Abstract
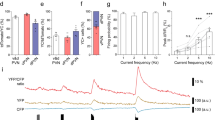
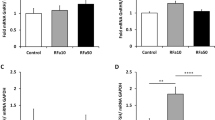
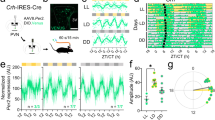
CORTICOTROPHIN RELEASING FACTOR (CRF) was the first of the postulated hypothalamic factors controlling the release of hormones from the pituitary gland to be demonstrated biologically1. However, it is extraordinary that after 24 years of research, techniques which have established the identity of the hypothalamic peptides involved in the release of thryotrophin, the gonadotrophins and growth hormone, have been unsuccessful when applied to the search for a factor responsible for adrenocorticotrophin (ACTH) release2,3. Vasopressin invariably releases ACTH from the anterior pituitary, but its partial agonistic properties in vitro4–6, its low potency in vivo7 and the isolation of active CRF fractions with little or no vasopressin activity2,3,8,9 have led to its rejection as a physiological CRF10,11. However, recent immunological and immunocytochemical findings have led to renewed interest in the role of vasopressin in ACTH release. High concentrations of immunoreactive vasopressin have been found in portal blood and a direct vasopressin-neurophysin containing axonal pathway to the hypophyseal portal system, which seems to be under the influence of the adrenal cortex, has been identified12,13. Using a sensitive releasing factor bioassay system, the perfused isolated anterior pituitary cell column14, and various immunological techniques, we have presented evidence to support the idea that vasopressin plays a major part in control of ACTH release6, and we now report the existence of hypothalamic factors with weak, labile CRF activity which potentiate the CRF activity of vasopressin to give it full agonistic properties indistinguishable from crude extracts of rat stalk median eminence (SME). Thus we propose that CRF is vasopressin modulated by other hypothalamic factor(s) released into the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guillemin, R. & Rosenberg, B. Endocrinology 57, 599–607 (1955).
Guillemin, R. Rec. Prog. Horm. Res. 20, 89–121 (1964).
Saffran, M. & Schally, A. V. Neuroendocrinology 26, 359–375 (1977).
Fehm, H. L., Voight, K. H. & Lang, R. Acta endocrinol. Suppl. 193, 129 (1975).
Buckingham, J. C. & Hodges, J. R. J. Endocr. 72, 187–193 (1977).
Gillies, G., Greidanus, T. B., van Wimsersma, B. and Lowry, P. J. Endocrinology 103, 528–534 (1978).
Yates, F. E. et al. Endocrinology 88, 3–15 (1971).
Rumsfield, H. W. & Porter, J. C. Endocrinology 64, 942–947 (1959).
Schally, A. V., Anderson, R. N., Lipscomb, H. S., Long, L. M. & Guilemin, R. Nature 188, 1192–1193 (1960).
Nichols, B. R., Jr, Vale J. Biol. Med. 33, 415–434 (1961).
Schally, A. V. Rec. Prog. Horm. Res. 24, 497–588 (1968).
Zimmerman, E. A. (Raven, New York, 1976).
Zimmerman, E. A. et al. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 297, 405–419 (1977).
Gillies, G. & Lowry, P. J. Endocrinology 103, 521–527 (1978).
Pearlmutter, A. F., Rapino, E. & Saffran, M. Endocrinology 97, 1336–1339 (1975).
Gillies, G. & Lowry, P. J. (in preparation).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
GILLIES, G., LOWRY, P. Corticotrophin releasing factor may be modulated vasopressin. Nature 278, 463–464 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/278463a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/278463a0
This article is cited by
-
Anatomy, development, and plasticity of the neurosecretory hypothalamus in zebrafish
Cell and Tissue Research (2019)
-
Coexisting peptides in hypothalamic neuroendocrine systems: Some functional implications
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (1989)
-
Psychiatric implications of altered limbic-hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical activity
European Archives of Psychiatry and Neurological Sciences (1989)
-
Peptidergic neurohormonal systems in the basal hypothalamus of the ferret and the mink: Immunocytochemical study of variations during the annual reproductive cycle
Cell and Tissue Research (1988)
-
Characteristics of neurosecretory centers of the hypothalamus of rats which are associated with regulation of the function of the adrenal cortex
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (1988)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.