Abstract
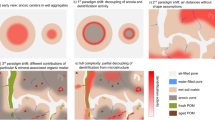
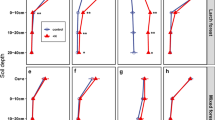
The atmospheric deposition of air pollutants was studied by means of monitoring canopy throughfall at six forest stands. The investigation was carried out in Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst.) forests in Southern Bavaria with high ambient ammonia concentrations due to either adjacent intensive agriculture or poultry housing. Five monitoring plots transected the forest edges and forest interior from the edge, at 50, 150, about 400 m and about 800m to the interior. Additionally, nutrient concentration in soil solution was sampled with suction cups at each plot, and C/N ratio of the humus layer was also determined. The variation of ambient ammonia concentration between three of the six investigated sites was estimated using diffusive samplers. In order to compare the effects of atmospheric deposition on European beech (Fagus sylvatica L.) and Norway spruce additional monitoring plotswere installed under each of these species in a mixed beech and spruce stand. Bulk deposition and soil water samples were analysed for major ions (NO3 -, NH4 +, SO4 2-, Cl-, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+M).The results show a substantial increase of deposition towards the forest edges for all ions. This so called 'edge effect' continued in most cases until a distance from 50 to 150 m from edge. For both ambient ammonia concentrations and nitrogen deposition, it can be concluded that increased dry deposition is the main reason for the edge effect. Over 76% of the nitrogen ratios in throughfall deposition between the edge and 50 m distance into the spruce forest exceed 1.0. Except for potassium, beech generally showed lower ratios than spruce.Due to high nitrogen deposition the forest floor, C/N ratios were lower at stand edges when compared to their interior. In contrast to the increase of nitrogen deposition at the edge, nitrate export below the main rooting zone was lower at the edge. Nitrate export was generally lower under beech than spruce. Nitrogen budgets of some plots were negative, indicating a reduction of total ecosystem nitrogen stock.The results show that forest edges, especially in areas with high air pollution, receive much more atmospheric deposition than the interior parts of closed forest stands. As many deposition studies in forests were conducted at field stations in the central parts of forests the estimated deposition for the whole forest may be underestimated. This may be important to consider in geo-statistical studies and models aiming to estimate spatial critical deposition values, especially with an increasing fragmentation of the forest cover.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asman, W. A. H.: 1994, 'Emission and deposition of ammonia and ammonium', Nova Acta Leopoldina NF 70(288), 263–297.
Bach, M. und Frede, H.-G.: 1998, 'Agricultural nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium balances in Germany – Methodology and trends 1970 to 1995'. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenk. 161, 385–393.
Bavarian agricultural report: 2000, Internet link http://www.stmlf.bayern.de/landwirtschaft/, Bayerisches Staatsministerium für Landwirtschaft und Forsten, Ludwigstr. 2, 80535 München, Germany.
Beier, C. and Gundersen, P.: 1989, 'Atmospheric deposition to the edge of a spruce forest in Denmark', Envir. Pollut. 60, 257–272.
Beier, C., Rasmussen, K., Pilegaard, K., Ambusi, P., Mikkelsen, T., Jensen, N.O., Kjoller, A., Prieme, A. and Ladekarl, U. L.: 2001, 'Fluxes of NO? 3, NH+ 4, NO, NO2, andN2O in an old Danish beech forest', Water, Air, Soil Pollut.: Focus 1, 187–195.
Bobbink, R., Boxman, D., Fremstadt, E., Heil, G., Houdijk, A. and Roelofs, J.: 1991, 'Critical Loads for Nitrogen Eutrophication of Terrestrial and Wetland Ecosystems Based Upon Changes in Vegetation and Fauna', in P. Grennfelt and E. Thörnelöf (Hrsg.), Critical Loads for Nitrogen, Report from a Workshop held at Lökeberg, Sweden, April 1992.
Callesen, I., Raulund-Rasmussen, K., Gundersen, P. and Stryhn, H.: 1999, 'Nitrate concentrations in soil solutions below Danish forests'. Forest Ecol. Manage. 114, 71–82.
Carleton, T. J. and Kavanagh, T.: 1990, 'Influence of stand age and spatial location on throughfall chemistry beneath black spruce'. Can. J. For. Res. 20, 1917–1925.
Cox, R. M. and Malcolm, J.W.: 1999, 'Passive ozone monitoring for forest health assessment'. Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 116, 339–344.
Dasch, J. M.: 1987, 'Measurement of dry deposition to surfaces in deciduous and pine canopies', Envir. Pollut. 44, 261–277.
Dise, N. B. and Wright, R. F.: 1995, 'Nitrogen leaching from European forests in relation to nitrogen deposition', Forest Ecol. Manage. 71, 153–161.
Draaijers, G. P. J., Ivens, W. P. M. F. and Bleuten, W.: 1988, 'Atmospheric deposition in forest edges measured by monitoring canopy throughfall', Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 42, 129–136.
Draaijers, G. P. J.: 1993, 'The variability of atmospheric deposition to forests', Nederlandse Geografische Studies 156, Utrecht.
DVWK: 1984, 'Ermittlung der Stoffdeposition in Waldökosystemen', DVWK – Deutscher Verband für Wasserwirtschaft und Kulturbau, Regeln zur Wasserwirtschaft, Verlag Paul Parey, Vol. 122.
Eichhorn, J., Haussmann, T., Paar, U., Reinds, G. J. and de Vries, W.: 2001, 'Assessment of Impacts of Nitrogen Deposition on Beech Forests', Results from the Pan-European Intensive Monitoring Programme, in Optimizing Nitrogen Management in Food and Energy Production and Environmental Protection, Proceedings of the 2nd International Nitrogen Conference on Science and Policy. The Scientific World 1.
Flaig, H. und Mohr, H.: 1996, 'Der überlastete Stickstoffkreislauf. Strategien einer Korrektur', Nova Acta Leopoldina 289, 70.
Harding, R., Hall, R., Neal, C., Roberts, J. M., Rosier, P. T. R. and Kinniburgh, D. G.: 1992, 'Hydrological Impacts of Broadleaf Woodlands: Implications forWater Use and Water Quality', Project Report 115/03/ST (National Rivers Authority, Bristol).
Hasselrot, B. and Grennfelt, P.: 1987, 'Deposition of air pollutants in a wind-exposed forest edge', Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 34, 135–143.
Heitz, R.: 1999, 'Umbau von Fichtenreinbeständen in naturnahe Mischwälder-Auswirkungen auf bodenchemischen Zustand und Bioelementhaushalt', . PhD Thesis, Technical University München, 307 pp.
Huebert, B. J. and Robert, C. H.: 1985, 'The dry deposition of nitric acid to grass', J. Geophys. Res. 90(D1), 2085–2090.
Ibrom, A., Oltchev, A., Constantin, J., Marques, M. und Gravenhorst, G.: 1994, 'Die Stickstoffimmission und-deposition in Wäldern', in Wirkungskomplex Stickstoff und Wald', Umweltbundesamt Texte 28/95, S. 20–29.
Internet link: www.umweltministerium.bayern.de/service/umwberat/; Bayerisches Staatsministerium für Landesentwicklung und Umweltfragen, Rosenkavalierplatz 2, 81925 München.
Kinniburgh, D. G. and Trafford, J. M.: 1996, 'Unsaturated zone pore water chemistry and the edge effect in a beech forest in southern England', Water, Air, Soil Pollut. 92, 421–450.
Kirchner, M., Braeutigam, S., Ferm, M., Haas, M., Hangartner, M., Hofschreuder, P., Kasper-Giebl, A., Römmelt, H., Striedner, J., Terzer, W., Thöni, L., Werner, H. and Zimmerling, R.: 1999, 'Field intercomparison of diffusive samplers for measuring ammonia', J. Environ. Monit. 1, 259–265.
KRdL: 1992, 'Schriftenreihe der Kommission der Reinhaltung der Luft (KRdL)', im VDI und DIN10.
Kriebitzsch, W.-U.: 1978, 'Stickstoffnachlieferung in sauren Waldböden Nordwestdeutschlands', Scripta Geobotanica, Vol 14, Verlag Erich Goltze KG, Göttingen, Germany.
Lamersdorf, N. P. and Meyer, R.: 1993, 'Nutrient cycling and acidification of a northwest German forest site with high atmospheric nitrogen deposition', Forest Ecol. Manage. 62, 323–354.
Lindberg, S. E. and Owens, J. G.: 1993, 'Throughfall studies of deposition to forest edges and gaps in montane ecosystems', Biogeochem. 19, 173–194.
Lovett, G. M. and Reiners, W. A.: 1986, 'Canopy structure and cloud water deposition in subalpine coniferous forests', Tellus 38B, 319–327.
Matzner, E. and Grosholz, C.: 1997, 'Beziehung zwischen NO3-Austrägen, C/N-Verhältnissen der Auflage und N-Einträgen in Fichtenwald (Picea abies Karst.)-Ökosystemen Mitteleuropas', Forstw. Centralbl. 116, 39–44.
Mellert, K.-H., Kölling, C. and Rehfuess, K. E.: 1996, 'Stoffauswaschung aus Fichtenwaldökosystemen Bayerns nach Sturmwurf', Forstw. Centralbl. 115, 363–377.
Mulder, J.: 1985, 'Deposition of NH3 in Forests and Heathlands in the Netherlands and Its Role in Soil Acidification', Info. Map staatsbosbeheer, Baarn/Utrecht, Holland.
Nagel, H.-D. and Gregor, H.-D.: 1999, 'Ökologische Belastungsgrenzen, Critical loads and levels', Springer Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 259 p.
Pahlsson, A.-M. and Bergkvist, B.: 1995, 'Acid deposition and soil acidification at a southwest facing edge of Norway spruce and European beech in south Sweden', Ecol. Bull. 44, 43–53.
Potts, M. J.: 1978, 'The pattern of deposition of air-borne salt of marine origin under a forest canopy', Plant and Soil 50, 233–236.
Preuhsler, T.: 1987, 'Wachstumsreaktionen nach Trassenaufhieb in Kiefernbeständen', Forstliche Forschungsberichte München, Vol 81, 200 pp.
Rothe, A., Kreutzer, K. and Küchenhoff, H.: 2001, 'Influence of tree species composition on soil and soil solution properties in two mixed spruce-beech stands with contrasting history in Southern Germany', Plant and Soil, accepted.
Spangenberg, A.: 2002, 'Stickstoffbelastung an Waldrändern – Untersuchungen in südbayerischen Regionen mit hoher Ammoniakemission', Forstliche Forschungsberichte München, Wissenschaftszentrum Weihenstephan für Ernährung, Landnutzung und Umwelt und Bayerische Landesanstalt für Wald und Forstwirtschaft, vol. 190, 188 p., ISBN-3-933506-21-2.
Spangenberg, A., Faißt, G, Kölling, Ch. and Mellert, K.-H.: 2002a, 'Das Nitrataustragsrisiko in BayernsWäldern', LWFaktuell no. 34: 9–14, Bayerische Landesanstalt fürWald und Forstwirtschaft ISSN 1435–4098.
Spangenberg, A., Hofmann, F. and Kirchner, M.: 2002b, 'Determining the agricultural ammonia immission using bark bio-monitoring: comparison with passive sampler measurements', J. Environ. Monit. 4, 865–869.
StMELF/StMLU: 1999, 'Verminderung der Nitratauswaschung', Merkblatt des Bayer. Staatsministeriums für Ernährung, Landwirtschaft und Forsten/Bayer. Staatsministerium für Landesentwicklung und Umweltfragen, Bavarian Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Munich.
Szibalski, M. and Felix-Henningsen, P.: 1999, 'Gradienten von Bodeneigenschaften im Randbereich kleinflächiger Waldstandorte des östlichen Münsterlandes', J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 162, 49–55.
UN/ECE: 2000, United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (www.emep.int/indexmscw.html), September 2000.
UN/ECE (United Nations Economic Commission for Europe): 1998, Convention on Long-Range Transboundery Air Pollution, International Co-operative Programme on Assessment and Monitoring of Air Pollution Effects on Forests (ICP-Forests), Manual on methods and criteria for harmonized sampling, assessment, monitoring and analysis of the effects of air pollution on forests, Part III (sampling and analysis of soil and submanual on soil solution collection and analysis), Part IV (sampling and analysis of needles and leaves), Part VI (measurement of deposition.
UN/ECE ICP: 1998, Convention on Long-Range Transboundery Air Pollution, International Cooperative Programme on Assessment and Monitoring of Air Pollution Effects on Forests (ICPForests), 'Integrated Monitoring Manual, subprogramme meteorology'.
Veen, A. W. L., Klaassen, W., Kruijt, B. and Hutjes, R. W. A: 1996, 'Forest edges and the soilvegetation-atmosphere interaction at the landscape scale: the state of affairs', Progress Phys. Geogr. 20(3), 292–310.
Weathers, K. C., Lovett, G. M. and Likens, G. E.: 1992, 'The Influence of a Forest Edge on Cloud Deposition', in W. G. N. Slinn (ed.), Precipitation Scavenging and Atmospheric-Surface Exchange, Vol 3, Applications and Appraisals, 1415–1424. Hemisphere Publ., Washington DC.
Winje, D. and Lühr, H.-P.: 1991, 'Der Einfluß der Gewässerverschmutzung auf die Kosten der Wasserversorgung in der Bundesrepublik Deutschland', Forschungsbericht 10103110/08 des Umweltbundesamtes, Nr. 2/91, Erich Schmidt Verlag Berlin, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spangenberg, A., Kölling, C. Nitrogen Deposition and Nitrate Leaching at Forest Edges Exposed to High Ammonia Emissions in Southern Bavaria. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 152, 233–255 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000015363.83436.a5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000015363.83436.a5