Abstract
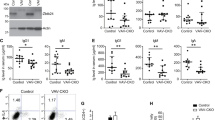
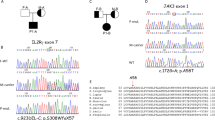
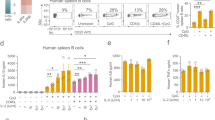
SIGNALLING for the B-cell immunoglobulin isotype switch requires T-cell-derived cytokines and T–B cell interaction, which operates primarily through the CD40 molecule on B cells with its ligand (CD40L) on activated T cells (reviewed in ref. 1). The CD40L is a type II membrane protein2–5 with homology to tumour necrosis factor-α and -β6,7, and has important functions in B-cell activation and differentiation2,4,8. Human CD40L maps on Xq26.3-27.1 (ref. 3), the region where a primary immunodeficiency characterized by an immunoglobulin isotype switch defect (the hyper-IgM immunodeficiency syndrome, HIGM1) has been localized9,10. The hypothesis that HIGM1 involves an abnormality of the CD40L has been tested. We report here the lack of CD40L expression in four unrelated male children with the hyper-IgM syndrome. CD40L transcripts in these patients showed either deletions or point mutations clustered within a limited region of the CD40L extracellular domain. These genetic alterations with abnormal CD40L expression provide a molecular basis for immunoglobulin isotype switch defects observed in this immunodeficiency.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Vries, J. E. et al. Curr. Opin. Immun. 3, 851–858 (1991).
Armitage, R. J. et al. Nature 357, 80–82 (1992).
Graf, D., Korthäuer, U., Mages, H. W., Senger, G. & Kroczek, R. A. Eur. J. Immun. 22, 3191–3194 (1992).
Hollenbaugh, D. et al. EMBO J. 11, 4313–4321 (1992).
Gauchat, J. F. et al. FEBS Lett. 315, 259–266 (1993).
Gray, P. W. et al. Nature 312, 721–724 (1984).
Wang, A. M. et al. Science 228, 149–154 (1985).
Noelle, R. J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 6550–6554 (1992).
Mensinck, E. J. B. M. et al. Hum. Genet. 76, 96–99 (1987).
Padayachee, M. et al. Genomics 14, 551–552 (1992).
Notarangelo, L. D., Duse, M. & Ugazio, A. G. Immunodef. Rev. 3, 101–122 (1992).
Mayer, L. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 314, 409–413 (1986).
Gougeon, M. L. et al. J. clin. Immun. 12, 92–100 (1992).
Lane, P. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 22, 2573–2578 (1992).
Noelle, R. J., Ledbetter, J. A. & Aruffo, A. Immun. Today 13, 431–433 (1992).
Mallett, S. & Barclay, A. N. Immun. Today 12, 220–223 (1991).
Eck, M. J. & Sprang, S. R. J. biol. Chem. 264, 17595–17605 (1989).
Geha, R. S. et al. J. clin. Invest. 64, 385–391 (1979).
Hendriks, R. W. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 20, 2603–2608 (1990).
DiSanto, J. P. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 23, 320–326 (1993).
Winship, P. R. Nucleic Acids Res. 17, 1266 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DiSanto, J., Bonnefoy, J., Gauchatt, J. et al. CD40 ligand mutations in X-linked immunodeficiency with hyper-IgM. Nature 361, 541–543 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/361541a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/361541a0
This article is cited by
-
CD40 Ligand Deficiency in Latin America: Clinical, Immunological, and Genetic Characteristics
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2022)
-
Infectious Complications Predict Premature CD8+ T-cell Senescence in CD40 Ligand-Deficient Patients
Journal of Clinical Immunology (2021)
-
Regulation of B cell differentiation by the ubiquitin-binding protein TAX1BP1
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Novel and recurrent AID mutations underlie prevalent autosomal recessive form of HIGM in consanguineous patients
Immunogenetics (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.