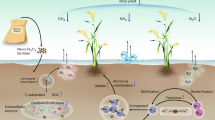
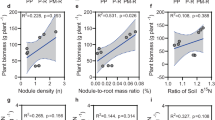
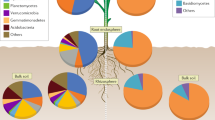
Abstract
BRADSHAW reported1 that root growth was inhibited when plants of Agrostis tenuis were grown in soil from the tip of an old Welsh lead mine, while plants originally growing on the tip produced normal roots. This suggested that some plants of A. tenuis were inherently more tolerant of the lead and zinc in the soil than others. On similar waste tips in Scotland, A. tenuis is replaced by Festuca ovina and Deschampsia flexuosa, and a method has been worked out for the measurement of lead tolerance in F. ovina from soils of different lead contents.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bradshaw, A., Nature, 169, 1098 (1952).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WILKINS, D. A Technique for the Measurement of Lead Tolerance in Plants. Nature 180, 37–38 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1038/180037b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/180037b0
This article is cited by
-
Chromium (III) removal by perennial emerging macrophytes in floating treatment wetlands
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Hexavalent chromium bioaccumulation mediated enhancement of pyrethrin production in African marigold (Tagetes erecta L.): a promising plant for phytoremediation
Acta Physiologiae Plantarum (2023)
-
Remediation of Agricultural Soil by the Use of Halophytic Crops Under Heavy Metals Conditions in Semi-Arid Environments
Gesunde Pflanzen (2023)
-
Computational and experimental analysis of foxtail millet under salt stress and selenium supplementation
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
-
Zinc Mediated Modulation of the Ascorbate–Glutathione Cycle for Salinity Stress Mitigation in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.)
Journal of Soil Science and Plant Nutrition (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.