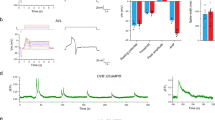
Abstract
THE functional properties of neuronal networks can be reconfigured by a variety of modulatory neurotransmitters, which may alter the excitable properties of neurons or the strengths of synaptic connections. Many of these neuromodulators act via the intracellular second messenger cyclic AMP, but their effects on the spatial distribution of cAMP concentration have never been examined in an intact neural circuit. We therefore used the cAMP-indicator dye FICRhR (refs 1,2) to investigate the effect of several neuromodulators (octopamine, dopamine, acetylcholine, serotonin and proctolin) on cAMP distribution in identified neurons of the lobster stomatogastric ganglion (STG). When added to the bath solution, each of these neuromodulators produced a unique pattern of cAMP transients among the different neurons of the STG. Electrical stimulation of neurons innervating the STG causes synaptic release of endogenous modulators, leading within a few seconds to local increases of cAMP in fine neurite branches, the site where many modulators are thought to act3,4. After prolonged stimulation, cAMP diffuses from the site of production to throughout the neuritic tree and eventually to the cell body. Diffusion of cAMP may explain how transient localized inputs to a neuron can produce long-range effects such as long-term changes in gene expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, S. R., Harootunian, A. T., Buechler, Y. J., Taylor, S. S. & Tsien, R. Y. Nature 349, 694–697 (1991).
Adams, S. R., Bacskai, B. J., Taylor, S. S. & Tsien, R. Y. in Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity (ed. Mason, W. T.) 133–149 (Academic, New York, 1993).
King, D. G. J. Neurocytol. 5, 239–266 (1976).
Hartline, D. K. & Graubard, K. in Dynamic Biological Networks: The Stomatogastric Nervous System (eds Harris–Warrick, R. M., Marder, E., Selverston, A. I. & Moulins, M.) 31–85 (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1992).
Johnson, B. R. & Hooper, S. L. in Dynamic Biological Networks: The Stomatogastric Nervous System (eds Harris–Warrick, R. M., Marder, E., Selverston, A. I. & Moulins, M.) 1–30 (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1992).
Harris-Warrick, R. M., Nagy, F. & Nusbaum, M. P. in Dynamic Biological Networks: The Stomatogastric Nervous System (eds Harris–Warrick, R. M., Marder, E., Selverston, A. I. & Moulins, M.) 87–137 (MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1992).
Flamm, R. E., Fickbohm, D. & Harris-Warrick, R. M. J. Neurophysiol. 58, 1370–1386 (1987).
Maynard, D. M. & Selverston, A. l. J. Comp. Physiol. 100, 161–182 (1975).
Tsien, R. Y. & Bacskai, B. J. in Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy (ed. Pawley, J. B.) 459–477 (Plenum, New York and London, 1995).
Tsien, R. Y., Bacskai, B. J. & Adams, S. R. Trends Cell Biol. 3, 242–245 (1993).
Flamm, R. E. & Harris-Warrick, R. M. J. Neurophysiol. 55, 847–865 (1986).
Flamm, R. E. & Harris-Warrick, R. M. J. Neurophysiol. 55, 866–881 (1986).
Hooper, S. L. & Marder, E. J. Neurosci. 7, 2097–2112 (1987).
Bal, T., Nagy, F. & Moulins, M. J. Neurosci. 3019–3035 (1987).
Heinzel, H.-G. J. Neurophysiol. 59, 551–565 (1988).
Russell, D. F. Brain Res. 177, 598–602 (1979).
Bacskai, B. J. et al. Science 260, 222–226 (1993).
Brindle, P. K. & Montminy, M. R. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2, 199–204 (1992).
Hagiwara, M. et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 4852–4859 (1993).
Alberini, C. M., Ghirardi, M., Huang, Y. Y., Nguyen, P. V. & Kandel, E. R. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 758, 261–286 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hempel, C., Vincent, P., Adams, S. et al. Spatio-temporal dynamics of cyclic AMP signals in an intact neural circuit. Nature 384, 166–169 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/384166a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/384166a0
This article is cited by
-
Dopaminergic tone regulates transient potassium current maximal conductance through a translational mechanism requiring D1Rs, cAMP/PKA, Erk and mTOR
BMC Neuroscience (2013)
-
Modulation of stomatogastric rhythms
Journal of Comparative Physiology A (2009)
-
Live-cell imaging of cAMP dynamics
Nature Methods (2008)
-
Real-time monitoring of cyclic nucleotide signaling in neurons using genetically encoded FRET probes
Brain Cell Biology (2008)
-
Oscillations and oscillatory behavior in small neural circuits
Biological Cybernetics (2006)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.