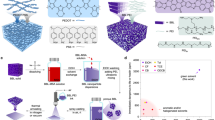
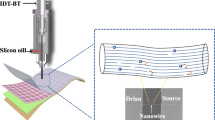
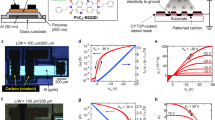
Abstract
Printed electronics is a revolutionary technology aimed at unconventional electronic device manufacture on plastic foils, and will probably rely on polymeric semiconductors for organic thin-film transistor (OTFT) fabrication. In addition to having excellent charge-transport characteristics in ambient conditions, such materials must meet other key requirements, such as chemical stability, large solubility in common solvents, and inexpensive solution and/or low-temperature processing. Furthermore, compatibility of both p-channel (hole-transporting) and n-channel (electron-transporting) semiconductors with a single combination of gate dielectric and contact materials is highly desirable to enable powerful complementary circuit technologies, where p- and n-channel OTFTs operate in concert. Polymeric complementary circuits operating in ambient conditions are currently difficult to realize: although excellent p-channel polymers are widely available, the achievement of high-performance n-channel polymers is more challenging. Here we report a highly soluble (∼60 g l-1) and printable n-channel polymer exhibiting unprecedented OTFT characteristics (electron mobilities up to ∼0.45–0.85 cm2 V-1 s-1) under ambient conditions in combination with Au contacts and various polymeric dielectrics. Several top-gate OTFTs on plastic substrates were fabricated with the semiconductor-dielectric layers deposited by spin-coating as well as by gravure, flexographic and inkjet printing, demonstrating great processing versatility. Finally, all-printed polymeric complementary inverters (with gain 25–65) have been demonstrated.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Malliaras, G. & Friend, R. H. An organic electronics primer. Phys. Today 58, 53–58 (2005)
Klauk, H. Organic Electronics: Materials, Manufacturing and Applications (Wiley-VCH, 2006)
Sirringhaus, H. et al. Two-dimensional charge transport in self-organized, high-mobility conjugated polymers. Nature 401, 685–688 (1999)
Briseno, A. L. et al. Patterning organic single-crystal transistor arrays. Nature 444, 913–917 (2006)
Vikram, C. S. et al. Elastomeric transistor stamps: Reversible probing of charge transport in organic crystals. Science 303, 1644–1646 (2004)
Muccini, M. A bright future for organic field-effect transistors. Nature Mater. 5, 605–613 (2006)
Zaumseil, J., Friend, R. H. & Sirringhaus, H. Spatial control of the recombination zone in an ambipolar light-emitting organic transistor. Nature Mater. 5, 69–74 (2006)
Kim, C., Facchetti, A. & Marks, T. J. Polymer gate dielectric surface viscoelasticity modulates pentacene transistor performance. Science 318, 76–80 (2007)
Gundlach, D. J. et al. Contact-induced crystallinity for high-performance soluble acene-based transistors and circuits. Nature Mater. 7, 216–221 (2008)
Dimitrakopoulos, C. D. et al. Low-voltage organic transistors on plastic comprising high-dielectric constant gate insulators. Science 283, 822–824 (1999)
Dodabalapur, A., Katz, H. E., Torsi, L. & Haddon, R. C. Organic heterostructure field-effect transistors. Science 269, 1560–1562 (1995)
Hulea, I. N. et al. Tunable Froehlich polarons in organic single-crystal transistors. Nature Mater. 5, 982–986 (2006)
See, K. C., Becknell, A., Miragliotta, J. & Katz, H. E. Enhanced response of n-channel naphthalenetetracarboxylic diimide transistors to dimethyl methylphosphonate using phenolic receptors. Adv. Mater. 19, 3322–3327 (2007)
Crone, B. et al. Large-scale complementary integrated circuits based on organic transistors. Nature 403, 521–523 (2000)
Gelinck, G. H. et al. Flexible active-matrix displays and shift registers based on solution-processed organic transistors. Nature Mater. 3, 106–109 (2004)
Bao, Z., Rogers, J. A. & Katz, H. E. Printable organic and polymeric semiconducting materials and devices. J. Mater. Chem. 9, 1895–1904 (1999)
Rogers, J. A. et al. Paper-like electronic displays: Large-area rubber-stamped plastic sheets of electronics and microencapsulated electrophoretic inks. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 4835–4840 (2001)
Gamota, D. R., Brazis, P., Kalyanasundaram, X. & Zhang, J. (eds) Printed Organic and Molecular Electronics (Kluwer Academic, 2004)
Garnier, F., Hajlaoui, R., Yassar, A. & Srivastava, P. All-polymer field-effect transistor realized by printing techniques. Science 265, 1864–1866 (1994)
Sivaramakrishnan, S. et al. Controlled insulator-to-metal transformation in printable polymer composites with nanometal clusters. Nature Mater. 6, 149–155 (2007)
Facchetti, A., Yoon, M.-H. & Marks, T. J. Gate dielectrics for organic field-effect transistors: New opportunities for organic electronics. Adv. Mater. 17, 1705–1725 (2005)
Cho, J. et al. High-capacitance ion gel gate dielectrics with faster polarization response times for organic thin film transistors. Adv. Mater. 20, 686–690 (2008)
McCulloch, I. et al. Liquid-crystalline semiconducting polymers with high charge-carrier mobility. Nature Mater. 5, 328–333 (2006)
Pan, H. et al. Low-temperature, solution-processed, high-mobility polymer semiconductors for thin-film transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 4112–4113 (2007)
Dhoot, A. S. et al. Beyond the metal-insulator transition in polymer electrolyte gated polymer field-effect transistors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 11834–11837 (2006)
Ando, S. et al. n-Type organic field-effect transistors with very high electron mobility based on thiazole oligomers with trifluoromethylphenyl groups. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 14996–14997 (2005)
Chesterfield, R. J. et al. Organic thin film transistors based on n-alkyl perylene diimides: Charge transport kinetics as a function of gate voltage and temperature. J. Phys. Chem. B 108, 19281–19292 (2004)
Anthopoulos, T. D. et al. High performance n-channel organic field-effect transistors and ring oscillators based on C60 fullerene films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 213504 (2006)
Waldauf, C., Schilinsky, P., Perisutti, M., Hauch, J. & Brabec, C. J. Solution-processed organic n-type thin-film transistors. Adv. Mater. 15, 2084–2088 (2003)
Newman, C. R. et al. Introduction to organic thin film transistors and design of n-channel organic semiconductors. Chem. Mater. 16, 4436–4451 (2004)
Chua, L.-L. et al. General observation of n-type field-effect behavior in organic semiconductors. Nature 434, 194–199 (2005)
Letizia, J. n-Channel polymers by design: Optimizing the interplay of solubilizing substituents, crystal packing, and field-effect transistor characteristics in polymeric bithiophene-imide semiconductors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 9679–9694 (2008).
Zhan, X. et al. A high-mobility electron-transport polymer with broad absorption and its use in field-effect transistors and all-polymer solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 7246–7247 (2007)
Huttner, S., Sommer, M. & Thelakkat, M. n-type organic field effect transistors from perylene bisimide block copolymers and homopolymers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 093302 (2008)
Briseno, A. et al. Self-assembly, molecular packing, and electron transport in n-type polymer semiconductor nanobelts. Chem. Mater. 20, 4712–4719 (2008)
Klauk, H., Zschieschang, U., Pflaum, J. & Halik, M. Ultralow-power organic complementary circuits. Nature 445, 745–748 (2007)
Chen, Z., Zheng, Y., Yan, H. & Facchetti, A. Naphthalenedicarboximide- vs. perylenedicarboximide-based copolymers. Synthesis and semiconducting properties in bottom-gate n-channel organic transistors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 8–9 (2009)
Jones, B. A., Facchetti, A., Wasielewski, M. R. & Marks, T. J. Tuning orbital energetics in arylene diimide semiconductors. Materials design for ambient stability of n-type charge transport. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 15259–15278 (2007)
Dholakia, G. R., Meyyappan, M., Facchetti, A. & Marks, T. J. Monolayer to multilayer nanostructural growth transition in n-type oligothiophenes on Au(111) and implications for organic field-effect transistor performance. Nano Lett. 6, 2447–2455 (2006)
Stoliar, P. et al. Charge injection across self-assembly monolayers in organic field-effect transistors: Odd-even effects. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 6477–6484 (2007)
Menard, E. et al. High-performance n- and p-type single-crystal organic transistors with free-space gate dielectrics. Adv. Mater. 16, 2097–2101 (2004)
Veres, J. et al. Low-k insulators as the choice of dielectrics in organic field-effect transistors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 13, 199–204 (2003)
Richards, T., Bird, M. & Sirringhaus, H. A quantitative analytical model for static dipolar disorder broadening of the density of states at organic heterointerfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 128, 234905 (2008)
Chang, J.-F., Sirringhaus, H., Giles, M., Heeney, M. & McCulloch, I. Relative importance of polaron activation and disorder on charge transport in high-mobility conjugated polymer field-effect transistors. Phys. Rev. B 76, 205204 (2007)
Kline, R. J. et al. Dependence of regioregular poly(3-hexylthiophene) film morphology and field-effect mobility on molecular weight. Macromolecules 38, 3312–3319 (2005)
Tse, N. N. et al. Gate bias stress effects due to polymer gate dielectrics in organic thin-film transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 103, 044506 (2008)
Richards, T. & Sirringhaus, H. Bias-stress induced contact and channel degradation in staggered and coplanar organic field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 023512 (2008)
Salleo, A. & Street, R. A. Light-induced bias stress reversal in polyfluorene thin-film transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 471–479 (2003)
Bredas, J.-L. et al. Charge transport in organic semiconductors. Chem. Rev. 107, 926–952 (2007)
Westenhoff, S., Howard, I. A. & Friend, R. H. Probing the morphology and energy landscape of blends of conjugated polymers with sub-10 nm resolution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 016102 (2008)
Guo, X. & Watson, M. D. Conjugated polymers from naphthalene bisimide. Org. Lett. 10, 5333–5336 (2008)
Acknowledgements
We thank P. Inagaki for his leadership, T. J. Marks for discussions and P. Eckerle and BASF Future Business for their support.
Author Contributions H.Y. supervised device fabrication and analysis, performed the humidity tests, and fabricated the complementary inverters. Z.C. designed and synthesized the semiconductor polymer. Y.Z. fabricated the devices by spin-coating and monitored the stability in ambient conditions. C.N. fabricated most of the gravure- and inkjet-printed devices and acquired all AFM images. J.Q. optimized NDI monomer and dielectric synthesis. F.D. and M.K. supported the synthetic efforts. A.F. directed the project and wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Notes and Supplementary Figures S1-S17 with Legends (PDF 1548 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, H., Chen, Z., Zheng, Y. et al. A high-mobility electron-transporting polymer for printed transistors. Nature 457, 679–686 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07727
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07727
This article is cited by
-
Unraveling the crucial role of trace oxygen in organic semiconductors
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Polymer field-effect transistors with inkjet-printed silver electrodes: from device fabrication to circuit simulation
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics (2024)
-
Advantages, challenges and molecular design of different material types used in organic solar cells
Nature Reviews Materials (2023)
-
Preparation of D-A copolymers based on dithiazologermole and germaindacenodithiazole as weak electron donor units
Polymer Journal (2023)
-
Correlating the structures and photovoltaic properties in phase-separated blends of conjugated donor polymers and acceptors
Polymer Journal (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.