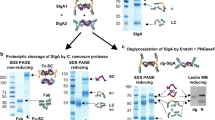
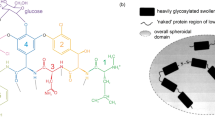
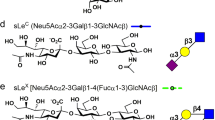
Abstract
THE colonisation of bacteria on human mucosal tissues is now recognised as an important step in the infectious process1,2. To colonise mucosal surfaces, the organisms must first bind to the epithelial cells of these tissues, or they are discarded by the host's physico-anatomical defence mechanism (sneezing, coughing, urine flush and so on). The attachment of bacteria to epithelial cells can be demonstrated in vitro3,4 and is probably mediated by surface components of both types of cell5. It was found4,5 that lipoteichoic acid on the surface of group A streptococci is responsible for the attachment of these organisms to oral mucosal cells. For Gram negative organisms, pili mediate their binding to epithelial cells6–9. In a study with Proteus mirabilis it was found10 that the presence of pili is important for the organisms to adhere to both oral and bladder mucosal cells as well as to initiate retrograde infection in experimental animals, probably by enabling the bacteria to adhere and to colonise pelvic epithelial cells11. Nothing is known, however, about the putative receptor sites required for bacterial attachment on the mucosal cell membrane. We present here data indicating that attachment of Escherichia coli to epithelial cells is mediated by mannose (or mannose-like) receptors present on the surface of the latter.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Savage, D. C. in Microbial Pathogenicity in Man and Animals (eds Smith, H. & Pearce, J. H.) 25–58 (Cambridge University Press, 1972).
Gibbons, R. J. & van Houte, J. A. Rev. Microbiol. 29, 19–44 (1975).
Gibbons, R. J. & van Houte, J. Infect. Immun. 3, 567–573 (1971).
Ofek, I., Beachey, E. H., Jefferson, W. & Campbell, G. L. J. exp. Med. 141, 990–1003 (1975).
Beachey, E. H. & Ofek, I. J. exp. Med. 143, 759–771 (1976).
Punsalang, A. P. jun. & Sawyer, W. D. Infect. Immun. 8, 255–263 (1973).
Swanson, J. J. exp. Med. 137, 571–589 (1973).
Pedersen, K. B., Frøholm, L. O. & Bøvre, K. Acta path. Microbiol. scand. B 80, 911–918 (1972).
Honda, E. & Yanagawa, R. Am. J. vet. Res. 36, 1663–1666 (1975).
Silverblatt, F. J. & Ofek, I. Clin. Res. 24, 454A (1976).
Silverblatt, F. J. J. exp. Med. 140, 1696–1711 (1974).
Hirota, Y., Ryter, A. & Jacob, F. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 33, 677–712 (1968).
Sharon, N. & Lis, H. Science 177, 949–959 (1972); A. Rev. Biochem. 42, 541–574 (1973).
Lotan, R., Skutelsky, E., Danon, D. & Sharon, N. J. biol. Chem. 250, 8518–8523 (1975).
Ballou, C. E. Adv. Enzymol. 40, 239–270 (1974).
Duguid, J. P. & Gillies, R. R. J. path. Bact. 76, 397–411 (1957).
Old, D. C. J. gen. Microbiol. 71, 149–157 (1972).
Colier, W. A. & de Miranda, J. C. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 21, 133–140 (1955).
Duguid, J. P., Smith, L. W., Dempster, G. & Edmunds, P. N. J. path. Bact. 70, 335–348 (1955).
Nagy, B., Moon, N. W. & Isaacson, R. E. Infect Immun. 13, 1214–1220 (1976).
Gould, K., Ramirez-Rona, C. H., Holmes, R. K. & Sanford, J. P. J. clin. Invest 56, 1364–1370 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
OFEK, I., MIRELMAN, D. & SHARON, N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature 265, 623–625 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/265623a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/265623a0
This article is cited by
-
Investigating the effects of peptide-based, MOS and protease feed additives on the growth performance and fecal microbial composition of weaned pigs
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2022)
-
Immunomodulation therapy offers new molecular strategies to treat UTI
Nature Reviews Urology (2022)
-
Diabetes downregulates the antimicrobial peptide psoriasin and increases E. coli burden in the urinary bladder
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Parallelism of intestinal secretory IgA shapes functional microbial fitness
Nature (2021)
-
Priority effects dictate community structure and alter virulence of fungal-bacterial biofilms
The ISME Journal (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.