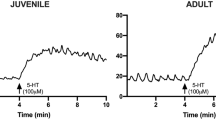
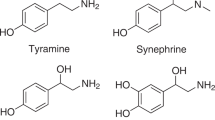
Abstract
VASOACTIVE INTESTINAL POLYPEPTIDE (VIP), originally isolated from porcine duodenum1, is a potent relaxant of vascular and nonvascular smooth muscle2, and a stimulant of adenylate cyclase activity3,4. The peptide has been localised in endocrine cells in the gastrointestinal tract and pancreatic islets5,6, as well as in nervous structures in these and other organs7–9, the peripheral autonomic nervous system and selected areas of the brain8–11. We report here immunological evidence that VIP, or a closely related peptide, occurs in mast cells, from which it can be released by compound 48/80 or by the Ca2+ ionophore A23187.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Said, S. I. & Mutt, V. Science 169, 1217–1218 (1970).
Said, S. I. in Gastrointestinal Hormones (ed. Thompson, J. S.) 591–597 (University of Texas Press, 1975).
Frandsen, E. K., Krishna, G. A. & Said, S. I. Br. J. Pharmac. 62, 367–369 (1978).
Laburthe, M., Besson, J., Hoa, D. H. B. & Rosselin, G. C.r. hebd. Séanc. Acad Sci., Paris 284, 2139–2142 (1977).
Buffa, R., Capella, C., Solcia, E., Frigerio, B. & Said, S. I. Histochemistry 50, 217–227 (1977).
Polak, J. M., Pearse, A. G. E., Garaud, J.-C. & Bloom, S. R. Gut 15, 720–724 (1974).
Alm, P., Alumets, J., Håkanson, R. & Sundler, F. Neuroscience 2, 751–754 (1977).
Fuxe, K., Hökfelt, T., Said, S. I. & Mutt, V. Neurosci. Lett. 5, 241–246 (1977).
Larsson, L.-I. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 73, 3197–3200 (1976).
Bryant, M. G. et al. Lancet i, 991–993 (1976).
Said, S. I. & Rosenberg, R. N. Science 192, 907–908 (1976).
Giachetti, A., Said, S. I., Reynolds, R. C. & Koniges, F. C. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 3424–3428 (1977).
Shore, P. A. Meth. biochem. Analysis, Suppl., 89, (1971).
Pearse, A. G. E. & Polak, J. M. Histochemistry 7, 179–186 (1975).
Lewis, R. A. & Austen, K. F. Fedn Proc. 36, 2676–2683 (1977).
Johansen, T. Br. J. Pharmac. 62, 471 P (1978).
Orange, R. P., Kaliner, M. A. & Austen, K. F. in Second Int. Symp. Biochem. Acute Allergic Reactions (eds Austen, K. F. & Becker, E. L.) 189–204, (Blackwell, Oxford, 1971).
Said, S. I. & Mutt, V. Nature 265, 84–86 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CUTZ, E., CHAN, W., TRACK, N. et al. Release of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in mast cells by histamine liberators. Nature 275, 661–662 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1038/275661a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/275661a0
This article is cited by
-
Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide Promotes Fracture Healing in Sympathectomized Mice
Calcified Tissue International (2021)
-
Prospect of vasoactive intestinal peptide therapy for COPD/PAH and asthma: a review
Respiratory Research (2011)
-
Mast cells in human bile duct obstruction
Journal of Molecular Histology (2004)
-
Evidence for a intimate relationship between mast cells and nerve fibers in the tongue of the frog,Rana esculenta
Rendiconti Lincei (1997)
-
The effects of four neuropeptides on the degranulation of mucosal mast cells from sheep
Immunology & Cell Biology (1996)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.