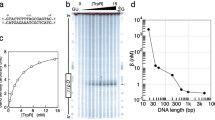
Abstract
ALTHOUGH hormonal regulation of gene expression and the nature of specific interactions between steroid hormone receptor and genome have attracted growing interest1–5, very little is known about the molecular nature of receptor–DNA interaction4–6. As a first step in unravelling the specificity and the dynamics of the interaction between uterine oestrogen receptor and DNA7–11, we have selected a well defined model system: a synthetic DNA and DNA–cellulose competition assay. We have found that the AT-rich segment of the double stranded DNA in its intact conformation is required for optimum receptor binding. We have examined oestrogen receptor binding to synthetic DNA with well defined sequences, and determined whether the receptor favours double-stranded or single-stranded regions of the DNA (unwinding protein generally binds preferentially to single-stranded DNA12). Finally, we have studied the effect of an intercalating drug, actinomycin D, on the receptor binding.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
King, R. J. B. & Mainwaring, W. I. P. Steroid-Cell Interactions (University Park Press, Baltimore, 1974).
Jensen, E. V. & DeSombre, E. R. A. Rev. Biochem. 41, 203–230 (1972).
Buller, R. E. & O'Malley, B. W. Biochem. Pharmac. 25, 1–12 (1976).
Gorski, J. & Gannon, F. A. Rev. Physiol. 38, 425–450 (1976).
Yamamoto, K. R. & Alberts, B. M. A. Rev. Biochem. 45, 721–746 (1976).
Kallos, J. Nature 265, 705–710 (1977).
Yamamoto, K. R. & Alberts, B. Cell 4, 301–310 (1975).
Yamamoto, K. R. & Alberts, B. J. biol. Chem. 249, 7076–7086 (1974).
Andre, J. & Rochefort, M. FEBS Lett. 50, 319 (1975).
King, R. J. & Gordon, J. J. Steroid Biochem. 240, 185–187 (1972).
Toft, D. O. J. Steroid Biochem. 3, 515–522 (1972).
Alberts, B. M. & Frey, L., Nature 227, 1313–1318 (1970).
Bourgeois, S. & Riggs, A. D., Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 38, 348–353 (1970).
Bourgeous, S. & Pfahl, M. Adv. Protein Chem. 30, 1–93 (1976).
Chamberlin, M. J. A. Rev. Biochem. 43, 721–775 (1974).
Simons, S. S., Jr Biochim. biophys. Acta 496, 349–359 (1977).
Chamness, G. C., Jennings, A. S. & McGuire, Wl L. Biochemistry 13, 327–331 (1974).
Von Hippel, P. H., Revzin, A., Gross, C. A. & Wang, A. C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 71, 4808–4812 (1974).
Von Hippel, P. H., Revzin, A., Gross, C. A. & Wang, A. C. in Protein-Ligand Interactions (de Gruyter, Berlin, 1975).
Von Hippel, P. H. & McGhee, J. D. A. Rev. Biochem. 41, 231–300 (1972).
Simons, S. S. Jr, Martines, H. M., Garcea, R. L., Baxter, J. D. & Tomkins, G. M. J. biol. Chem. 251, 334–343 (1976).
MacLeod, K. M. & Baxter, J. D. J. biol. Chem. 251, 7380–7387 (1976).
Andre, J., Pfeiffer, A. & Rochefort, H. Biochemistry 15, 2964–2969 (1976).
Sobell, H. M. & Jain, S. C. J. molec. Biol. 68, 21–34 (1972).
Spelsberg, T. C. in Acidic Proteins of the Nucleus (ed. Cameron, J. L. & Jeter, J. R., Jr) (Academic, New York, 1974).
Jovin, T. M. A. Rev. Biochem. 45, 889–920 (1976).
Lin, S. Y. & Riggs, A. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 69, 2574–2576 (1972).
Ogata, R. & Gilbert, W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 4973–4976 (1977).
Alberts, B. & Herrick, G. Methods Enzymol. 21 D, 198–217 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KALLOS, J., HOLLANDER, V. Assessment of specificity of oestrogen receptor-DNA interaction by a competitive assay. Nature 272, 177–179 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/272177a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/272177a0
This article is cited by
-
Glucocorticoid mechanism of action: Monoclonal antibodies as experimental tools
Medical Oncology and Tumor Pharmacotherapy (1986)
-
How do steroid hormones function to induce the transcription of specific genes?
Bioscience Reports (1983)
-
Do steroid receptors recognize DNA sequences?
Nature (1982)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.