Abstract
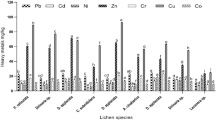
The purpose of this research is to present toxic effects of some heavy metals (cadmium, lead and zinc) on lichen physiology. In the North of France, those metals are concentrated for example in industrial polluted soils near metallurgic plants and waste dumps. Our investigations were conducted on Diploschistes muscorum (Scop.) R. Sant, a terricolous lichen growing on previously quoted soils as well as on non-contaminated ones. Different stress parameters were investigated as potassium leakage – which is related to the loss of membrane integrity – and oxidative stress through following parameters: malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD). It seems, therefore, that heavy metals induce oxidative stress in this lichen, in which we found membrane damage and enhancement of SOD activity and GSH concentrations. With regard to very high concentrations of Cd, Pb and Zn, a resistance involving antioxidant mechanisms limits the expected damage. Those mechanisms involve GSH, SOD as well as secondary metabolites, which have this resistance property. This study is a first step of investigation to use – in the future– physiological parameters as tool for environment assessment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boutin, A. C., Shirali, P., Garçon, G., Gosset, P., Leleu, B., Marez, T., Bernard, A. and Haguenoer, J. M.: 1998, 'Peripheral Markers (Clara Cell protein and ?-glutathione S-transferase) and lipidoperoxidation (Malondialdehyde) assessment in Sprague-Dawley rats instilled with haematite and benzo[a]pyrene', J. Appl. Toxicol. 17, 39–45.
Branquinho, C. and Brown, D. H.: 1994, 'A new method for studying the cellular location of lead in lichens', Lichenologist 26, 83–90.
Branquinho, C., Brown, D. H., Máquas, C. and Catarino, F.: 1997, 'The cellular location of Cu in lichens and its effects on membrane integrity and chlorophyll fluorescence', Environm. Exp. Bot. 38(1), 55–169.
Brennan, R. and Schiestl, R. H.: 1996, 'Cadmium is an inducer of oxidative stress in yeast', Mut. Res. 356, 161–178.
Cañas, M. S. and Pignata, M. L.: 1998, 'Temporal variation of pigments and peroxidation products in the lichen Parmotrema uruguense (Kremplh.) Hale transplanted to urban and non-polluted environments', Symbiosis 24, 147–152.
Carreras, H. A., Gudiño, G. L. and Pignata,M. L.: 1998, 'Comparative biomonitoring of atmospheric quality in five zones of Cordoba city (Argentina) employing the transplanted lichen Usnea sp.', Environ. Pollut. 103, 317–325.
Clijsters, H., Cuypers, A. and Vangronsveld, J.: 1999, 'Physiological responses to heavy metals in higher plants: Defence against oxidative stress', Z. Naturforsch. 54c, 730–734.
Cuny, D., Pignata, M. L., Kranner, I. and Beckett, R.: 2002, 'Biomarkers of Pollution-induced Oxidative Stress and Membrane Damage in Lichens', in P. L. Nimis, C. Scheidegger and P. A. Wolseley (eds), Monitoring with Lichens – Monitoring Lichens, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 97–110.
Cuny, D., Van Haluwyn, C. and Pesch, R.: 2001, 'Biomonitoring of trace elements in air and soil compartments along the major motorway in France', Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 125, 273–289.
Cuny, D., Imbenotte, M., Van Haluwyn, C., Chavatte, P. and Caron, B.: 1995, 'Etude préliminaire sur le rôle des acides lichéniques dans la bioaccumulation du zinc par le lichen Diploschistes muscorum (Scop.) R. Sant', in INRA (ed.), Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on the Biochemistry of Trace Elements, Paris, France, 15–19 May.
Deltoro, V. I., Gimeno, C., Calatayud, A. and Barreno, E.: 1999, 'Effects of SO2 fumigations on photosynthetic CO2 gas exchange, chlorophyll IIa fluorescence emission and antioxidant enzymes in the lichens Evernia prunastri and Ramalina farinacea', Physiol. Pl. 105, 648–654.
Dembitsky, V., Rezanka, T. and Bychek, I. A.: 1994, 'Seasonal variation of lipids and fatty acids from tree-growing lichens of the genus Physcia', Phytochemistry 36, 601–608.
Dhinsa, R. C.: 1987, 'Glutathione status and protein synthesis during drought and subsequent rehydratation in Tortula ruralis', Pl. Physiol. 83, 816–819.
Dhinsa, R. S.: 1982, 'Inhibition of protein synthesis by products of lipid peroxidation', Phytochemistry 21, 309–313.
Dietz, K. J., Baier, M. and Krämer, U.: 1999, 'Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species as Mediators of Heavy Metal Toxicity in Plants', in M. N. V. Prasad and J. Hagemayer (eds), Heavy Metal Stress in Plants. From Molecules to Ecosystems, Springer, Berlin, Germany, pp. 73–97.
Egger, R., Schlee, D. and Türk, R.: 1994, 'Changes of physiological and biochemical parameters in the lichen Hypogymnia physodes (L.) Nyl. due to the action of air pollutants – A field study', Phyton 34 229–242.
Garty, J.: 1993, 'Lichens as Biomonitors for Heavy Metal Pollution', in B. Markert (ed.), Plants as Biomonitors. Indicators for Heavy Metals in the Terrestrial Environment, VCH, Weinheim, Germany, pp. 193–263.
Gonzalez, C. M., Orellana, L. C., Casanovas, S. S. and Pignata, M. L.: 1998, 'Environmental conditions and chemical response of a transplanted lichen to an urban area', J. Environ. Manage. 53, 73–81.
Gonzalez, C. M. and Pignata,M. L.: 1994, 'The influence of air pollution on soluble proteins, chlorophyll degradation, MDA, sulphur and heavy metals in a transplanted lichen', Chem. and Ecol. 9, 105–113.
González, C. M. and Pignata, M. L.: 1999, 'Effect of pollutants emitted by different urban-industrial sources on the chemical response of the transplanted Ramalina ecklonii (Spreng.)Mey. and Flot', Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 69, 61–73.
Gwozdz, E. A., Przymusinski, R. and Rucinska, R.: 1997, 'Plant cell responses to heavy metals: Molecular and physiological aspects', Acta Physiol. Pl. 184, 459–465.
Kranner, I. and Grill, D.: 1994, 'Rapid changes of the glutathione status and the enzymes involved in the reduction of glutathione disulfide during the initial stage of wetting of lichens', Cryptog. Bot. 4, 203–206.
Kranner, I., Guttenberger, H., Grill, D., Delefont, M. and Türk, R.: 1992, 'Investigations of thiols in lichens', Phyton 32, 69–73.
Kranner, I.: 1998, 'Determination of Glutathione, Glutathione Disulphide and Two Related Enzymes, Glutathione Reductase and Glucose-6-phosphate Deshydrogenase, in Fungal and Plant Cells', in A. Varna (ed.), Mycorrhiza Manual, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Germany, pp. 228–241.
Lambinon, J., Maquinay, A. and Ramault, J. L.: 1964, 'La teneur en zinc de quelques lichens calaminaires belges', Bull. Jard. Bot. Etat 34, 273–282.
Lapshina, E. A., Jaruga, E., Bilinski, T. and Bartorz, G.: 1995, 'What determine the antioxidant potential in yeast cells?', Biochem. Molec. Biol. 37, 903–908.
Luna, C. M., Gonzalez, C. A. and Trippi, V. S.: 1994, 'Oxidative damage caused by excess of copper in oat leaves', Pl. Cell Physiol. 35, 11–15.
Miersch, J., Bärlocher, F., Bruns, I. and Krauss, G. J.: 1997, 'Effects of cadmium, copper and zinc on growth and thiol content of aquatic hyphomycetes', Hydrobiologia 346, 77–84.
Murphy, A. and Taiz, L.: 1997, 'Correlation between potassium efflux and copper sensitivity in 10 Arabidopsis ecotypes', New Phytol. 136, 211–222.
Nash III, T. H.: 1996, 'Nutrients Elemental Accumulation and Mineral Cycling', in T. H. Nash III (ed.), Lichen Biology, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom, pp. 136–153.
Pandolfini, T., Gabbrielli, R. and Comparini, C.: 1992, 'Nickel toxicity and peroxidase activity in seedlings of Triticum aestivum L.', Plant Cell Environ. 15, 719–725.
Piervittori, R., Alessio, F. and Maffei, M.: 1994, 'Fatty acid variations in the lichen Xanthoria parietina', Phytochemistry 36, 853–856.
Purvis, O. W.: 1996, 'Interactions of lichens with metals', Sci. Progr. 79, 283–309.
Rüegsegger, A., Schmutz, D. and Brunold, C.: 1990, 'Regulation of glutathione synthesis by cadmium in Pisum sativum L.', Pl. Physiol. 93, 1579–1584.
Sarret, G., Manceau, A., Cuny, D., Van Haluwyn, C., Deruelle, S., Hazemann, J. L., Soldo, Y., Eybert-Berard, L. and Menthonnex, J. J.: 1998, 'Mechanism of lichen resistance to metallic pollution', Environ. Sci. Technol. 32, 3325–3330.
Schulte-Frohlinde, D. and Von Sonntag, C.: 1985, 'Radiolysis of DNA and Model Systems in the Presence of Oxygen', in H. Sies (ed.), Oxidative Stress, Academic Press, London, United Kingdom, pp. 11–40.
Shapiro, I. A., Ravinska, A. P. and Bychek, I. A.: 1998, 'Physiological and lipid composition changes in lichens due to acute gamma radiation', J. Hattori Bot. Lab. 84, 315–324.
Silberstein, L., Siegel, B. Z., Siegel, S. M., Mukhtar, A. and Galun, M.: 1996, 'Comparative studies on Xanthoria parietina a pollution-resistant lichen and Ramalina duriaei a sensitive species. II Evaluation of possible air pollution-protection mechanisms', Lichenologist 28, 367–383.
Smith, P. K., Krohn, R. I., Hermanson, G. T., Mallia, A. K., Gartner, F. H., Provenzana, M. D., Fujimoto, E. K., Goeke, N. M., Olson, B. J. and Klenk, D. C.: 1985, 'Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid', Anal. Biochem. 150, 76–85.
Weckx, J. E. J. and Clijsters, H. M. M.: 1997, 'Zn phytotoxicity induces oxidative stress in primary leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris', Pl. Physiol. Biochem. 35, 405–440.
Wonisch, W., Hayn, M., Schaur, R. J., Tatzber, F., Kranner, I., Grill, D., Winkler, R., Bilinski, T., Kohlwein, S. D. and Esterbauer, H.: 1997, 'Increased stress parameter synthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae after treatment with 4-hydroxy-2-nonelel', FEBS Lett. 405, 11–15.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuny, D., Van Haluwyn, C., Shirali, P. et al. Cellular Impact of Metal Trace Elements in Terricolous Lichen Diploschistes muscorum (Scop.) R. Sant. – Identification of Oxidative Stress Biomarkers. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 152, 55–69 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000015332.94219.ff
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000015332.94219.ff