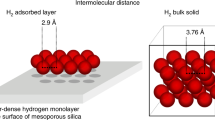
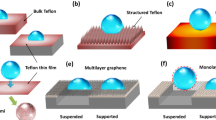
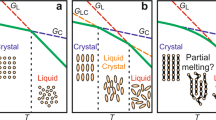
Abstract
INVESTIGATIONS using a thermostated double-acting recording surface balance of the Wilhelmy-Dervichian type1,2 reveal an interesting series of phase changes in condensed monolayers of normal chain fatty acids of high molecular weight. As an example, we may take the surface pressure – area curves for n-docosanoic (behenic) acid3 spread on acid (0·01 N hydrochloric acid) substrate shown in Fig. 1. At the lowest temperature the solid film gives a smooth pressure – area curve and the area can be reduced down to about 18·6 sq. A. per molecule before a gradual collapse sets in. At this area the chains are evidently vertical and as closely packed as in the normal three-dimensional hydrocarbon crystal, in which the cross-section of the chains is about 18·4 sq. A. This close-packed solid phase may be denoted by CS. When the temperature is raised, another phase, L2, appears5, the stability range of which increases with temperature. At 8·2° a new phase, which we may call L'2, appears and is quite marked in the curve for 10° in Fig. 1. At 13·8° the high-pressure phase S appears and the curve for 14·8° shows a transition S &rlarr2; CS which is rapidly displaced towards higher pressures with raising temperature. Above 18°, CS has disappeared and S shows a sharp collapse at about 55 dynes pressure. The smallest area at which the phase S is stable is about 19·3 sq. A. It seems likely, therefore, that the molecules are vertical and perform strong torsional oscillations6 or complete rotations, as the area per chain corresponds to that found in hydrocarbon crystals near the melting point4. (A few degrees below the melting point some hydrocarbons show a gradual, others an abrupt, change from a state of lower symmetry into one of hexagonal symmetry, in which the vertical chains are rotating about the long axis.)
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, K. J. I., StÃllberg-Stenhagen, S., and Stenhagen, E., article in âœThe Svedberg 1884-30/8 1944â (Uppsala, 1944), p. 11.
The instrument used in the work described is a modification of that described in ref. 1. The monolayer is compressed symmetrically with respect to the Wilhelmy glass slide by two barriers moving in opposition to each other. This arrangement is necessary when very solid monolayers are investigated.
A very pure specimen of n-docosanoic acid (impurityp resent amounting only to a few parts per 10,000) obtained from Prof. F. Francis, Bristol, was used. Cf. Francis, F., and Piper, S. H., J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 61, 577 (1939).
Müller, A., Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 138, 514 (1932).
The nomenclature used by Harkins and Copeland, ref. 7, and Lifshitz, ref. 9, is employed.
Alexander, A. E., Trans. Far. Soc., 37, 426 (1941), Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 179, 470, 486 (1942).
Harkins, W. D., and Copeland, L. E., J. Chem. Physics, 10, 272 (1942); Copeland, L. E., Harkins, W. D., and Boyd, G. E., J. Chem. Physics, 10, 357 (1942). The existence of a first-order transition over a certain temperature range in monolayers of n-eicosanol-1 might be inferred from earlier work by Schulman, J. H., and Hughes, A. H., Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 138, 430 (1932).
Compare Harkins, W. D., Young, T. F., and Boyd, E., J. Chem. Physics, 8, 954 (1940).
Lifshitz, E., Acta Physicochim. U.R.S.S., 19, 248 (1944).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
STÄLLBERG-STENHAGEN, S., STENHAGEN, E. Phase Transitions in Condensed Monolayers of Normal Chain Carboxylic Acids. Nature 156, 239–240 (1945). https://doi.org/10.1038/156239a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/156239a0
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.