Abstract
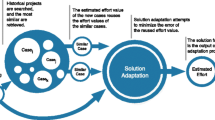
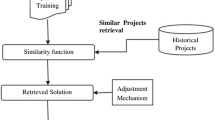
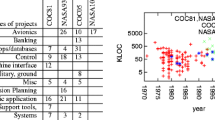
Conventional approaches to software cost estimation have focused on algorithmic cost models, where an estimate of effort is calculated from one or more numerical inputs via a mathematical model. Analogy-based estimation has recently emerged as a promising approach, with comparable accuracy to algorithmic methods in some studies, and it is potentially easier to understand and apply. The current study compares several methods of analogy-based software effort estimation with each other and also with a simple linear regression model. The results show that people are better than tools at selecting analogues for the data set used in this study. Estimates based on their selections, with a linear size adjustment to the analogue's effort value, proved more accurate than estimates based on analogues selected by tools, and also more accurate than estimates based on the simple regression model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boehm, B. W. 1981. Software Engineering Economics. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Briand, L. C., El Emam, K., Surmann, D., and Wieczorek, I. 1998. An assessment and comparison of common software estimation modeling techniques. International Software Engineering Research Network Technical Report, ISERN–98–27.
Burbridge, J. 1990. Within Reason: A Guide to Non-deductive Reasoning. Ontario: Broadview Press.
Clark, B., Devnani-Chulani, S., and Boehm, B. 1998. Calibrating the COCOMO II post-architecture model. Proceedings of the 20 th International Conference on Software Engineering. Kyoto: IEEE Computer Society, pp. 477–482.
Heemstra, F. J. 1992. Software cost estimation. Information and Software Technology 34(10):627–639.
Hughes, R. T. 1996. Expert judgement as an estimating method. Information and Software Technology 38: 67–75.
Jeffery, D. R., and Low, G. C. 1990. Calibrating estimation tools for software development. Software Engineering Journal 5(4): 215–221.
Jeffery, D. R., and Stathis, J. 1996. Function point sizing: Structure, validity and applicability. Empirical Software Engineering 1(1): 11–30.
Kemerer, C. F. 1987. An empirical validation of software cost estimation models. Communications of the ACM 30(5): 416–429.
Kolodner, J. L. 1993. Case-Based Reasoning. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann.
Lederer, A. L., and Prasad, J. Information systems software cost estimating: A current assessment. Journal of Information Technology 8: 22–33.
Mukhopadhyay, T., Vicinanza, S., and Pietula, M. J. 1992. Estimating the feasibility of a case-based reasoning model for software effort estimation. MIS Quarterly 16(2): 155–171.
Shepperd, M., and Schofield, C. 1997. Estimating software project effort using analogies. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering 23(12): 736–743.
Shepperd, M., Schofield, C., and Kitchenham, B. 1996. Effort estimation using analogy. Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Software Engineering. Berlin, Germany.
Stensrud, E., and Myrtveit, I. 1998. Human performance estimating with analogy and regression models: An empirical validation. Proceedings of the 5th International Symposium on Software Metrics. Bethesda, Maryland, USA.
Srinivasan, K., and Fisher, D. 1995. Machine learning approaches to estimating software development effort. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering 21(2): 126–137.
Vicinanza, S. S., Mukhopadhyay, T., and Prietula, M. J. 1991. Software effort estimation: An exploratory study of expert performance. Information Systems Research 2(4): 243–262.
Walkerden, F., and Jeffery, R. 1997. Software cost estimation: A review of models, process and practice. Advances in Computers 44: 59–125.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Walkerden, F., Jeffery, R. An Empirical Study of Analogy-based Software Effort Estimation. Empirical Software Engineering 4, 135–158 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009872202035
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009872202035