Abstract
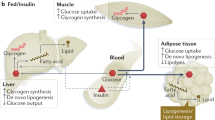
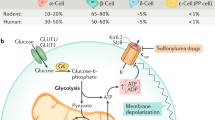
The epidemic of type 2 diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance is one of the main causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide. In both disorders, tissues such as muscle, fat and liver become less responsive or resistant to insulin. This state is also linked to other common health problems, such as obesity, polycystic ovarian disease, hyperlipidaemia, hypertension and atherosclerosis. The pathophysiology of insulin resistance involves a complex network of signalling pathways, activated by the insulin receptor, which regulates intermediary metabolism and its organization in cells. But recent studies have shown that numerous other hormones and signalling events attenuate insulin action, and are important in type 2 diabetes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klip, A. & Paquet, M. R. Glucose transport and glucose transporters in muscle and their metabolic regulation. Diabetes Care 13, 228–243 (1990).
Bruning, J. C. et al. A muscle-specific insulin receptor knockout exhibits features of the metabolic syndrome of NIDDM without altering glucose tolerance. Mol. Cell 2, 559–569 (1998).
Abel, E. D. et al. Adipose-selective targeting of the GLUT4 gene impairs insulin action in muscle and liver. Nature 409, 729–733 (2001).
Gavrilova, O. et al. Surgical implantation of adipose tissue reverses diabetes in lipoatrophic mice. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 271–278 (2000).
Kulkarni, R. N. et al. Tissue-specific knockout of the insulin receptor in pancreatic beta cells creates an insulin secretory defect similar to that in type 2 diabetes. Cell 96, 329–339 (1999).
Patti, M. E. & Kahn, C. R. The insulin receptor—a critical link in glucose homeostasis and insulin action. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 9, 89–109 (1998).
Butler, A. A. & LeRoith, D. Tissue-specific versus generalized gene targeting of the igf1 and igf1r genes and their roles in insulin-like growth factor physiology. Endocrinology 142, 1685–1688 (2001).
Skorokhod, A. et al. Origin of insulin receptor-like tyrosine kinases in marine sponges. Biol. Bull. 197, 198–206 (1999).
White, M. F. The IRS-signalling system: a network of docking proteins that mediate insulin action. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 182, 3–11 (1998).
Pessin, J. E. & Saltiel, A. R. Signaling pathways in insulin action: molecular targets of insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 165–169 (2000).
Tamemoto, H. et al. Insulin resistance and growth retardation in mice lacking insulin receptor substrate-1. Nature 372, 182–186 (1994).
Araki, E. et al. Alternative pathway of insulin signaling in mice with targeted disruption of the IRS-1 gene. Nature 372, 186–190 (1994).
Kido, Y. et al. Tissue-specific insulin resistance in mice with mutations in the insulin receptor, IRS-1, and IRS-2. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 199–205 (2000).
Withers, D. J. et al. Disruption of IRS-2 causes type 2 diabetes in mice. Nature 391, 900–904 (1998).
Fantin, V. R., Wang, Q., Lienhard, G. E. & Keller, S. R. Mice lacking insulin receptor substrate 4 exhibit mild defects in growth, reproduction, and glucose homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 278, E127–E133 (2000).
Fasshauer, M. et al. Essential role of insulin receptor substrate 1 in differentiation of brown adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 319–329 (2001).
Mendez, R., Myers, M. G. Jr, White, M. F. & Rhoads, R. E. Stimulation of protein synthesis, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E phosphorylation, and PHAS-I phosphorylation by insulin requires insulin receptor substrate 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 2857–2864 (1996).
Tsuruzoe, K., Emkey, R., Kriauciunas, K. M., Ueki, K. & Kahn, C. R. Insulin receptor substrate 3 (IRS-3) and IRS-4 impair IRS-1- and IRS-2-mediated signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 26–38 (2001).
Hotamisligil, G. S. et al. IRS-1-mediated inhibition of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity in TNF-alpha- and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Science 271, 665–668 (1996).
Craparo, A., Freund, R. & Gustafson, T. A. 14-3-3 (ɛ) interacts with the insulin-like growth factor I receptor and insulin receptor substrate I in a phosphoserine-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11663–11669 (1997).
Yuan, M. et al. Reversal of obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance with salicylates or targeted disruption of Ikkβ. Science 293, 1673–1677 (2001).
Kim, J. K. et al. Prevention of fat-induced insulin resistance by salicylate. J. Clin. Invest. 108, 437–446 (2001).
Elchebly, M. et al. Increased insulin sensitivity and obesity resistance in mice lacking the protein tyrosine phosphatase-1B gene. Science 283, 1544–1548 (1999).
Shepherd, P. R., Nave, B. T. & Siddle, K. Insulin stimulation of glycogen synthesis and glycogen synthase activity is blocked by wortmannin and rapamycin in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: evidence for the involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinase and p70 ribosomal protein-S6 kinase. Biochem. J. 305, 25–28 (1995).
Myers, M. G. Jr et al. IRS-1 activates phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase by associating with src homology 2 domains of p85. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 10350–10354 (1992).
Pons, S. et al. The structure and function of p55PIK reveal a new regulatory subunit for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 4453–4465 (1995).
Antonetti, D. A., Algenstaedt, P. & Kahn, C. R. Insulin receptor substrate 1 binds two novel splice variants of the regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in muscle and brain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 2195–2203 (1996).
Fruman, D. A., Cantley, L. C. & Carpenter, C. L. Structural organization and alternative splicing of the murine phosphoinositide 3-kinase p85 alpha gene. Genomics 37, 113–121 (1996).
Kerouz, N. J., Horsch, D., Pons, S. & Kahn, C. R. Differential regulation of insulin receptor substrates-1 and-2 (IRS-1 and IRS-2) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase isoforms in liver and muscle of the obese diabetic (ob/ob) mouse. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 3164–3172 (1997).
Fruman, D. A. et al. Hypoglycaemia, liver necrosis and perinatal death in mice lacking all isoforms of phosphoinositide 3-kinase p85α. Nature Genet. 26, 379–382 (2000).
Terauchi, Y. et al. Increased insulin sensitivity and hypoglycaemia in mice lacking the p85α subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Nature Genet. 21, 230–235 (1999).
Lietzke, S. E. et al. Structural basis of 3-phosphoinositide recognition by pleckstrin homology domains. Mol. Cell 6, 385–394 (2000).
Kessler, A., Uphues, I., Ouwens, D. M., Till, M. & Eckel, J. Diversification of cardiac insulin signaling involves the p85 alpha/beta subunits of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 280, E65–E74 (2001).
Peterson, R. T. & Schreiber, S. L. Kinase phosphorylation: keeping it all in the family. Curr. Biol. 9, R521–R524 (1999).
Mackay, D. J. & Hall, A. Rho GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 20685–20688 (1998).
Ziegler, S. F., Bird, T. A., Schneringer, J. A., Schooley, K. A. & Baum, P. R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel receptor protein tyrosine kinase from human placenta. Oncogene 8, 663–670 (1993).
Alessi, D. R. et al. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Balpha. Curr. Biol. 7, 261–269 (1997).
Cross, D. A. et al. The inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin or insulin-like growth factor 1 in the rat skeletal muscle cell line L6 is blocked by wortmannin, but not by rapamycin: evidence that wortmannin blocks activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in L6 cells between Ras and Raf. Biochem. J. 303, 21–26 (1994).
Nakae, J., Park, B. C. & Accili, D. Insulin stimulates phosphorylation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR on serine 253 through a Wortmannin-sensitive pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 15982–15985 (1999).
Brady, M. J., Bourbonais, F. J. & Saltiel, A. R. The activation of glycogen synthase by insulin switches from kinase inhibition to phosphatase activation during adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 14063–14066 (1998).
Cho, H. et al. Insulin resistance and a diabetes mellitus-like syndrome in mice lacking the protein kinase Akt2 (PKBβ). Science 292, 1728–1731 (2001).
Standaert, M. L. et al. Protein kinase C-ζ as a downstream effector of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase during insulin stimulation in rat adipocytes. Potential role in glucose transport. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 30075–30082 (1997).
Ogg, S. & Ruvkun, G. The C. elegans PTEN homolog, DAF-18, acts in the insulin receptor-like metabolic signaling pathway. Mol. Cell 2, 887–893 (1998).
Wada, T. et al. Role of the Src homology 2 (SH2) domain and C-terminus tyrosine phosphorylation sites of SH2-containing inositol phosphatase (SHIP) in the regulation of insulin-induced mitogenesis. Endocrinology 140, 4585–4594 (1999).
Clement, S. et al. The lipid phosphatase SHIP2 controls insulin sensitivity. Nature 409, 92–97 (2001).
Ribon, V. & Saltiel, A. R. Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the proto-oncogene product of c-Cbl in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. J. 324, 839–845 (1997).
Ribon, V., Herrera, R., Kay, B. K. & Saltiel, A. R. A role for CAP, a novel, multifunctional Src homology 3 domain-containing protein in formation of actin stress fibers and focal adhesions. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 4073–4080 (1998).
Ribon, V., Johnson, J. H., Camp, H. S. & Saltiel, A. R. Thiazolidinediones and insulin resistance: peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma activation stimulates expression of the CAP gene. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 14751–14756 (1998).
Kimura, A., Baumann, C. A., Chiang, S. H. & Saltiel, A. R. The sorbin homology domain: a motif for the targeting of proteins to lipid rafts. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9098–9103 (2001).
Baumann, C. A. et al. CAP defines a second signalling pathway required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. Nature 407, 202–207 (2000).
Chiang, S. H. et al. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation requires the CAP-dependent activation of TC10. Nature 410, 944–948 (2001).
Watson, R. T. et al. Lipid raft microdomain compartmentalization of TC10 is required for insulin signaling and GLUT4 translocation. J. Cell Biol. 154, 829–840 (2001).
Boulton, T. G. et al. ERKs: a family of protein-serine/threonine kinases that are activated and tyrosine phosphorylated in response to insulin and NGF. Cell 65, 663–675 (1991).
Lazar, D. F. et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase inhibition does not block the stimulation of glucose utilization by insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 20801–20807 (1995).
Raught, B., Gingras, A. C. & Sonenberg, N. The target of rapamycin (TOR) proteins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 7037–7044 (2001).
Nave, B. T., Ouwens, M., Withers, D. J., Alessi, D. R. & Shepherd, P. R. Mammalian target of rapamycin is a direct target for protein kinase B: identification of a convergence point for opposing effects of insulin and amino-acid deficiency on protein translation. Biochem. J. 344, 427–431 (1999).
Thomas, G. & Hall, M. N. TOR signalling and control of cell growth. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 9, 782–787 (1997).
Miron, M. et al. The translational inhibitor 4E-BP is an effector of PI(3)K/Akt signalling and cell growth in Drosophila. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 596–601 (2001).
Cross, D. A., Alessi, D. R., Cohen, P., Andjelkovich, M. & Hemmings, B. A. Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378, 785–789 (1995).
Brady, M. J., Nairn, A. C. & Saltiel, A. R. The regulation of glycogen synthase by protein phosphatase 1 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Evidence for a potential role for DARPP-32 in insulin action. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 29698–29703 (1997).
Newgard, C. B., Brady, M. J., O'Doherty, R. M. & Saltiel, A. R. Organizing glucose disposal: emerging roles of the glycogen targeting subunits of protein phosphatase-1. Diabetes 49, 1967–1977 (2000).
Michael, M. D. et al. Loss of insulin signaling in hepatocytes leads to severe insulin resistance and progressive hepatic dysfunction. Mol. Cell 6, 87–97 (2000).
Bergman, R. N. & Ader, M. Free fatty acids and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 11, 351–356 (2000).
Bergman, R. N. New concepts in extracellular signaling for insulin action: the single gateway hypothesis. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 52, 359–385 (1997).
Pilkis, S. J. & Granner, D. K. Molecular physiology of the regulation of hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycolysis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 54, 885–909 (1992).
Sutherland, C., O'Brien, R. M. & Granner, D. K. New connections in the regulation of PEPCK gene expression by insulin. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 351, 191–199 (1996).
Yoon, J. C. et al. Control of hepatic gluconeogenesis through the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. Nature 413, 131–138 (2001).
Shimomura, I. et al. Insulin selectively increases SREBP-1c mRNA in the livers of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 13656–13661 (1999).
Foretz, M. et al. ADD1/SREBP-1c is required in the activation of hepatic lipogenic gene expression by glucose. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 3760–3768 (1999).
Shimomura, I. et al. Decreased IRS-2 and increased SREBP-1c lead to mixed insulin resistance and sensitivity in livers of lipodystrophic and ob/ob mice. Mol. Cell 6, 77–86 (2000).
Anthonsen, M. W., Ronnstrand, L., Wernstedt, C., Degerman, E. & Holm, C. Identification of novel phosphorylation sites in hormone-sensitive lipase that are phosphorylated in response to isoproterenol and govern activation properties in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 215–221 (1998).
Kitamura, T. et al. Insulin-induced phosphorylation and activation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase 3B by the serine-threonine kinase Akt. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 6286–6296 (1999).
Cusi, K. et al. Insulin resistance differentially affects the PI 3-kinase- and MAP kinase-mediated signaling in human muscle. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 311–320 (2000).
Taylor, S. I. & Arioglu, E. Syndromes associated with insulin resistance and acanthosis nigricans. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 9, 419–439 (1998).
Stern, M. P. Strategies and prospects for finding insulin resistance genes. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 323–327 (2000).
Bruning, J. C. et al. Development of a novel polygenic model of NIDDM in mice heterozygous for IR and IRS-1 null alleles. Cell 88, 561–572 (1997).
Terauchi, Y. et al. Development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in the double knockout mice with disruption of insulin receptor substrate-1 and β cell glucokinase genes. Genetic reconstitution of diabetes as a polygenic disease. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 861–866 (1997).
Kulkarni, R. N. et al. Altered function of insulin receptor substrate-1-deficient mouse islets and cultured beta-cell lines. J. Clin. Invest. 104, R69–R75 (1999).
Bruning, J. C. et al. Role of brain insulin receptor in control of body weight and reproduction. Science 289, 2122–2125 (2000).
Zisman, A. et al. Targeted disruption of the glucose transporter 4 selectively in muscle causes insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. Nature Med. 6, 924–928 (2000).
Katz, E. B., Stenbit, A. E., Hatton, K., DePinho, R. & Charron, M. J. Cardiac and adipose tissue abnormalities but not diabetes in mice deficient in GLUT4. Nature 377, 151–155 (1995).
Kim, J. K. et al. Redistribution of substrates to adipose tissue promotes obesity in mice with selective insulin resistance in muscle. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 1791–1797 (2000).
Shulman, G. I. Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 171–176 (2000).
Hwang, J. H., Pan, J. W., Heydari, S., Hetherington, H. P. & Stein, D. T. Regional differences in intramyocellular lipids in humans observed by in vivo 1H-MR spectroscopic imaging. J. Appl. Physiol. 90, 1267–1274 (2001).
Kim, J. K. et al. Tissue-specific overexpression of lipoprotein lipase causes tissue-specific insulin resistance. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 7522–7527 (2001).
Ventre, J. et al. Targeted disruption of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene: metabolic consequences in obese and nonobese mice. Diabetes 46, 1526–1531 (1997).
Ofei, F., Hurel, S., Newkirk, J., Sopwith, M., Taylor, R. Effects of an engineered human anti-TNF-alpha antibody (SDP571) on insulin sensitivity and glycemic control in patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 45, 881–885 (1996).
Halaas, J. L. et al. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 269, 543–546 (1995).
Shimomura, I., Hammer, R. E., Ikemoto, S., Brown, M. S. & Goldstein, J. L. Leptin reverses insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus in mice with congenital lipodystrophy. Nature 401, 73–76 (1999).
Lee, Y. et al. Liporegulation in diet-induced obesity. The antisteatotic role of hyperleptinemia. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 5629–5635 (2001).
Fruebis, J. et al. Proteolytic cleavage product of 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein increases fatty acid oxidation in muscle and causes weight loss in mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 2005–2010 (2001).
Yamauchi, T. et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nature Med. 7, 941–946 (2001).
Berg, A. H., Combs, T. P., Du, X., Brownlee, M. & Scherer, P. E. The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nature Med. 7, 947–953 (2001).
Vionnet, N. et al. Genomewide search for type 2 diabetes-susceptibility genes in French whites: evidence for a novel susceptibility locus for early-onset diabetes on chromosome 3q27-qter and independent replication of a type 2-diabetes locus on chromosome 1q21-q24. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67, 1470–1480 (2000).
Steppan, C. M. et al. A family of tissue-specific resistin-like molecules. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 502–506 (2001).
Nagaev, I. & Smith, U. Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are not related to resistin expression in human fat cells or skeletal muscle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 285, 561–564 (2001).
Accili, D., Nakae, J., Kim, J. J., Park, B. C. & Rother, K. I. Targeted gene mutations define the roles of insulin and IGF-I receptors in mouse embryonic development. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 12, 475–485 (1999).
Postic, C. et al. Dual roles for glucokinase in glucose homeostasis as determined by liver and pancreatic β cell-specific gene knock-outs using Cre recombinase. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 305–315 (1999).
Pessin, J. E., Thurmond, D. C., Elmendorf, J. S., Coker, K. J. & Okada, S. Molecular basis of insulin-stimulated GLUT4 vesicle trafficking. Location! Location! Location! J. Biol. Chem. 274, 2593–2596 (1999).
Guilherme, A. et al. Perinuclear localization and insulin responsiveness of GLUT4 requires cytoskeletal integrity in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 38151–38159 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We apologize to the many investigators whose work we could not cite owing to a limit on the number of references.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saltiel, A., Kahn, C. Insulin signalling and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature 414, 799–806 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/414799a
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/414799a
This article is cited by
-
Obesity causes mitochondrial fragmentation and dysfunction in white adipocytes due to RalA activation
Nature Metabolism (2024)
-
An experiment on the glucose metabolite, serum electrolytes, and somatic characteristics of the Levantine Barbel Luciobarbus pectoralis (Heckel, 1843) under the effect of heavy metals
Environmental Geochemistry and Health (2024)
-
Arsenic and adipose tissue: an unexplored pathway for toxicity and metabolic dysfunction
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2024)
-
Single-base editing in IGF2 improves meat production and intramuscular fat deposition in Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs
Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2023)
-
Plasma lipidomic profiling reveals metabolic adaptations to pregnancy and signatures of cardiometabolic risk: a preconception and longitudinal cohort study
BMC Medicine (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.