Abstract
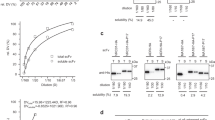
IN antibodies, a heavy and a light chain variable domain, VH and VL, respectively, pack together and the hypervariable loops on each domain contribute to binding antigen1–4. We find, however, that isolated VH domains with good antigen-binding affinities can also be prepared. Using the polymerase chain reaction5, diverse libraries of VH genes were cloned from the spleen genomic DNA of mice immunized with either lysozyme or keyhole-limpet haemocyanin. From these libraries, VH domains were expressed and secreted from Escherichia coli. Binding activities were detected against both antigens, and two VH domains were characterized with affinities for lysozyme in the 20 nM range. Isolated variable domains may offer an alternative to monoclonal antibodies and serve as the key to building high-affinity human antibodies. We suggest the name 'single domain antibodies (dAbs)' for these antigen binding demands.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amit, A. G., Mariuzza, R. A. Phillips, S. E. V. & Poljak, R. J. Science 233, 747–754 (1986).
Satow, Y., Cohen, G. H., Padlan, E. A. & Davies, D. R. J. molec. Biol. 190, 593–603 (1986).
Colman, P. M. et al. Nature 326, 358–362 (1987).
Sheriff, S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 8075–8079 (1987).
Saiki, R. K. et al. Science 230, 1350–1354 (1985).
Skerra, A. & Plückthun, A. Science 240, 1038–1040 (1988).
Better, M., Chang, C. P., Robinson, R. R. & Horwitz, A. H. Science 240, 1041–1043 (1988).
Riechmann, L., Foote, J. & Winter, G. J. molec. Biol. 203, 825–828 (1988).
Laemmli, U. K. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Matsudaira, P. J. biol. Chem. 262, 10035–10038 (1987).
Fearnley, I. M., Runswick, M. J. & Walker, J. E. EMBO J. 8, 665–672 (1989).
Fleischman, J. B., Porter, R. R. & Press, E. M. Biochem. J. 88, 220–228 (1963).
Utsumi, S. & Karush, F. Biochemistry 3, 1329–1338 (1964).
Jaton, J-C., Klinman, N. R., Givol, D. & Sela, M. Biochemistry 7, 4185–4195 (1968).
Edmundson, A. B., Ely, K. R. & Herron, J. N. Molec. Immunology 21, 561–576 (1984).
Fersht, A. R. et al. Nature 314, 235–238 (1985).
Fersht, A. R., Wilkinson, A. J., Carter, P. & Winter, G. Biochemistry 24, 5858–5861 (1985).
Chothia, C., Lesk, A. M., Dodson, G. G. & Hodgkin, D. C. Nature 302, 500–505 (1983).
Orlandi, R., Güssow, D. H., Jones, P. T. & Winter, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 3833–3837 (1989).
Kabat, E. A., Wu, T. T., Reid-Miller, M. & Gottesman, K. S. in Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest (US Department of Health and Human Services. US Government Printing Office, 1987).
Sastry, L. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86, 5728–5732 (1989).
Towbin, H., Staehelin, T. & Gordon, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 4350–4354 (1979).
Evan, G. I., Lewis, G. K. Ramsay, G. & Bishop, J. M. Molec. Cell Biol. 5, 3610–3616 (1985).
Munro, S. & Pelham, H. Cell 46, 291–300 (1986).
Rossman, M. G. et al. Nature 317, 145–153 (1985).
Weis, W. et al. Nature 333, 426–431 (1988).
Jones, P. T., Dear, P. H., Foote, J., Neuberger, M. S. & Winter, G. Nature 321, 522–525 (1986).
Levison, S. A., Kierszenbaum, F. & Dandliker, W. B. Biochemistry 9, 322–331 (1970).
Yanisch-Perron, C., Vieira, J. & Messing, J. Gene 33, 103–119 (1985).
Lei, S-P., Lin, H-C., Wang, S-S., Callaway, J. & Wilcox, G. J. Bact. 169, 4379–4383 (1987).
Gronenborn, B. Molec. gen. Genet. 148, 243–250 (1976).
Miller, J. H. Experiments in Molecular Genetics (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York, 1972).
Baldwin, E. & Schultz, P. G. Science 245, 1104–1107 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ward, E., Güssow, D., Griffiths, A. et al. Binding activities of a repertoire of single immunoglobulin variable domains secreted from Escherichia coli. Nature 341, 544–546 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/341544a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/341544a0
This article is cited by
-
Development of anti-aflatoxin B1 nanobodies from a novel mutagenesis-derived synthetic library for traditional Chinese medicine and foods safety testing
Journal of Biological Engineering (2023)
-
Molekulares Design von Nanobodies als Werkzeuge in der Allergologie: Diagnostik und mehr
Allergo Journal (2023)
-
Extract-Shaped Immune Repertoires as Source for Nanobody-Based Human IgE in Grass Pollen Allergy
Molecular Biotechnology (2023)
-
Molecular engineering of nanobodies as tools in allergology: diagnostics and beyond
Allergo Journal International (2023)
-
Backbone and side-chain resonance assignments of the NISTmAb-scFv and antigen-binding study
Biomolecular NMR Assignments (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.