Abstract
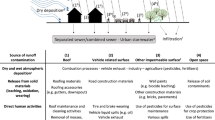
Hydrocarbons (aliphatic and aromatic) and metals (heavy metals and major elements) were measured in both atmospheric deposition and roof runoff in central Paris (France). Atmospheric deposition (wet and dry) was collected from December 2001 to October 2002 and roof runoff was sampled on three buildings with different covering materials, i.e., slate tiles and zinc sheets. This paper gives an overview of the results on the flux and distribution points of view for both atmospheric deposition and roof runoff. Results show that atmospheric fluxes of hydrocarbons and major elements increase during cold seasons, due to residential heating occurrence, while heavy metals, whose major sources have constant emission fluxes, exhibit steady atmospheric loads throughout the year. Moreover, hydrocarbon fingerprints reveal mainly biogenic and pyrolytic origins for aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons, respectively. The results about roof runoff contamination suggest that the scavenging processes for hydrocarbons and metals are dependent on rainfall amount rather than on the rain event characteristics (number, intensity, duration), and dry deposition weakly contributes to the pollutant loads in roof runoff. Results also highlight that both metallic and slate roofs do not act as a source of hydrocarbons and major elements—exclusively originating from atmospheric deposition—while they act as a source of some heavy metals. Zinc-covered roofs largely release Zn and Ti, while slate roofs mainly release Pb, Ti and Cu. Whatever the material used for roof covering, roof runoff presents high Ni and V loads due to the vicinity of the chimney stacks of heating boilers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azimi, S., Ludwig, A., Thévenot, D. R. and Colin, J. L.: 2003, ‘Trace metal determination in total atmospheric deposition in rural and urban areas’, Sci. Total Environ. 308, 247–254.
Baek, S. O., Field, R. A., Goldstone, M. E., Kirk, P. W. W., Lester, J. N. and Perry, R.: 1991, ‘A review of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: sources, fate and behavior’, Water Air Soil Pollut. 60, 279–300.
Bannerman, R. T., Owens, D. W., Dodds, R. B. and Hornewer, N. J.: 1993, ‘Sources of pollutants in Wisconsin stormwater’, Water Sci. Technol. 28, 241–259.
Bomboi, M.T. and Hernandez, A.: 1991, ‘Hydrocarbons in urban runoff: Their contribution to the wastewaters’, Water Res. 25, 557–565.
Bouloubassi, I. and Saliot, A.: 1993, ‘Investigation of anthropogenic and natural organic inputs in estuarine sediments using hydrocarbon markers (NAH, LAB, PAH)’, Oceanol. Acta 16, 145–161.
Chebbo, G.: 1992, ‘Solides des rejets pluvieux urbains: caractérisation et traitabilité’, Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, pp. 413.
Colombo, J. C., Landoni, P. and Bilos, C.: 1999, ‘Sources, distribution and variability of airborne particles and hydrocarbons in La Plata area, Argentina’, Environ. Pollut. 104, 305–314.
Colombo, J. C., Pelletier, E., Brochu, C. and Khalil, M.: 1989, ‘Determination of hydrocarbon sources using n-alkane and polyaromatic hydrocarbon distribution indexes. Case study: Rio de la Plata estuary, Argentina’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 23, 888–894.
Daub, J., Förster, J., Herrmann, R., Robien, A. and Striebel, T.: 1994, ‘Chemodynamics of trace pollutants during snowmelt on roof and street surfaces’, Water Sci. Technol. 30, 73–85.
Förster, J.: 1996, ‘Patterns of roof runoff contamination and their potential implications on practice and regulation of treatment and local infiltration’, Water Sci. Technol. 33, 39–48.
Förster, J.: 1999, ‘Variability of roof runoff quality’, Water Sci. Technol. 39, 137–144.
Gao, Y., Nelson, E. D., Field, M. P., Ding, Q., Li, H., Sherrell, R. M., Gigliotti, C. L., Van Ry, D. A., Glenn, T. R. and Eisenreich, S. J.: 2002, ‘Characterization of atmospheric trace elements on PM2.5particulate matter over the New York—New Jersey harbor estuary’, Atmos. Environ. 36, 1077–1086.
Garnaud, S.: 1999, ‘Transfert et évolution géochimique de la pollution métallique en bassin versant urbain’, Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, pp. 395.
Gogou, A., Stratigakis, N., Kanakidou, M. and Stephanou, E. G.: 1996, ‘Organic aerosols in eastern mediterranean: Components source reconciliation by using molecular markers and atmospheric back trajectories’, Org. Geochem. 25, 79–96.
Golomb, D., Barry, E., Fisher, G., Varanusupakul, P., Koleda, M. and Rooney, T.: 2001, ‘Atmospheric deposition of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons near New England coastal waters’, Atmos. Environ. 35, 6245–6258.
Gonzalez, A., Garnaud, S., Carpentier, S., Moilleron, R. and Thévenot, D.: 1999, ‘Significance of dissolved and particulate metal and hydrocarbon determinations in urban runoff samples’, in Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Urban Storm Drainage, Sydney, Australia, pp. 1816–1824.
Gough, M. A., Rhead, M. M. and Rowland, S. J.: 1992, ‘Biodegradation studies of unresolved complex mixtures of hydrocarbons and aliphatic UCM’, Org. Geochem. 18, 17–22.
Gough, M. A. and Rowland, S. J.: 1990, ‘Characterization of unresolved complex mixtures of hydro-carbons in petroleum’, Nature 344, 648–650.
Gromaire, M. C.: 1998, ‘La pollution des eaux pluviales urbaines en réseau d'assainissement unitaire: Origines et caracteristiques’, Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chaussées, pp. 507.
Gromaire-Mertz, M. C., Garnaud, S., Gonzalez, A. and Chebbo, G.: 1999, ‘Characterization of urban runoff pollution in Paris’, Water Sci. Technol. 39, 1–8.
Halsall, C. J., Coleman, P. J. and Jones, K. C.: 1997, ‘Atmospheric deposition of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins/dibenzofurans and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in two UKcities’, Chemosphere 35, 1919–1931.
Huang, S., Rahn, K. A. and Arimoto, R.: 1999, ‘Testing and optimizing two factor analysis techniques on aerosol at Narragansett, Rhode Island’, Atmos. Environ. 33, 2169–2185.
Khalili, N. R.: 1995, ‘PAH fingerprints for coke ovens, diesel and gasoline engines, highway tunnels and wood combustion emissions’, Atmos. Environ. 29, 533–542.
Lang, Q., Zhang, Q. and Jaffé, R.: 2002, ‘Organic aerosols in the Miami area, USA: Temporal variability of atmospheric particles and wet/dry deposition’, Chemosphere 47, 427–441.
Moilleron, R., Gonzalez, A., Chebbo, G. and Thévenot, D. R.: 2002, ‘Determination of aliphatic hydrocarbons in urban runoff samples from the “Le Marais” experimental catchment in Paris centre’, Water Res. 36, 1275–1285.
Moreda, J. M., Arranz, A., Fdez De Betono, S., Cid, A. and Arranz, J. F.: 1998, ‘Chromatographic determination of aliphatic hydrocarbons and polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a sewage sludge’, Sci. Total Environ. 220, 33–43.
Ollivon, D., Blanchoud, H., Motelay-Massei, A. and Garban, B.: 2002, ‘Atmospheric deposition of PAHs to an urban site, Paris, France’, Atmos. Environ. 36, 2891–2900.
Pacyna, J. M. and Graedel, T. E.: 1995, ‘Atmospheric emissions inventories: Status and prospects’, Annu. Rev. Energy Environ. 20, 265–300.
Pakkanen, T. A., Loukkola, K., Korhonen, C. H., Aarnio, P., Koskentalo, T. and Maenhaut, W.: 2001, ‘Sources and chemical composition of atmospheric fine and coarse particles in the Helsinki area’, Atmos. Environ. 35, 5381–5391.
Polkowska, Z., Kot, A., Wiergowski, M., Wolka, L., Wolowska, K. and Namiesnik, J.: 2000, ‘Organic pollutants in precipitation: Determination of pesticides and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Gdansk, Poland’, Atmos. Environ. 34, 1233–1245.
Simoneit, B. R. T.: 1985, ‘Application of molecular marker analysis to vehicular exhaust for source reconciliation’, Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 22, 203–233.
Simoneit, B. R. T., Sheng, G., Chen, X., Fu, J., Zhang, J. and Xu, Y.: 1991, ‘Molecular markers study of extractable organic matter in aerosols from urban areas of China’, Atmos. Environ. 25A, 2111–2129.
Soclo, H. H., Garrigues, P. and Ewald, M.: 2000, ‘Origin of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in coastal marin sediments: Case studies in Cotonou (Benin) and Aquitaine (France) areas’, Mar. Pollut. Bull. 40, 387–396.
Van Metre, P. C. and Mahler, B. J.: 2003, ‘The contribution of particles washed from rooftops to contaminant loading to urban streams’, Chemosphere 52, 1727–1741.
Wang, Z., Fingas, M., Landriault, M., Sigouin, L., Feng, Y. and Mullin, J.: 1997, ‘Using systematic and comparative analytical data to identify the source of an unknown oil on contaminated birds’, J. Chromatogr. 775, 251–265.
Wang, Z., Fingas, M. and Page, D. S.: 1999, ‘Oil spill identification’, J. Chromatogr. 843, 369–411.
Yang, H. H., Lee, W. J., Chen, S. J. and Lai, S. O.: 1998, ‘PAH emission from various industrial stacks’, J. Hazard. Mater. 60, 159–174.
Yaziz, M. I., Gunting, H., Sapri, N. and Ghazali, A. W.: 1989, ‘Variations in rain water quality from roof catchments’, Water Res. 23, 761–765.
Yunker, M. B., Snowdon, L. R., Macdonald, R. W., Smith, J. N., Fowler, M. G., Skibo, D. N., Mclaughlin, F. A., Danyushevskaya, A. I., Petrova, V. I. and Ivanov, G. I.: 1996, ‘Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon composition and potential sources for sediment samples from the Beaufort and Barents seas’, Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 1310–1320.
Zeng, E. Y. and Vista, C. L.: 1997, ‘Organic pollutants in the coastal environment off San Diego, California. 1. Source identification and assessment by compositional indices of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons’, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 16, 179–188.
Zheng, M. and Wan, T.: 1997, ‘Characterisation of the non volatile organic compounds in the aerosols of Hong Kong: Identification, abundance and origin’, Atmos. Environ. 31, 227–237.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocher, V., Azimi, S., Gasperi, J. et al. Hydrocarbons and Metals in Atmospheric Deposition and Roof Runoff in Central Paris. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution 159, 67–86 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000049165.12410.98
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:WATE.0000049165.12410.98