Abstract
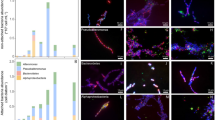
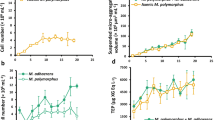
Sedimentation of phytodetrital aggregates from euphotic waters to the deep sea has been recognized in recent years as probably the most important source of energy for the deep-sea ecosystem1–3. Little is known, however, of the processes by which the detritus is degraded. We report here on phytodetrital aggregates collected from the sediment surface 4,500 m deep in a mid-oceanic area of the northeastern Atlantic. The aggregates contained a rich community of active bacteria and cyanobacteria. The abundance of intact cyanobacteria indicates that the phytodetritus is sedimented rapidly and that picoplankton, which form a significant fraction of primary production during summer months, can be transported from surface waters to the deep sea by attachment to aggregates. Rapid bacterial growth occurred on the detrital material when incubated under deep-sea conditions and similar growth rates were found under surface-water incubation conditions. The results show that phytodetritus is rapidly used by deep-sea adapted bacterial populations and that the biological degradation and transformation of sedimented detrital material in the deep sea is faster than hitherto assumed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Billett, D. S. M., Lampitt, R. S., Rice, A. L. & Mantoura, R. F. C. Nature 302, 520–522 (1983).
Honjo, S. Science 218, 883–884 (1982).
Fowler, S. W. & Knauer, G. A. Prog. Oceanogr. 16, 147–194 (1986); 332, 70–73 (1988).
Lampitt, R. S. Deep Sea Res. 32, 885–897 (1985).
Rice, A. L. et al. Proc. R. Soc. Edinb. 88B, 265–279 (1986).
Graf, G., Bengtson, W., Diesner, U., Schulz, R. & Theede, H. Mar. Biol. 67, 201–208 (1982).
Jannasch, H. W. & Wirsen, C. O. Science 180, 641–643 (1973).
Deming J. W. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 25, 305–312 (1985).
Cole, J. J., Honjo, S. & Erez, J. Nature 327, 703–704 (1987).
Cruise Report of Research Vessel METEOR, cruise No. 3, leg BIOTRANS IV (Abteilung Hydrobiologie, Zeiseweg 9, D-2000 Hamburg 50, FRG, 1986).
Johnson, P. W. & Sieburth, J. McN. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24, 928–935 (1979).
Silver, M. W. & Alldredge, A. L. J. Mar. Res. 39, 501–530 (1981).
Fogg, G. E. Proc. R. Soc. B228, 1–30 (1986).
Silver, M. W., Gowing, M. M. & Davoll, P. J. Can. Bull. Fish. Aq. Sci. 214, 311–341 (1986).
Barnett, P. R. O., Watson, J. & Connelly, D. Oceanologica Acta 7, 399–408 (1984).
Lochte, K. & Pfannkuche, O. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 39, 153–164 (1987).
Ducklow, H. W. Bioscience 33, 494–501 (1983).
Turley, C. M., Lochte, K. & Patterson, D. J. Deep Sea Res. (in the press).
Fenchel, T. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 8, 225–231 (1982).
Mantoura, R. F. C. & Llewellyn, C. A. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 47, 1293–1309 (1983).
Gooday, A. Nature 332, 70–73 (1988).
Billett, D. S. M., Llewellyn, C. & Watson, J. Proc. 6th Int. Echinoderm Conf. (ed. Burke, R.D) (in the press).
Altenbach, A. V. J. foram. Res. 17, 106–109 (1987).
Nagata, T. Appl. envir. Microbiol. 52, 28–32 (1986).
Newell, R. C., Lucas, M. I. & Linley, E. A. S. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 6, 123–136 (1981).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lochte, K., Turley, C. Bacteria and cyanobacteria associated with phytodetritus in the deep sea. Nature 333, 67–69 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/333067a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/333067a0
This article is cited by
-
Sinking Trichodesmium fixes nitrogen in the dark ocean
The ISME Journal (2022)
-
Evaluating sediment and water sampling methods for the estimation of deep-sea biodiversity using environmental DNA
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Dissolved organic carbon contribution to oxygen respiration in the central Red Sea
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Temperature-dependent impacts of allelopathy on growth, pigment, and lipid content between a subpolar strain of Synechocystis sp. CCBA MA-01 and coexisting microalgae
Hydrobiologia (2019)
-
Picocyanobacteria and deep-ocean fluorescent dissolved organic matter share similar optical properties
Nature Communications (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.