Abstract
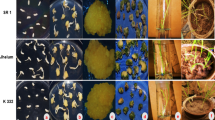
An attempt has been taken to establish an efficient plant regeneration system in vitro from 3, 5, 7 and 9-days-old root segments of four Indica (Bangladeshi) rice genotypes. Genotypic effects were observed in callus induction and subsequent plant regeneration. Moreover, the stage of development of the root explants also played a significant role in callus formation and subsequent plant regeneration. Younger explants were more efficient in both callus induction and plant regeneration. Plants regenerated in vitro were successfully established in soil and produced fertile seeds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe T & Futsuhara Y (1984) Varietal difference of plant regeneration from root callus tissues in rice. Jap. J. Breed. 34: 147–155
Abe T & Futsuhara Y (1985) Efficient plant regeneration by somatic embryogenesis from root callus tissues of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Physiol. 121: 111–118
Abe T & Futsuhara Y (1986) Genotypic variability for callus formation and plant regeneration in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 72: 3–10
Adkins SW (1992) Cereal tissue cultures: control of headspace gases can optimize the conditions for callus proliferation. Aust. J. Bot. 40: 737–749
Basu S, Gangopadhyay G, Mukherjee BB & Gupta S (1997) Plant regeneration of salt adapted callus of Indica rice (var. Basmati 370) in saline conditions. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 50: 153–159
Chand S & Sahrawat AK (2000) Efficient plant regeneration from root callus tissues of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J. Plant Physiol. 156: 401–407
Chowdhry CN, Tyagi AK, Maheshwari N & Maheshwari SC (1993) Effect of L-proline and L-tryptophan on somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration of rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Pusa 169). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 32: 357–361
Chu QR & Croughan TP (1990) Genetics of plant regeneration in immature panicle culture of rice. Crop Sci. 30: 1194–1197
Hartke S & Lörz H (1989) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from various Indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) genotypes. J. Genet. Breed. 43: 205–214
Jain RK (1997) Effect of some factors on plant regeneration from Indica rice cells and protoplasts - a review. Ind. J. Exp. Biol. 35: 323–331
Kawata SI & Ishihara A (1968) The regeneration of rice plant, Oryza sativa L., in the callus derived from the seminal root. Proc. Jap. Acad. 44: 549–553
Khanna HK & Raina SK (1998) Genotype × culture media interaction effects on regeneration response of three Indica rice cultivars. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 52: 145–153
Kunanuvatchaidach R, Godwin ID & Adkins SW (1995) High effi-ciency plant regeneration from callus induced on mature Indica rice caryopses. Aust. J. Bot. 43: 337–348
Lee SH, Shon YG, Lee SI, Kim CY, Koo JC, Lim CO, Choi YJ, Han CD, Chung CH, Choe ZR & Cho MJ (1999) Cultivar variability in the Agrobacterium-rice cell interaction and plant regeneration. Physiol. Plant 107: 338–345
Linsmaier EM & Skoog F (1965) Organic growth factor requirements of tobacco tissue culture. Physiol. Plant 18: 100–127
Morrish F, Vasil V & Vasil IK (1987) Developmental morphogenesis and genetic manipulation in tissue and cell cultures of the gramineae. Adv. Genet. 24: 432–499
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant 15: 473–497
Peng J & Hodges TK (1989) Genetic analysis of plant regeneration in rice (Oryza sativa L.). In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 25: 91–94
Rueb S, Leneman M, Schilperoot RA & Hensgens LAM (1994) Efficient plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from callus induced on mature rice embryos (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 36: 259–264
Vasil IK & Vasil V (1986) Regeneration in cereals and other grass species. In: Vasil IK (ed) Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants, Vol. 3 (pp. 121–150). Academic Press, New York
Wang CC, Sun CS, Chu CC & Wu SC (1978) Studied on the albino pollen plantlets of rice. In: Hu H (ed) Proc. Symp. Plant Tissue Culture (pp. 149–160). Science Press, Beijing
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoque, M.E., Mansfield, J.W. Effect of Genotype and Explant Age on Callus Induction and Subsequent Plant Regeneration from Root-derived Callus of Indica Rice Genotypes. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 78, 217–223 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TICU.0000025640.75168.2d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:TICU.0000025640.75168.2d