 277:4597–600.
Hubler, T. R., Denny, W. B., Valentine, D. L., Cheung-Flynn, J., Smith, D. F., and Scammell, J. G. 2003. The FK506-binding immunophilin FKBP51 is transcriptionally regulated by progestin and attenuates progestin responsiveness. Endocrinology 144:2380–7.
Vermeer, H., Hendriks-Stegeman, B. I., van der Burg, B., van Buul-Offers, S. C., and Jansen, M. 2003. Glucocorticoid-induced increase in lymphocytic FKBP51 messenger ribonucleic acid expression: a potential marker for glucocorticoid sensitivity, potency, and bioavailability. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88:277–84.
Pratt, W. B. and Toft, D. O. 2003. Regulation of signaling protein function and trafficking by the hsp90/hsp70-based chaperone machinery. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 228:111–33.
Tillman, J. B., Mote, P. L., Dhahbi, J. M., Walford, R. L., and Spindler, S. R. 1996. Dietary energy restriction in mice negatively regulates hepatic glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) expression at the posttranscriptional level. J. Nutr. 126:416–23.
Dhahbi, J. M., Mote, P. L., Tillman, J. B., Walford, R. L., and Spindler, S. R. 1997. Dietary energy tissue-specifically regulates endoplasmic reticulum chaperone gene expression in the liver of mice. J. Nutr. 127:1758–64.
Mote, P. L., Tillman, J. B., and Spindler, S. R. 1998. Glucose regulation of GRP78 gene expression. Mech. Ageing Dev. 104:149–58.
Dhahbi, J. M., Cao, S. X., Tillman, J. B., Mote, P. L., Madore, M., Walford, R. L., and Spindler, S. R. 2001. Chaperone-mediated regulation of hepatic protein secretion by caloric restriction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 284:335–9.
Tindal, M. H., Lee, K. L., Isham, K. R., Cadilla, C., and Kenney, F. T. 1988. Structure of a multihormonally regulated rat gene. Gene. 71:413–20.
Lee, K. L., Makkinje, A., Ch'Ang, L. Y., and Kenney, F. T. 1989. Molecular cloning and analysis of full-length cDNAs cognate to a rat gene under multihormonal control. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 269:106–13.
Makkinje, A., Quinn, D. A., Chen, A., Cadilla, C. L., Force, T., Boventre, J. V., and Kyriakis, J. M. 2000. Gene 33/Mig-6, a transcriptionally inducible adapter protein that binds GTP-Cdc42 and activates SAPK/JNK. A potential marker transcript for chronic pathologic conditions, such as diabetic nephropathy. Possible role in the response to persistent stress. J. Biol. Chem. 275:17838–47.
Mastaitis, J., Isoda, F., Yen, K., E., W., Sealfon, S. C., and Mobbs, C. V. 2003. Hypoglycemia and fasting induce hypothalamic expression of GLUT-1, angiotensinogen, and IkBeta. 63rd Scientific Sessions (ADA):632-Poster.
Mizuno, T. M. and Mobbs, C. V. 1999. Hypothalamic agouti-related protein messenger ribonucleic acid is inhibited by leptin and stimulated by fasting. Endocrinology 140:814–7.
Yen, K., Mastaitis, J. W., Salton, S. R., Wurmbach, E., Sealfon, S. C., and Mobbs, C. V. 2002. Fasting combined with hypoglycemia down-regulates hypothalamus serotonin receptor mRNA. Workshop on Functional Genomics in Neuroendocrinology, Berkeley, CA:18-Poster.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mobbs, C.V., Yen, K., Mastaitis, J. et al. Mining Microarrays for Metabolic Meaning: Nutritional Regulation of Hypothalamic Gene Expression. Neurochem Res 29, 1093–1103 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NERE.0000023596.49140.e0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NERE.0000023596.49140.e0