Abstract
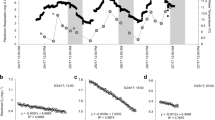
Electron transport system activity (ETS) and respiration rates (R) of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, were determined monthly from April to November over 2 years at two sites in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. The sites were located in the inner and outer bay and contrasted in food quantity and quality. ETS ranged from 2 to 40 μg O2 mg DW−1 h−1 over the study period. Both ETS and respiration were strongly related to temperature, and maximum values were found between June and August. ETS also peaked in June/July when assays were conducted at a constant temperature (25 °C), indicating other factors besides temperature affected metabolic activity. R:ETS ratios decreased with increased temperature at the inner bay site, but trends were minimal at the outer bay site. In late summer, blooms of the cyanophyte Microcystis occurred in the inner bay, likely depressing filtration rates, and leading to lower respiration rates relative to ETS. ETS activity was consistently higher in the outer bay and was likely a result of higher food quality. Despite these spatial differences, annual mean R:ETS ratios varied only from 0.04 to 0.09 at the two sites over the 2-year period. Based on these values, ETS may be useful as an indicator of long-term metabolic activity in annual energy budgets of D. polymorpha. However, food conditions differentially affect respiration relative to ETS, and variability in this ratio must be considered when interested in shorter time scales.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, J. E., Jr., J. H. Thorp & R. D. Fell, 1994. Turbidity and temperature effects on oxygen consumption in the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 51: 179–184.
Bamstedt, U., 1980. ETS activity as an estimator of respiratory rate of zooplankton populations. The significance of variations in environmental factors. J. exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 42:267-283.
Bayne, B. L. & R. C. Newell, 1983. Physiological energetics of marine mollusks. In Wilbur, K. M. (ed.), The Mollusca 4: 407–515.
Beeton, A. M., S. H. Smith & F. H. Hooper, 1967. Physical limnology of Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. Great Lakes Fishery Commission Tech. Rep. 12.
Broberg, A., 1985. A modified method for studies of electron transport system activity in freshwater sediments. Hydrobiologia 120: 181–187.
Cammen, L. M., S. Corwin & J. P. Christensen, 1990. Electron transport system (ETS) activity as a measure of benthic macrofaunal metabolism. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 65: 171–182.
Del Giorgio, P. A., 1992. The relationship between ETS (electron transport system) activity and oxygen consumption in lake plankton: a cross-system calibration. J. Plankton Res. 14: 1723–1741.
Effler, S. W. & C. Siegfried, 1994. Zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) populations in the Seneca River, New York: impact on oxygen resources. Envir. Sci. Technol. 28: 2216–2221.
Fahnenstiel, G. L., G. A. Lang, T. F. Nalepa & T. H. Johengen, 1995. Effects of zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) colonization on water quality parameters in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. J. Great Lakes Res. 21: 435–448.
Fanslow, D. L., T. F. Nalepa & G. A. Lang, 1995. Filtration rates of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) on natural seston from Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. J. Great Lakes Res. 21: 489–500.
Gardner, W. S., J. F. Cavaletto, T. H. Johengen, J. R. Johnson, R. T. Heath & J. B. Cotner Jr., 1995. Effects of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, on community nitrogen dynamic in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. J. Great Lakes Res. 21: 529–544.
James, M. R., 1987. Respiratory rates in the cladoceran Ceriodaphnia dubia in Lake Rotongaio, a monomictic lake. J. Plankton Res. 9: 573–578.
Johengen, T. H., T. F. Nalepa, G. L. Fahnenstiel & G. Goudy, 1995. Nutrient changes in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron, after the establishment of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). J. Great Lakes Res. 21: 449–464.
Jones, J. G. & B. M. Simon, 1979. The measurement of electron transport system activity in freshwater benthic and planktonic samples. J. Appl. Bacter. 46: 305–315.
King, F. D. & T. T. Packard, 1975. Respiration and the respiratory electron transport in marine zooplankton.Limnol. Oceanogr.20: 849–854.
Lavrentyev, P. J., W. S. Gardner, J. F. Cavaletto & J. R. Beaver, 1995. Effects of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha Pallas) on protozoa and phytoplankton from Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. J. Great Lakes Res. 21: 545–557.
Lyashenko, A. V. & T. A. Karchenko, 1989. Annual dynamics of energy metabolism in a freshwater clam. Gidrobiol. Zh.25: 31–38.
MacIsaac, H. J., 1996. Potential abiotic and biotic impacts of zebra mussels on the inland waters of North America. Am. Zool. 36: 287–299.
Madon, S. P., D.W. Schneider & J. A. Stoeckel, 1998. In situ estimation of zebra mussel metabolic rates using the electron transport system (ETS) assay. J. Shellfish Res. 17: 195–203.
Madenjian, C. P., 1995. Removal of algae by the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) population in western Lake Erie: a bioenergetics approach. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 52: 381–390.
McMahon, R. F., 1996. The physiological ecology of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, in North America and Europe. Amer. Zool.36: 339–363.
Nalepa, T. F., J. A. Wojcik, D. L. Fanslow & G. A. Lang, 1995. Initial colonization of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron: population recruitment, density and size structure. J. Great Lakes Res. 21: 417–434.
Nalepa, T. F., G. L. Fahnenstiel, M. J. McCormick, T. H. Johengen, G. A. Lang, J. F. Cavaletto & G. Goudy, 1996. Physical and chemical variables of Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron in 1991–93. NOAA Tech. Memo. ERL GLERL-91. 78 pp.
Nalepa, T. F., G. L. Fahnenstiel & T. H. Johengen, 1999. Impacts of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) on water quality: a case study in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. In Claudi, R. & J. H. Leach (eds), Non-Indigenous Freshwater Organisms in North America: Their Biology and Impact. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida: 253–269.
Owens, T. G. & F. D. King, 1975. The measurement of respiratory electron-transport-system activity in marine zooplankton. Mar. Biol. 30: 27–36.
Packard, T. T. 1971. The measurement of respiratory electrontransport activity in marine phytoplankton. J. Mar. Res. 29: 235–244.
Packard, T. T., M. L. Healy & F. A. Richards, 1971. Vertical distribution of the activity of the respiratory electron transport system in marine plankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 16: 60–70.
Quigley, M. A.,W. S. Gardner & W. M. Gordon, 1993. Metabolism of the zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) in Lake St. Clair of the Great Lakes. In Nalepa, T. F. & D.W. Schloesser (eds), Zebra Mussels: Biology, Impacts and Control. Boca Raton, FL: Lewis Publishers/CRC Press: 295–306.
Schneider, D. W., 1992. A bioenergetics model of zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha, growth in the Great Lakes. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 49: 1406–1416.
Smith, V. E., K. W. Lee, J. C. Filkins, K. W. Hartwell, K. R. Rygwelski & J. M. Townsend, 1977. Survey of chemical factors in Saginaw Bay (Lake Huron). Ecological Research Series. EPA-600/3-77-125. Environmental Protection Agency, Duluth, MN.
Sprung, M., 1995a. Physiological energetics of the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha in lakes. I. Growth and reproductive effort. Hydrobiologia 304: 117–132.
Sprung, M., 1995b. Physiological energetics of the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha in lakes. II. Food uptake and gross growth efficiency. Hydrobiologia 304: 133–146.
Sprung, M., 1995c. Physiological energetics of the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha in lakes. III. Metabolism and net growth efficiency. Hydrobiologia 304: 147–158.
Strayer, D. L., N. F. Caraco, J. J. Cole, S. Findlay & M. L. Pace, 1999. Transformation of freshwater ecosystems by bivalves. Bioscience 49: 19–27.
Stoeckmann, A. M. & D. W. Garton, 1997. A seasonal energy budget for zebra mussels (Dreissena polymorpha) in western Lake Erie. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 54: 2743–2751.
Strickland, J. D. H. & T. R. Parsons, 1972. A practical handbook of seawater analysis. 2nd edn. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd Can. No. 167.
Vandeploeg, H. A., T. H. Johengen, J. R. Liebig, T. F. Nalepa & G. L. Fahnenstiel, 1999. From individual behavior to ecosystem response: interactions among zebra mussels, the algal community, and nutrient cycling. Annual Conference. Am. Soc. Limnol. & Oceanog. (abstract).
Vollenweider, R. A., M. Munawar & P. Stadelman, 1974.A comparative review of phytoplankton and primary production in the Laurentian Great Lakes. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 31: 739–762.
Walz, N., 1978a. The energy balance of the freshwater mussel Dreissena polymorpha Pallas in laboratory experiments and in Lake Constance. I. Pattern of activity, feeding and assimilation efficiency. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 55: 83–105.
Walz, N., 1978b. The energy balance of the freshwater mussel Dreissena polymorpha Pallas in laboratory experiments and in Lake Constance. II. Reproduction. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 55: 106–119.
Walz, N., 1978c. The energy balance of the freshwater mussel Dreissena polymorpha Pallas in laboratory experiments and in Lake Constance. III. Growth under standard conditions. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. 55: 121–141.
Widdows, J. & A. J. Hawkins, 1989. Partitioning of rate of heat dissipation by Mytilus edulus into maintenance, feeding and growth components. Physiol. Zool. 62: 764–784.
Woynarovich, E., 1961. The oxygen consumption of Dreissena polymorpha (Lamellibranchiata) at different temperatures. Ann. Biol. Tihany 28: 211–216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fanslow, D.L., Nalepa, T.F. & Johengen, T.H. Seasonal changes in the respiratory electron transport system (ETS) and respiration of the zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha in Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron. Hydrobiologia 448, 61–70 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017582119098
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1017582119098